AV Fistula Surgery for Dialysis | Types & Cost
PACE Hospitals provides the safest and most successful AV Fistula Surgery in Hyderabad, India. The team of urology doctors has extensive expertise in performing AV fistula for dialysis with minimal discomfort and maximum efficacy.
At PACE Hospitals, our team of highly experienced urologists and nephrologists is skilled in handling all patient needs and creating precise AV fistulas to efficiently support the dialysis process.
Why choose PACE Hospitals for AV Fistula Surgery ?
20,000+ AV fistula surgery performed for dialysis
Team of the best urologist with 40+ years of expertise
Cost-effective treatment with 99.9% success rate
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
What is AV Fistula?
AV fistula definition
Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are abnormal connections between arteries and veins. In some instances, they can also be called arteriovenous malformations. AVFs can be found almost anywhere in the body. AVFs may result from a congenital or genetic defect or develop because of accidental trauma or injury.
Due to high-pressure arterial flow in the affected veins, the fistula may result in chronic venous insufficiency, which can manifest as peripheral edema, varicose veins, and stasis pigmentation.
Signs of arterial insufficiency include ulceration brought on by decreased arterial flow or ischemia. Clinical diagnosis of fistulas is based on thrill, murmur, and other symptoms. The most effective confirmatory test is Doppler ultrasonography. In the past, most arteriovenous fistula patients were managed conservatively during times of war and, if necessary, surgically.
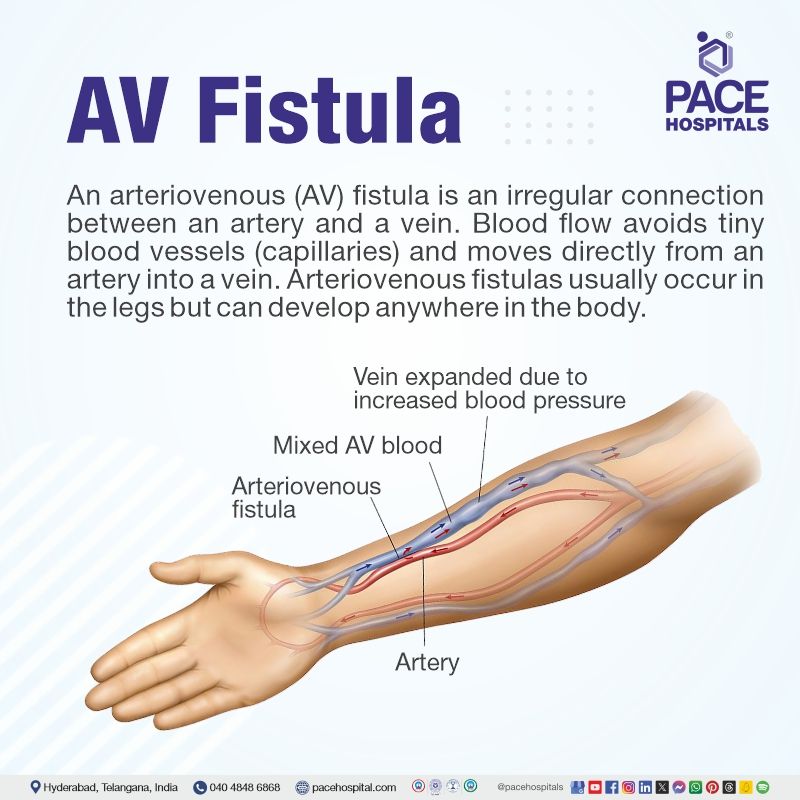
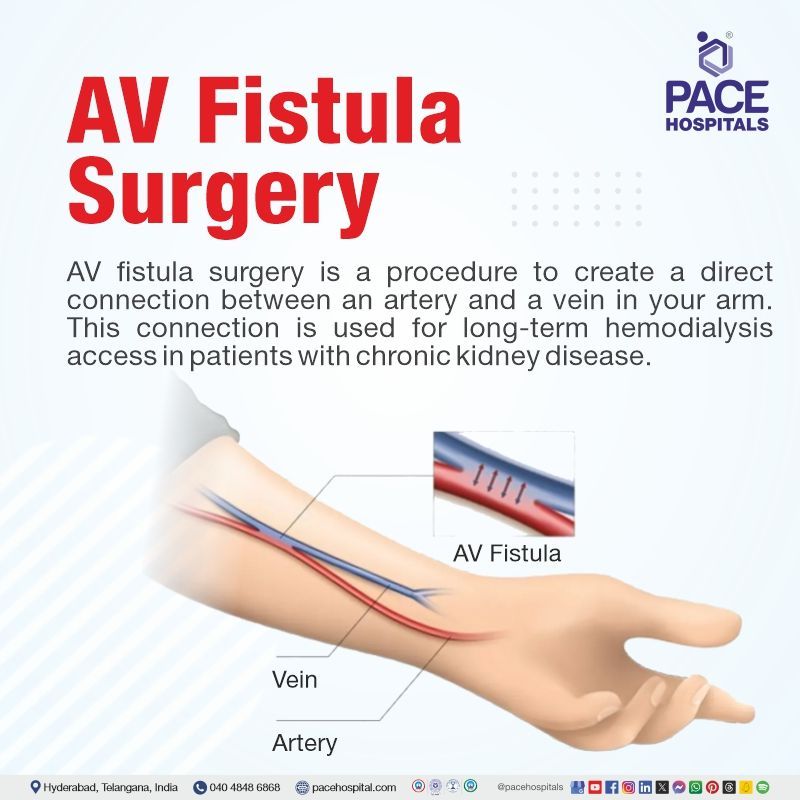
In some instances, as part of treatment, AVFs may be surgically created, especially among patients suffering from end-stage renal disease (ESRD) who need permanent vascular access for hemodialysis. An arteriovenous fistula is surgically created by an Urologist joining an artery to a vein. It is most frequently sited on an arm but, if there are no suitable vessels in the arms, sited on a leg. In rare cases, fistula may be made using a synthetic graft. They may be reversed once normal renal function is established.
Once an arteriovenous fistula has been formed, the arterial pressure causes the vein to dilate. Over the following weeks, the vein will enlarge and strengthen, enabling frequent needle insertion required for hemodialysis treatment. Compared to hemodialysis catheters or prosthetic grafts, arteriovenous fistulas are recommended as the first access.
Types of AV fistula surgery for dialysis
Depending on the patient's vascular anatomy, multiple dialysis fistula formation sites may be formed. Below are the three types of AV fistula:
- Radiocephalic fistula
- Brachiocephalic fistula
- Transposition brachiobasilic fistula
Radiocephalic fistula: The radial artery and the cephalic vein are anastomosed (connected) to form the distal forearm fistula known as the radiocephalic fistula. The wrist is cut transversely. Vessel loops divide, mobilize, and secure the cephalic vein and radial artery.
Brachiocephalic fistula: An upper arm fistula formed by anastomosing (connecting) the cephalic vein to the brachial artery is known as a brachiocephalic fistula. A transverse incision is made over the antecubital fossa. Vessel loops are used to dissect, mobilize, and secure the brachial artery and cephalic vein.
Transposition brachiobasilic fistula: The brachiobasilic fistula is performed when the above techniques have failed and are not feasible. Since the basilic vein is deep and medial, it needs to be transposed into a more superficial and lateral region to be easily accessed. This can be done in one or two stages.
AV fistula surgery indications
A successful and long-lasting arteriovenous fistula (AVF) can increase life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for patients on hemodialysis (HD) who depend on vascular access as their lifeline. Below are some of the indications of arteriovenous fistula (AVF):
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD): For patients with end-stage renal disease who need permanent vascular access for hemodialysis, arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is frequently performed. Compared to hemodialysis catheters or prosthetic grafts, arteriovenous fistulas are the recommended first access.
- Uremic pericarditis: Patients with acute or chronic renal failure, either before dialysis treatment or during dialysis, may experience uremic pericarditis, a severe renal disease consequence.
- Ideal vascular access: Global recommendations and multiple research teams, including the National Kidney Foundation-Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI) 2006 CPG 2.1, European Best Practice Guidelines, and Canadian Society of Nephrology recommend that native vessel AVFs are preferred over central venous catheters (CVCs) for the start of hemodialysis (HD). Compared to patients receiving dialysis through catheter access and arteriovenous grafts (AVGs), those receiving dialysis across a functioning AVF have reduced complication rates and longer event-free patency durations.
AV fistula surgery contraindications
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is unsafe in some conditions; hence, it is not recommended. Below are some of the situations where AVF is not recommended:
- Advanced peripheral artery disease with necrosis on the side of AV fistula creation: Patients with advanced peripheral artery disease (a slow and progressive disorder of the blood vessels) with necrosis (uncontrolled cell death) are not suitable for the creation of AV fistula.
- Venous occlusion: The term "venous occlusion" refers to a condition in which adjacent structures such as clots, muscles, arteries, or other veins compress, narrow, or obstruct a vein, resulting in blood pooling and backward flow.
- Central venous stenosis: Arteriovenous access is a potentially dangerous option for dialysis since central vein stenosis (CVS) is frequently observed in patients undergoing hemodialysis via an arteriovenous route.
- Active infection: Individuals with active infection are unsuitable for creating AV fistula.
- Elderly individuals, those with advanced heart failure, and those with shortened lifespans: Though AVF may be superior to arteriovenous graft (AVG) and central venous catheter (CVC), a lower rate of AVF patency is seen in older people due to a high burden of comorbidities and inadequate vasculature for fistula maturation.
Amputation of extremities, pacemaker placement, and prior axillary node dissection are some of the other contraindications of arteriovenous fistula (AVF).
AV fistula procedure
The steps involved in the AV fistula include:
Before AV fistula procedure
- Before the procedure, when patients meet the surgeon, they are admitted to either an inpatient ward or the day surgery unit in the ward.
- When evaluating a patient before surgery to develop an AV fistula, a careful assessment should determine the cause of renal failure, which upper extremity is dominant, and the patient's past use of a central catheter and any additional venous system implants like transvenous pacemakers.
- An assessment of the flow and vascularization in the extremities should be part of the physical examination to decide whether fistula development is necessary or not. One should palpate the brachial and radial pulses. Although vascular steal is uncommon following the establishment of a forearm fistula, Allen's test may still be carried out.
- Patients will be asked about the usage of tablets or other medications, such as over-the-counter medications from a pharmacy or health food store or ones that were prescribed by a doctor. Bringing information about the medications, such as the package or the repeat prescription, will be helpful to doctors.
- It is crucial that patients need to inform doctors about the usage of any anticoagulants, such as warfarin, aspirin or heparin, are the drugs that prevent blood clots.
- If they are not taking an anticoagulant, patients will begin taking aspirin one week before their planned procedure unless it is contraindicated. It is essential to inform the doctor about any stomach upset or gastrointestinal ulcerations patients may experience.
- If patients use warfarin, they must stop taking it five days before the surgery.
- The surgeon may advise blood tests, chest X-ray, and electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Without the use of duplex ultrasound imaging, evaluating vasculature in some patient populations (such as obese people) might be challenging. When a physical examination reveals that no vein is visible, ultrasound mapping may identify a transposable vein that was previously missed.
- Patients need to fast for 12 hours before surgery.
- In some instances, the medical staff might require hair removal to examine the skin. If necessary, the surgical team may remove the hair on the day of the procedure by utilizing an electric hair clipper with a disposable, single-use head.
- The surgeon will take the signature of the patient on a consent form before proceeding for surgery.
During AV fistula procedure
- Patients will be given the appropriate sedative and/or anesthesia before the surgery.
- Before the surgery, local anesthetic medication injections will be administered to the patients around the vein and artery.
- The surgeon will make an incision to examine the vein and move it closer to the artery once the skin has been made numb. Surgical sutures (stitches) will be used to join them.
- Transparent dressings or dissolvable sutures will be used to close the skin.
- The wound will heal, and no sutures will need to be taken out.
- The process will be the same whether patients receive a general anesthetic, although they might or might not receive injections of local anesthetic medication.
After AV fistula procedure
- If patients are given a local anesthetic, they can resume their regular diet and liquids after the procedure. If not, they need to wait to recover from the general anesthetic or sedation.
- After 30 minutes, most patients undergoing this surgery under local anesthesia can leave the hospital. Patients might need to stay for a few hours or overnight if they received general anesthesia or sedation until they have completely recovered from the effects of the anesthetic.
- The length of the hospital stay will be determined by the patient's overall health, how fast they heal following treatment, and on the advice of the vascular surgeon.
- After the procedure, most patients can return to their regular activities the following day. However, it may be necessary to wait a little longer before engaging in more strenuous activities.
- The timing of getting back to work will depend on patients' typical level of health, the speed at which they heal, and the nature of the job.
- For a maximum of three days following the procedure, surgeons advise patients not to drive.
- Patients and their family members are advised to avoid extended pressure, blood pressure cuffs, tight clothes or jewelry, and venipunctures on the operated side.
- Before being discharged, patients are instructed in handball exercises.
- Patients receive counseling regarding warning indicators such as numbness, coldness, sores, or discoloration at the tips of their fingers.
- Patients are called for a first follow-up assessment on day three. After that, they are evaluated and the sutures removed, and they are reviewed again after four weeks to check for signs of maturation of the AV fistula.
Advantages of AV fistula surgery
For patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are thought to be the most efficient way to provide hemodynamics. This is because hemolysis via central venous catheterization (CVC) is usually associated with an increased risk of bloodstream infection, hospital stay, and related costs. Below are the benefits of AVFs:
- An arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is usually the ideal vascular access method for hemodialysis.
- AVFs often have longer lifespans.
- People with arteriovenous fistula (AVF) have fewer complications (like infections) when compared with other types of vascular access.
- AVFs have decreased the risk of hospitalizations.
- AVFs have a decreased risk of mortality when compared to dialysis catheters or prosthetic grafts.
- Compared to AV grafts, AV fistulas have a lower risk of thrombosis.
- Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) has a longer patency rate (the condition of not being blocked or obstructed).
- AVFs have the possibility of increased blood flow rates
AV fistula complications
Bleeding, infection, and injury to neighboring structures are risks of surgical treatment. Patients with elevated risk may experience a higher likelihood of complications leading to considerable morbidity. Complications of arteriovenous fistula (AVF) are categorized as immediate, early (days to months), and late complications (after maturity).
- Immediate complications
- Ischemic steal syndrome
- Early complications
- Infection
- Thrombosis
- Central venous stenosis
- Failure to mature
- Late complications
- Aneurysm
Immediate complications
- Ischemic steal syndrome: After an AV fistula forms, blood flow to the distal extremities is reduced, leading to steal syndrome. Pain, diminished motor function or sensation, or neuropathy are examples of clinically significant consequences.
Early complications
- Infection: Erythema, edema, and possibly systemic symptoms are the most common manifestations of perivascular cellulitis in AV fistula infections. Based on wound and blood cultures, localized infections can be treated with the proper antibiotics. More severe infections associated with hematomas, abscesses, or aneurysms need to be surgically excised and drained.
- Thrombosis: The most frequent consequence of fistulas is thrombosis, which can happen at the anastomosis or fistula vein in stenotic locations. The degree of stenosis raises the risk of thrombosis. However, Fistulas have a lower incidence of thrombotic events than AV grafts.
- Central venous stenosis: Central venous stenosis can lead to venous hypertension, which involves swelling in the upper extremities and may eventually result in reduced movement. The insertion of central venous catheters and devices is the most frequent cause of central venous stenosis.
- Failure to mature: Anastomotic stricture resulting from neointimal hyperplasia is a frequent cause of unsuccessful maturation. A patient's age above 65, reduced vascular compliance, and associated illnesses such as diabetes, obesity, heart failure, hypertension, and peripheral atherosclerosis are risk factors that impair the maturation of an AV fistula.
Late complications
- Aneurysm: Aneurysm formation can result from repeated needle punctures in a localized place, which weakens the vascular access wall. High blood flow can also cause aneurysmal dilatation over time. If there is a loss of skin integrity, ulceration, or a restricted number of puncture sites, aneurysms usually need to be surgically repaired. If left untreated, high-risk aneurysms can burst and cause lethal exsanguination (severe loss of blood).
Questions that the patients can ask the healthcare team about AV fistula surgery ?
- How long will it take for my wound to heal?
- When am I allowed to drive again?
- When can I resume my job?
- What should I do if my fingers or hands start to swell?
- How should I take care of my fistula at home?
- How long is my fistula going to last?
- If my fistula bleeds, what should I do?
- Will I have to make a follow-up appointment?
Difference between AV fistula and Graft
AV fistula vs Graft
A direct connection between the patient's artery and a nearby vein is known as an AV fistula, whereas an indirect connection between the artery and vein is known as an AV graft, also referred to as a bridge graft. The following parameters can distinguish AV fistula and graft:
| Parameters | AV fistula | Graft |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | An arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a surgical connection between an artery and a vein. It is commonly performed in patients with end-stage renal illness who need permanent vascular access for hemodialysis. | A fistula and an arteriovenous graft are comparable. However, a plastic tube connects the artery and vein rather than directly connecting them. |
| Thrombosis (blood clots) rate | Has a lower thrombosis rate | Has a higher thrombosis rate |
| Infection rate | Has a lower infection rate | Has a higher infection rate |
| How soon it can be used | It may take three to six months to mature | It may be used within a few weeks |
| How long does it last for | It lasts longer | It does not last longer |
History of AV fistula surgery
- The first autologous arteriovenous fistula (AVF), later known as the Brescia-Cimino fistula, was created by Appel in 1965.
- Appel used a side-to-side anastomosis (connection) between the wrist's cephalic antebrachial vein and radial artery to create an AVF.
- Soon after, end-to-end and end-to-side anastomosis, as well as the use of other extremity vessels, emerged as the most popular access option for HD patients: surgically produced AVFs using autologous vessels.
- According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, more than 468,000 individuals were receiving hemodialysis as of 2013. About 20% of those undergo dialysis through an arteriovenous (AVF) created surgically.
AV Fistula Surgery Cost in Hyderabad, Telangana, India
The
cost of AV Fistula Surgery in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹25,000 to ₹85,000 (approximately US $300 – US $1,020). The exact AV Fistula Surgery cost in India varies depending on several factors such as the type of fistula created (radiocephalic, brachiocephalic, brachiobasilic), vein and artery condition, need for vein transposition, patient comorbidities, vascular surgeon expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown Based on Type of AV Fistula Procedure
- Radiocephalic (Wrist) AV Fistula – ₹25,000 – ₹45,000 (US $300 – US $540)
- Brachiocephalic (Elbow) AV Fistula – ₹35,000 – ₹65,000 (US $420 – US $780)
- Brachiobasilic AV Fistula with Transposition – ₹55,000 – ₹85,000 (US $660 – US $1,020)
- Revision / Secondary AV Fistula Surgery – ₹40,000 – ₹75,000 (US $480 – US $900)
- Temporary Access (Tunneled Catheter) if Required – ₹18,000 – ₹35,000 (US $215 – US $420)
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on AV Fistula Surgery
Can dialysis be started immediately after AV fistula surgery?
About 30-50% of AVFs fail to develop, which is a significant barrier to successful AVF creation. The average period for maturation ranges from one to four months. However, it usually happens four to six weeks following the initial fistula surgery. After the maturation of the AV fistula, dialysis can be started.
How to know if the AV fistula is working?
To check if the AV fistula is working, we need to look, feel, and listen to it. Try placing your fingertips on the skin covering the fistula; patients need to experience a "thrill" or vibration. A fistula's "bruit" or "shoosh-shoosh" noise should be heard.
Which is the Best Hospital for AV Fistula Surgery in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is considered one of the most trusted centres for AV fistula creation, vascular access management, and dialysis-related surgical care.
Our vascular surgeons specialise in creating durable, high-flow, long-lasting AV fistulas using advanced ultrasound-guided mapping, microvascular techniques, and precision vessel handling to ensure successful maturation and reliable dialysis access.
With modern operating suites, real-time vascular imaging, continuous post-operative monitoring, and comprehensive nephrology support, PACE Hospitals provides safe, effective, and successful AV fistula outcomes — supported by cashless facilities, TPA corporate tie-ups, and seamless medical insurance assistance for eligible patients.
How to decrease the swelling after AV fistula?
It can be reduced by elevating the arm on multiple pillows while the patient is sleeping and by not wearing bracelets, rings, or sleeves with elastic. If the swelling worsens, patients can go to the hospital.
Why we prefer AV fistula?
An AV fistula provides the most efficient blood supply access for long-term hemodialysis patients. It implies that a plastic dialysis line isn't available for infection, which is crucial because infections weaken the blood vessel's lining and make it narrower.
What is the Cost of AV Fistula Surgery in Hyderabad, India?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of AV Fistula Surgery typically ranges from ₹25,000 to ₹85,000 and above (approximately US $300 – US $1,020), depending on:
- Type of AV fistula created (RCF, BCF, BBF with transposition)
- Vessel quality and need for vein mapping
- Complexity of the patient’s vascular condition
- Requirement for additional procedures (e.g., catheter insertion)
- Surgeon expertise and surgical time
- Hospital stay duration and post-operative monitoring
Simple wrist (radiocephalic) fistulas fall at the lower end of the range, while complex or transposition fistulas are usually at the higher end.
After a detailed vascular evaluation and duplex ultrasound mapping, our surgical team provides a personalised treatment plan and an accurate cost estimate based on your specific medical needs.
Why do AV fistulas fail?
The fistula should have sufficient blood flow to support dialysis and the size necessary to enable successful repeated cannulation. Failure to mature can be caused by three main reasons: issues with the arteries and veins and the existence of accessory veins.
Is AV fistula surgery painful?
AVF pain is a condition that is underreported and poorly understood. Even though it is uncommon, extreme pain might cause substantial problems and the eventual discontinuation of AVF. Pain is frequently a sign of an underlying anatomic issue.
What to do if AV fistula bleeds?
Use whatever gauze is available from your emergency pack to apply hard pressure to the bleeding location. Hold the place for a minimum of ten minutes. If the bleeding stops, use clean pressure pads or new gauze and tape. If the bleeding continues, immediately visit the hospital.
Can we take blood sample from AV fistula hand?
No, the hand with the AV fistula cannot be used to draw blood samples. Never allow someone to insert a cannula or draw blood from the fistula arm, and the arm with the fistula cannot be used to take blood pressure.
What is an AV fistula in the brain?
Vascular abnormalities in the tissues surrounding the brain or spinal cord are known as arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). They occur when there is a direct connection between one or more arteries and one or more veins, often known as sinuses.
Who first used AV fistula to conduct hemodialysis?
Dr. Kenneth Charles Appell first created the radiocephalic arteriovenous fistula (AVF), which is still a dependable technique for vascular access today and enables patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to receive hemodialysis.
Can AV fistula cause heart failure?
A surgically made arteriovenous fistula is the recommended vascular access method for hemodialysis patients. One less common but potentially serious side effect of this surgery is the development of high-output heart failure.
What is the rule of 6 for dialysis fistula?
To determine whether an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) will support dialysis or not, the rule of 6, which states flow volume >600 mL/min, vein diameter >6 mm, and vein depth <6 mm, is tested in clinical practice.
What is the success rate of AVF surgery?
The first-time AVF creation success rate was 98% (13/99, 95%CI: 8.74–21.18%). AVF failure rates were 13.13% (13/99, 95%CI: 8.74–21.18%) for the primary AVF and 16.87% (14/83, 95%CI: 10.32–26.25%) for the secondary AVF. Bleeding (1%) and early anastomosis thrombosis (2%), among other early complications, were reported.




