COPD - Symptoms, Causes, Complications and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
Overview | Prevalence | Types | Causes | Symptoms | Risk Factors | Complications | Diagnosis | Treatment | Prevention | COPD vs Asthma | FAQs | When to consult a Doctor
COPD full form in medical - Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
COPD definition
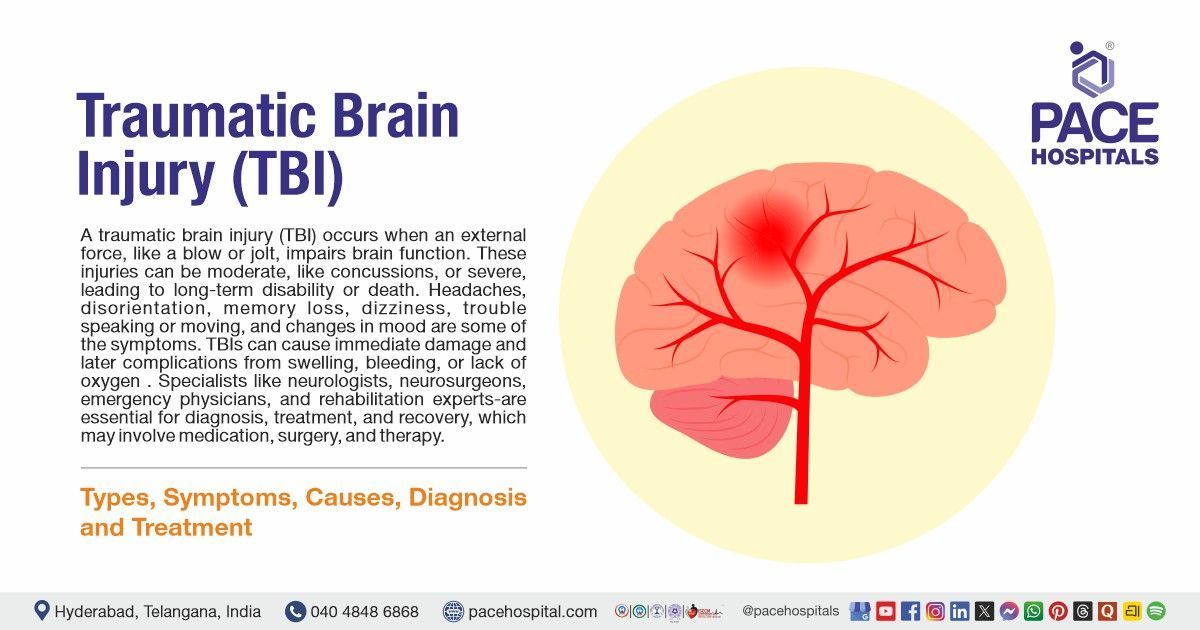
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung condition caused by damage to the lung's airways or other parts. This damage restricts airflow and makes breathing difficult.
It is associated with structural lung changes caused by long-term, chronic inflammation from exposure to harmful particles or gases, most frequently cigarette smoke. Chronic inflammation leads to the narrowing of airways and decreased lung recoil. Individuals suffering from COPD may experience lung damage or phlegm formation. The symptoms include tiredness, wheezing, breathing difficulties, and coughing, usually with phlegm. Symptoms may vary from being asymptomatic (no symptoms) to respiratory failure.
To manage patients with COPD disease, a multidisciplinary team of medical professionals comprising a
pulmonologist, a thoracic surgeon, an intensivist, and a respiratory therapist is essential.
COPD meaning
The word “chronic” is coined from the Greek word "Chronos," meaning it is long-lasting. The word “obstructive” is derived from the Latin word “obstruere", meaning having the quality of obstructing, serving, or intending to hinder. The word “pulmonary” is derived from the Latin word “pulmonarius”, meaning the lungs. The word “disease” is derived from the Latin word meaning sickness or illness.
COPD Prevalence
COPD prevalence worldwide
Worldwide, the prevalence of COPD was predicted to be 10.6% or 48 crore cases in 2020 among both males and females. It was estimated that by 2050, there will be 59.2 crore cases of COPD worldwide (which is 9.5% of the eligible population), representing a relative rise of 23.3% from 2020 to 2050 of 11.2 crore cases.
Prevalence of COPD in India
A cross-sectional study by Johnson et al. in Southern India found a prevalence of 2.4%, whereas a study by Koul et al. in Northern India found a prevalence of 16.1%. It included eight studies of COPD. Bengal has a significantly greater frequency of COPD cases in its rural areas than the projected national standard, and the patient's health is generally poor.

Types of COPD
The term "COPD" indicates a group of lung conditions that can make breathing difficult. Most COPD patients also have chronic bronchitis and emphysema, while individual differences may exist in the severity of each condition. Below are the two main types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis: It is a long-term inflammation of the bronchi (the lungs' breathing passages) that causes mucus production to increase along with other changes. Such changes may cause breathing problems, frequent infections, coughing and weakness.
Emphysema: Emphysema is a long-term lung condition that can cause the lungs' alveoli, or the air sacs, to become destroyed, narrowed, collapsed, stretched, or overinflated. Breathlessness and a decrease in respiratory function may result from it. Damage to the air sacs causes permanent "holes" in the lung tissue, which is irreversible.
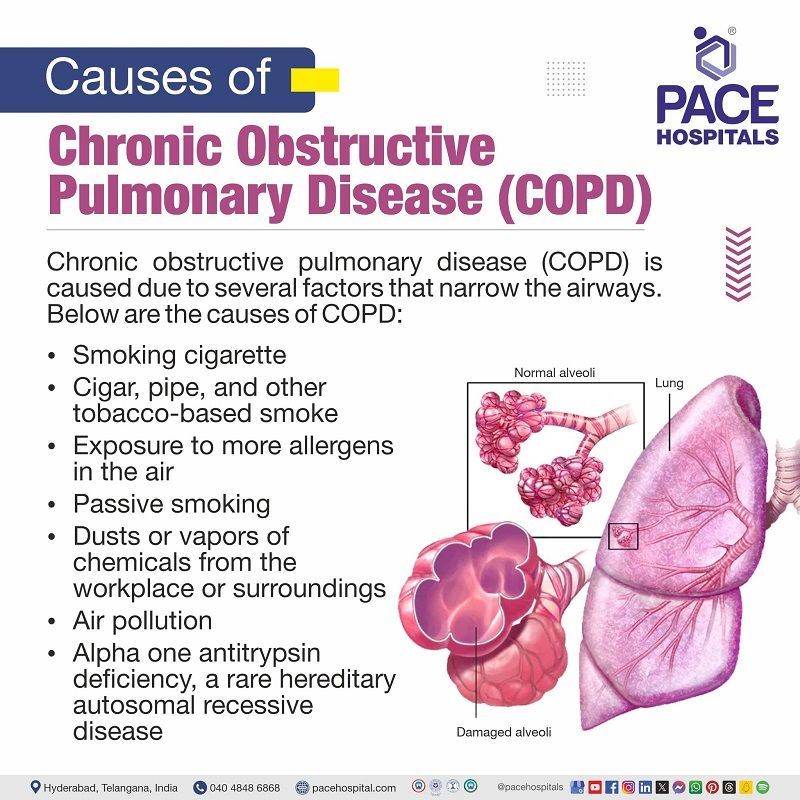
COPD Causes
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is caused due to several factors that narrow the airways. There could be inflammation and swelling of the lining of the airways, destruction of parts of the lung, and mucus obstructing the airways. Below are the causes of COPD:
Chronic bronchitis
Long-term exposure to allergens that harm the airways and lungs is typically the cause of chronic bronchitis. Many medical experts agree that smoking cigarettes is the primary cause of chronic bronchitis. The atmosphere at work and air pollution may also be factors. The causes of chronic bronchitis include:
- Smoking cigarette
- Cigar, pipe, and other tobacco-based smoke
- Exposure to more allergens in the air
- Passive smoking
- Dusts or vapors of chemicals from the workplace or surroundings
- Air pollution
- Chronic gastroesophageal reflux
- In rare cases, it is caused by a genetic disorder known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Emphysema
Emphysema develops gradually over time. It could result from:
- Prolonged and significant exposure to harmful gases, the most prevalent cause, which continues to be smoking cigarettes
- Other pollutants in the environment, such as sulphur dioxide and particulate matter, as well as biomass fuels
- Alpha one antitrypsin deficiency, a rare hereditary autosomal recessive disease
- Lung infections
- Allergies
- Passive smoking
- Low birth weight
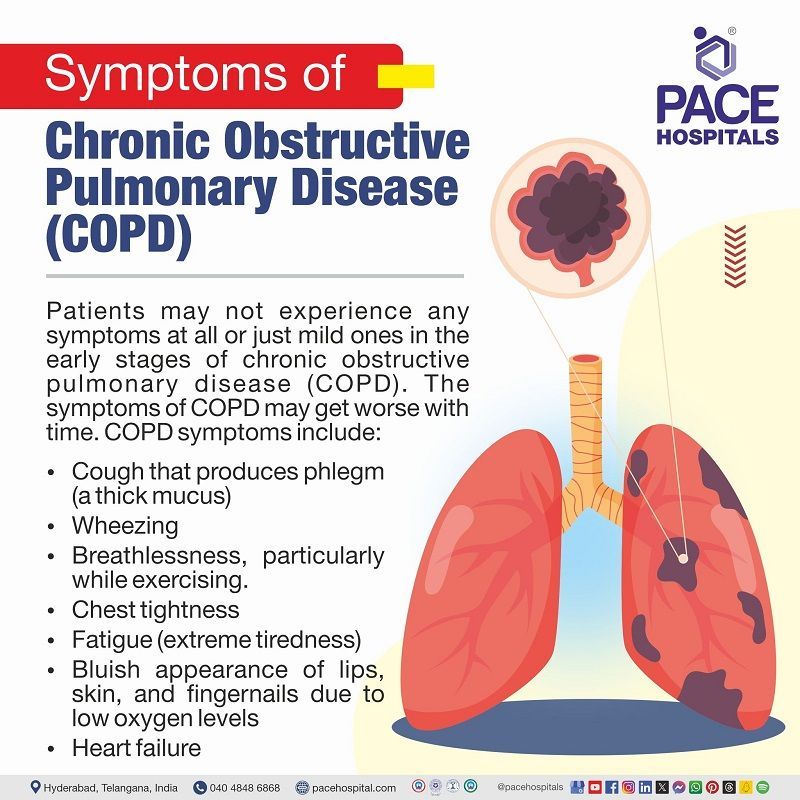
COPD Symptoms
Patients may not experience any symptoms at all or just mild ones in the early stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The symptoms of COPD may get worse with time, and it includes the following:
Chronic bronchitis
Some individuals who suffer from chronic bronchitis frequently get respiratory illnesses like the flu and colds. Severe cases of chronic bronchitis can result in ankle, foot, or leg edema, as well as weight loss and weakness in the lower muscles. Below are the common symptoms of chronic bronchitis:
- Regular coughing, often known as smoker's cough or coughing up a lot of mucus
- A whistling or squeaky sound that one may make while breathing
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Breathlessness, particularly while exercising.
- Heart failure
- Bluish appearance of lips, skin, and fingernails due to low oxygen levels
Emphysema
Each person may experience slightly different symptoms. Below are the most common symptoms of emphysema:
- Cough that produces phlegm (a thick mucus)
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Breathing difficulties during physical activity and, in the last stages of severe illness, breathing problems most of the time
- Chance of respiratory infections
- Cyanosis, an oxygen-deficient condition that gives the skin a blue color
- Wheezing
- The ribcage expands to make space for enlarged lungs, resulting in a barrel-shaped chest.
COPD Risk Factors
Several factors may contribute to increasing the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The following are some of the risk factors that are associated with the development of COPD:
Chronic bronchitis
The risk factors of chronic bronchitis include:
- Age
- Genetics
- Cigarette smoking
- Passive smoking (breathing in other people's tobacco smoke)
- Long-term exposure to lung irritants
- A family history of COPD
- Exposure to specific types of dust or fumes
Emphysema
The risk factors of emphysema include:
- Smoking cigarette
- Family history of lung disease
- Lower body mass index
- Environmental pollution
- Genetic factors
- Coal worker pneumoconiosis (lung condition brought on by prolonged exposure to coal, graphite, or man-made carbon dust)
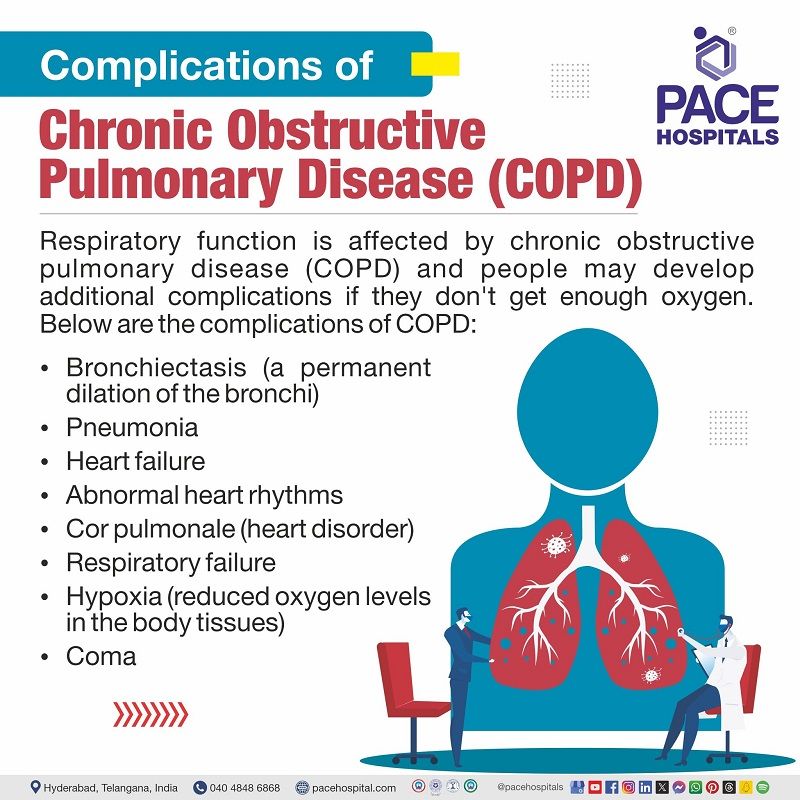
Complications of COPD
Respiratory function is affected by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and people may develop additional complications if they don't get enough oxygen. Below are the complications of COPD:
Chronic bronchitis
The possible complications of chronic bronchitis include:
- Bronchiectasis (a permanent dilation of the bronchi)
- Pneumonia
- Heart failure
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Cor pulmonale (heart disorder)
- Emphysema
- Respiratory failure
Emphysema
Individuals with emphysema are at risk for several problems, some of which can be severe. The following are some of the most common emphysema complications that are encountered:
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumonia
- Respiratory failure
- Cor pulmonale
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections
- Interstitial emphysema
- Respiratory acidosis
- Hypoxia (reduced oxygen levels in the body tissues)
- Coma
- Chronic atelectasis (a partial or whole collapse of the lung or a lobe- a specific portion of the lung)
COPD Diagnosis
Any patient with dyspnea, a persistent cough or production of sputum, and/or a history of exposure to disease-related risk factors should be evaluated for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The diagnosis of COPD involves the following:
Chronic bronchitis
A typical medical history is the most critical component in ruling out additional possible lower respiratory tract illnesses when diagnosing chronic bronchitis. Below are the investigations that assist in confirming the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis:
- Complete medical history
- Family history
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Serum procalcitonin level
- Pulse oximetry
- Arterial blood gas
- Chest x-ray
- Pulmonary function tests
- Sputum culture
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Influenza tests
- Laryngoscopy
Emphysema
The diagnosis of emphysema is pathological. Routine laboratory and radiographic studies are therefore not recommended. Below are the tests used in the diagnosis of emphysema:
- Complete medical history
- Family history
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Chest x-ray
- Arterial blood gases
- Pulmonary function tests
- Postbronchodilator test
- Sputum culture
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) test
COPD Treatment
Yet, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has no known cure; however, the below treatment can help manage symptoms and decrease the disease's progression.
Chronic bronchitis
The main objectives of treating chronic bronchitis are to reduce symptoms, avoid complications, and delay the disease's course. The treatment options for chronic bronchitis include the following:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Pharmacological therapy
- Bronchodilators
- Steroids
- Antibiotics
- Vaccines
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation program
- Surgery
- Lung transplant
Emphysema
There is no proven cure that can change the course of the disease. On the other hand, managing symptoms and modifying risk factors can effectively reduce the progression of the disease and improve quality of life.
- Medical therapy
- Bronchodilator
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Corticosteroids, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors
- Supportive therapy
- Oxygen therapy
- Ventilatory support
- Pulmonary rehabilitation of COPD
- Palliative care
- Interventional therapy
- Lung volume reduction surgery
- Lung transplantation
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support
COPD Prevention
Most chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) cases are preventable. If patients don't smoke, they may significantly reduce the risk of getting COPD. Below are some of the preventive measures of COPD:
Chronic bronchitis
The quality of life and morbidity are significantly impacted by chronic bronchitis. By taking the following preventative measures, people may be able to avoid bronchitis or reduce the risk of developing it again:
- Cessation of smoking
- Avoiding passive smoking
- Avoiding dust and chemical fumes
- Avoiding air pollution
- Alteration in the lifestyle
- Regular vaccination against pneumonia can lower the morbidity rate in those with chronic bronchitis.
- Taking regular vaccinations for influenza every year.
Emphysema
Following are some of the preventive measures of emphysema:
- Cessation of smoking
- Engaging in physical activity and being fit
- Wearing masks or other personal protection equipment (PPE) whenever people work in an environment with dust or chemicals.
- Getting vaccinated against “pneumococci”
- Vaccination against “Haemophilus influenzae”
- Protecting from a cold environment
- Avoiding other respiratory irritants
Difference between Asthma and COPD
COPD vs Asthma
Despite their many similarities,
asthma and COPD are very different. They are two distinct diseases with respect to their etiology, symptoms, mediators, inflammatory cells, consequences of inflammation, responsiveness to therapy, and course. Below are some of the parameters that help differentiate asthma and COPD.
| Parameters | Asthma | COPD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Asthma is a chronic lung condition that affects people of all ages. Breathing becomes more difficult because of the inflammation and tightness in the muscles surrounding the airways. | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), is a common lung condition resulting from damage to the lung's airways or other parts, restricting airflow and making breathing difficult. |
| Symptoms | Persistent cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness | Breathing difficulty, chronic cough (with phlegm in some cases), and feeling tired |
| Risk factors | Allergies, cold air, family history | Long-term cigarette smoking, occupational exposure, pneumonia, air pollution |
| Presentation | It usually affects younger people | It commonly affects elderly patients who smoke or have smoked in the past. |
| Treatment | Bronchodilators, oral steroids, inhaled corticosteroids | Bronchodilators, oxygen therapy, COPD medications, surgery, hospitalization |
| Lifestyle modifications | Avoiding air pollution, avoiding allergens | Cessation of smoking, avoiding air pollution |
A Guide to Air Travelling with COPD
If you suffer from COPD and have plans to travel by air, you need to first consult your pulmonologist to confirm your fitness through a fly assessment. This typically involves checking your breathing conditions using spirometry and measuring your oxygen levels.
Before travelling, remember to pack all medicines, such as inhalers. If you are going through oxygen therapy, inform your travel operator and airline prior to booking your ticket, as you may need a medical form from your pulmonologist.
If you are using long-term oxygen therapy, you need to make sure you have an adequate oxygen supply. Usually, airlines do not allow oxygen cylinders but may permit oxygen concentrator devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on COPD
Is COPD genetic?
Genetic association studies have found hundreds of genetic variations that affect lung function, the risk of COPD, and other COPD-related traits. Having a close relative with COPD increases a person's risk of developing the illness, which implies that certain people may be genetically vulnerable to the condition.
Is COPD curable?
Although there is no known cure for COPD, treatment can reduce symptoms, prevent hospitalization, and halt the disease's progression. Treatment's goals are to lessen the likelihood of complications, stop additional harm, and ease some of the symptoms. Options for treatment include oxygen therapy, medications, and pulmonary rehabilitation.
What diseases are included in COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to a group of lung diseases that impair breathing. Emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and non-reversible chronic asthma are three of the most prevalent COPD diseases. These conditions may appear separately or together.
How to treat COPD?
Although COPD causes irreversible damage to the lungs, medication can help the disease progress more slowly. Treatment options include smoking cessation, inhalers and medications for easier breathing, pulmonary rehabilitation of COPD (a specific exercise and education program), surgery, or lung transplantation.
What are the four stages of COPD?
The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) has released a four-stage classification of the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to guide the therapeutic approach. The four stages of COPD are mild, moderate, severe, and very severe.
What is COPD?
COPD is a common lung disease caused due to injury to the airways or other lung areas, which limits airflow and makes breathing challenging. It is linked to long-term, chronic inflammation from exposure to dangerous particles or gases, most commonly cigarette smoke, which results in structural lung abnormalities.
Are asthma and COPD the same?
Despite many similarities, asthma and COPD are distinct conditions. Both conditions differ in terms of their etiology, symptoms, types of airway inflammation, inflammatory cells, mediators, effects of inflammation, response to treatment, and duration.
How do bronchodilators work in COPD?
Bronchodilators are a class of drugs that ease breathing by widening the bronchi and relaxing the muscles in the lungs. They are frequently used to manage long-term conditions that may cause the airways to narrow and become inflamed.
Can COPD cause pulmonary edema?
Yes, pulmonary edema (buildup of fluid in the lungs that can impair lung function) can be caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Cor pulmonale, another condition associated with COPD, may resemble heart failure-related pulmonary edema.
Why is COPD worse in the morning?
Due to the circadian variation in lung function or the fact that the morning is the most active period and problematic part of the day concerning activity limitations, for COPD patients, the evening is the second most difficult time of day.
What is COPD aspiration?
Aspiration, the inhalation of food, drink, or objects into the lungs or airway, is common in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Many factors can contribute to it, such as dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), rapid drinking, altered lung capacity, and impaired laryngeal closure.
Why is oxygen bad for COPD?
Hypercapnia (abnormally elevated blood carbon dioxide levels) can result from uncontrolled oxygen therapy for COPD patients. A saturation target of 88–92% has also been advised for patients with other conditions that put them at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure, such as neuromuscular disorders, chest wall disorders, and morbid obesity.
Which predominant biomarkers are involved in the pathogenesis of COPD?
Numerous markers, including CRP (C-reactive protein), tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-6, IL-8, fibrinogen, and neutrophil counts and activity, are understandably elevated in COPD patients since the disease is inflammatory.
What is the best diet for COPD patients?
According to one research study, people with COPD or at risk for the disease need to stay away from eating processed meats altogether or significantly cut down and replace them with healthier foods such as whole grains, nuts, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and long-chain omega-3 fats.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868