Erectile dysfunction (Impotence) - Types, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention
PACE Hospitals
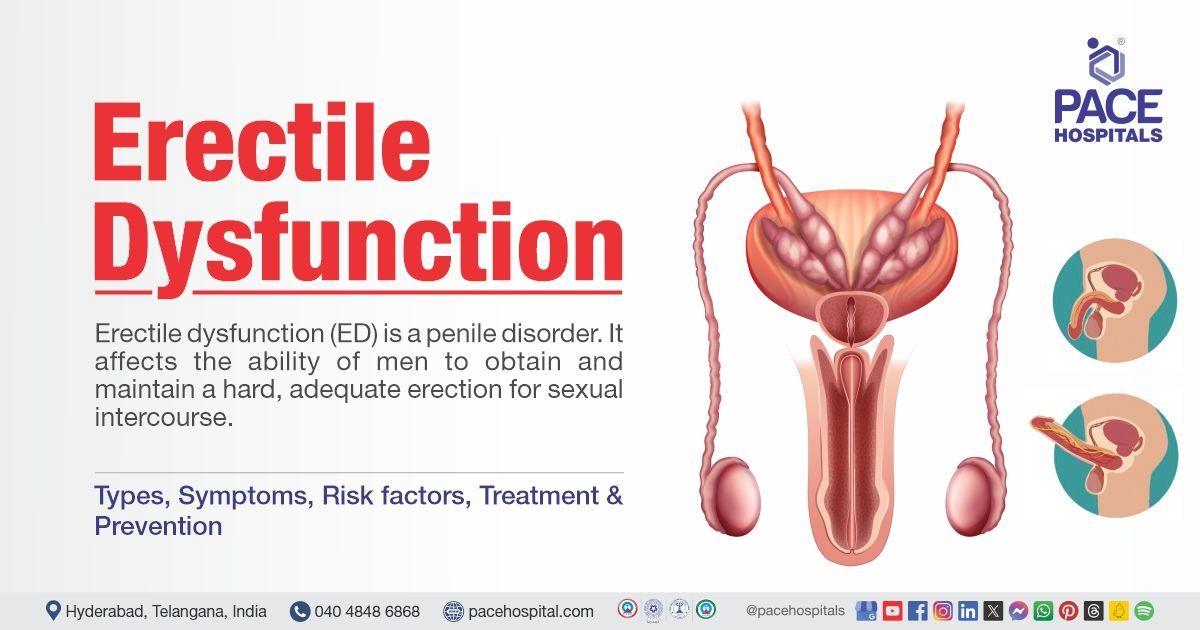
What is erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction, often known as impotence or ED, is the inability to form or sustain an adequate erection for sexual intercourse. Most of the erectile dysfunction cases can be effectively treated.
Unwillingness to seek medical care remains the most significant barrier to recover from erectile dysfunction. A
general physician or
urologist can help in diagnosing and treating erectile dysfunction (ED).
Erectile dysfunction meaning
The word "erectile dysfunction" was coined in the 1970s by combining the words "erectile" and "dysfunction". The word first appeared in the Oxford English Dictionary in 1970.
Erectile dysfunction is the combination of two words in which erectile is derived from the French word “erectile” which means pertaining to muscular erection
The term “dysfunction” is derived from the English words “dys” and “function”, and it was first reported in use between 1915 and 1920.
- Dys- :means "bad" or "abnormal"
- Function: means "proper purpose”
Erectile dysfunction prevalence
Erectile dysfunction prevalence worldwide
In 1995, it was estimated that over 15.2 crore men globally had erectile dysfunction. The global incidence of erectile dysfunction is expected to be around 32.2 crore by 2025. Historically, erectile dysfunction was thought to be caused by psychological difficulties.
Because of reporting bias, cultural differences, general neglect to enquire about the sexual health of their male patients, and embarrassment difficulties, these figures probably represent a severe underestimation of the true number of men with erectile dysfunction (ED). Age and other co-morbidities like diabetes, hypogonadism, and cardiovascular disease are associated with a higher prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED).
According to the best available data from the Massachusetts Male Ageing Study, the incidence rises with age and the overall prevalence is 52%. Approximately 40% of males experience ED at age 40, and by age 70, 70% will report having erectile dysfunction (ED). These results were validated by comparable research and the National Health and Social Life Survey.
Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in India
Research on India's sexual health issues shows that, in comparison to other nations, a significant portion of Indian men experience impotence, making India the world's epicentre of impotence. In India, impotence affects one in ten males; the number may be greater in larger cities. Approximately 25% of patients with erectile dysfunction (ED) are younger than 30 years old. Ten years ago, the range was approximately 5-7%.
Types of erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can be categorised into different types based on the patient’s condition, cause, and other physiological factors.
Based on the condition, erectile dysfunction is categorised into:
- Primary erectile dysfunction
- Secondary erectile dysfunction
Primary erectile dysfunction: In primary erectile dysfunction it has never been possible for a man to achieve or sustain an erection.
Secondary erectile dysfunction: An individual with secondary erectile dysfunction has erection difficulties later in life but has normal erections previously.
Based on the cause of erectile dysfunction it is categorised into:
- Hormonal erectile dysfunction
- Drug-induced erectile dysfunction
- Neurogenic erectile dysfunction
- Psychogenic erectile dysfunction
Hormonal erectile dysfunction: Hormonal erectile dysfunction (ED) is a kind of erectile dysfunction that is characterised by inappropriate hormone levels. These irregularities may include:
- Low testosterone (male sex hormone) level
- Increased prolactin (female reproductive hormone, but present minimally in males)
- Thyroid gland issues
- Steroid abuse
Drug-induced erectile dysfunction: This type of erectile dysfunction develops due to prescription drugs like blood pressure medications, antidepressants, glaucoma eye drops, etc.
Neurogenic erectile dysfunction: This results from inadequate nerve transmission to the corpora cavernosa (two columns of spongy tissue in the shaft of the penis)
Psychogenic erectile dysfunction: Psychogenic erectile dysfunction (PED) is defined as the continuous inability to acquire or sustain an erection during sexual activity due to psychological reasons. These factors may include:
- Anxiety and stress
- Depression
- Guilt
- Low self-esteem
Based on other physiological factors erectile dysfunction can be:
- Vasculogenic erectile dysfunction
- Iatrogenic erectile dysfunction
- Arteriogenic erectile dysfunction
Vasculogenic erectile dysfunction: This is caused due to reduced blood flow to the penis resulting due to a vascular disease
Latrogenic erectile dysfunction: Radical pelvic surgery is frequently the cause of this kind of impotence.
Arteriogenic erectile dysfunction: Arteriogenic erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent kind of vascular erectile dysfunction caused by insufficient blood flow to the cavernous bodies (erectile tissues in the penis). It can account for 25-70 percent of ED cases.

Erectile dysfunction symptoms
The symptoms of erectile dysfunction vary from person to person. The most predominant symptoms that a man can experience include:
- Inability to get an erection
- Inability to maintain an erection for sufficient period of time
- Decreased libido (sexual desire)
- Having an erection occasionally, but not every time
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is often a sign of another health problem or health-related issue.
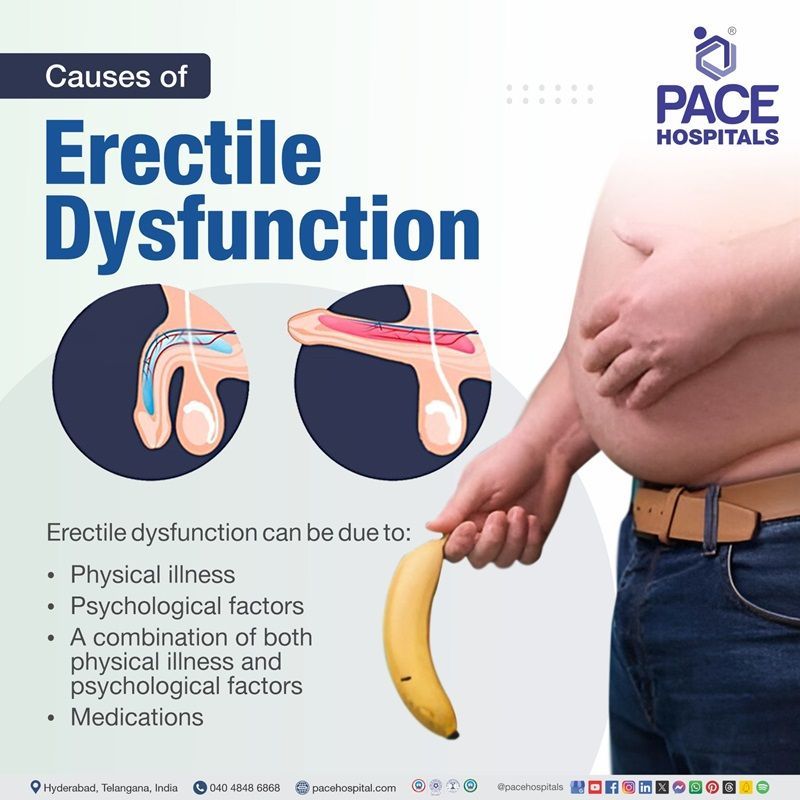
Erectile dysfunction causes
Medical practitioners used to believe that erectile dysfunction was mostly caused by psychological problems like depression and anxiety. In fact, a physical disease is the most common reason for erectile dysfunction.
Physical erectile dysfunction typically occurs over months or years and is characterised by a gradual decrease in function. If erections continue to occur spontaneously overnight or in the morning, the cause may be psychological.
Erectile dysfunction can be due to:
- Physical illness: Conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, cigarette smoking, obesity, sleep apnea, osteoporosis, arthritis, heart disease, and multiple sclerosis are frequently related to erectile dysfunction.
- Psychological factors: Stress, such as work troubles, marital issues, or financial concerns, might have an impact on a man's sexual drive or performance. Erectile dysfunction can be caused by psychiatric problems, as well as feelings of depression or anxiety about poor sexual performance.
- A combination of physical illness and psychological factors: Physical issues with keeping an erection may cause the male to feel worried about sexual performance, which exacerbates the problem.
- Medications: Prescribed medications used to treat high blood pressure, high cholesterol, depression and psychiatric problems, and prostate illness may cause or worsen erectile dysfunction symptoms.

Risk factors of erectile dysfunction
Understanding the risk factors linked to erectile dysfunction is essential for both prevention and treatment. The following could be considered direct risk factors for erectile dysfunction:
- Prostate issues
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (increased blood glucose)
- Hypogonadism (production of less or no hormones by sex glands)
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Vascular disease and vascular surgery (disease or surgery related to blood vessels)
- High levels of blood cholesterol
- Low levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
- Chronic sleep disorders (obstructive sleep apnea, insomnia)
- Drugs
- Neurogenic disorders
- Distortion or curvature of the penis (Peyronie's disease)
- Inflammation of the penis (Priapism)
- Depression
- Alcohol abuse
- Lack of sexual knowledge
- Poor sexual techniques
- Inadequate interpersonal relationships
- Many chronic diseases, especially renal failure (kidney failure) and dialysis (a procedure to eliminate waste materials and extra fluid from the circulation when the kidneys fail)
Smoking can trigger the effects of other risk factors such as hypertension (increased blood pressure) or vascular disease (disease related to blood vessels)
Age appears to be an important indirect risk factor because it is connected with an increased likelihood of direct risk variables, some of which are described above.
To prevent or cure erectile dysfunction, it is critical to accurately identify and characterise risk factors.
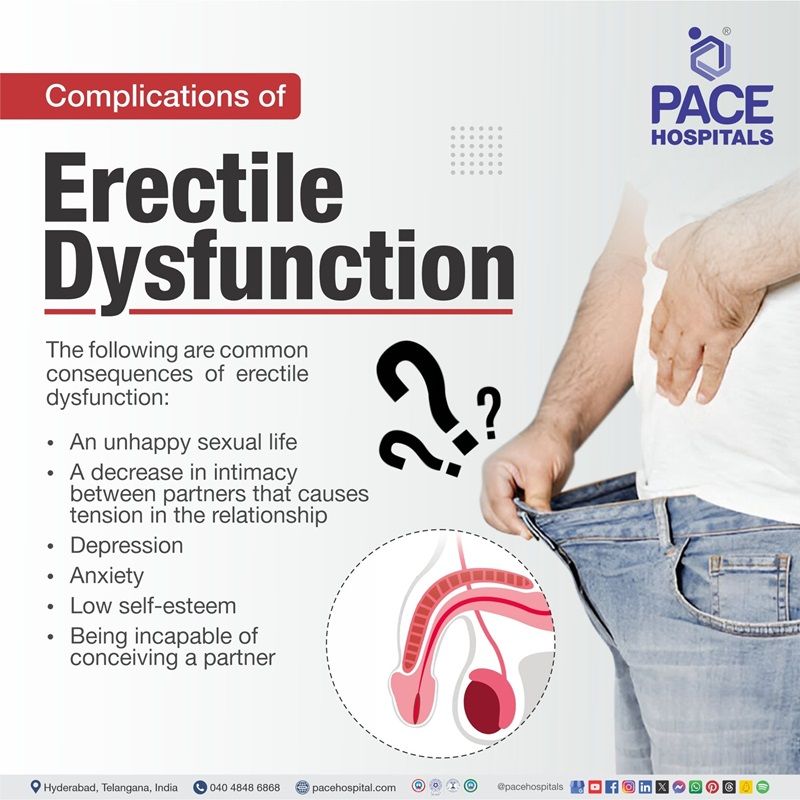
Erectile dysfunction complications
Erectile dysfunction can give rise to a variety of problems, both internal and external. It can alter interactions with others, particularly potential partners. It can also alter the perception of life, perhaps leading to mental health difficulties.
The following are common consequences of erectile dysfunction:
- An unhappy sexual life
- A decrease in intimacy between partners that causes tension in the relationship
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Low self-esteem
- Incapable of conceiving a partner
Depression, worries, and low self-esteem, can all lead to erectile dysfunction, resulting in a cycle of health issues.
Erectile dysfunction diagnosis
Patients initially may consult a general physician with worrying symptoms. The general physician after a careful evaluation, may refer the patient to a urologist who predominantly indulges in treating diseases pertaining to the urinary tract and reproductive organs.
A urologist diagnoses erectile dysfunction (ED) based on a medical and sexual history, as well as a psychological and physical evaluation and may also perform the necessary diagnostic tests and procedures. It may be difficult to discuss with a healthcare practitioner about erectile dysfunction. However, having a healthy sex life is a crucial part of overall health. The more information the doctor has about the patient, the better he or she will be able to treat the condition.
Medical and sexual history: One of the first steps a urologist will take to diagnose erectile dysfunction is to obtain a medical and sexual history. This information will assist the urologist to better understand the condition. Examining the sexual behaviour of the patient might assist the urologist to diagnose issues with sexual desire, erection, climax, or ejaculation.
Mental and physical health examination: Urologist may ask the patient, some personal questions and administer a questionnaire to help assess any psychological or emotional concerns that may be contributing to erectile dysfunction. Urologist may also enquire about the patient’s sexual relationship with the partner and how it may be affecting the erectile dysfunction. Urologist will also do a physical examination to aid in the diagnosis of the condition (erectile dysfunction).
Laboratory tests: Patient’s blood may be drawn and tested in a lab to look for indicators of diabetes, heart disease, low testosterone, and other illnesses that may be the reason for erectile dysfunction.
Imaging tests
- Doppler ultrasound
Other tests
- Nocturnal erection test
- Injection test
Erectile dysfunction treatment
Finding the underlying cause of erectile dysfunction is the first step in treating it. Depending on the patient's type, the urologist or andrologist will assist in determining the appropriate course of treatment plan. Possible erectile dysfunction treatments may include:
Non-pharmacological treatment for erectile dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction exercises: Regular exercise, particularly moderate to vigorous aerobic activity, has been shown to improve erectile dysfunction. Cardiovascular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, bicycling, and jumping rope, can help reverse mild erectile dysfunction if done for at least 45 minutes three times a week. Kegel exercises for erectile dysfunction also known as pelvic floor muscle exercises have proven to be successful in dealing with erectile dysfunction, and it could be utilized as the first line of treatment.
- Yoga for erectile dysfunction: A study found that yoga is a realistic, safe, and cost-effective comprehensive treatment approach for erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation
- Lifestyle changes: Losing weight if overweight, following a nutritious diet, and smoking cessation can alleviate erectile dysfunction symptoms to some extent. Reducing stress and tension could also help.
- Sex therapy: Sex therapy can help with psychogenic erectile dysfunction (erectile dysfunction due to physiological factors) and can be combined with other treatments for other types of erectile dysfunction.
- Vacuum erection devices:
A vacuum erectile device (VED) is used to assist men with erectile dysfunction in achieving and maintaining an erection. These devices are also known as vacuum constriction devices or penis pumps.
Pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction
The primary pharmacological treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED) is the use of drugs that enhance the effects of nitric oxide, a natural chemical produced by the body that relaxes muscles in the penis and increases blood flow to penis.
Erectile dysfunction medicine that is used to manage this condition include:
- Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors
- Testosterone (male sex hormone) supplementation
- Amino acid supplements
- Topical gels
- Urethral suppositories
- Alpha blockers
- Erectile dysfunction medication that blocks an enzyme called CYP3A4 (CYP3A4 inhibitors)
- Nitrates
Surgical interventions for erectile dysfunction
- Penile revascularization surgery
- Arterial balloon angioplasty
- Venous ligation surgery
- Penile prostheses
Other treatments
- Low-intensity shockwave therapy
- Combination therapy using medications
Prevention of Erectile dysfunction
Taking a comprehensive approach to general health and fitness is necessary to prevent erectile dysfunction (ED). Men can lower their chance of acquiring erectile dysfunction (ED) by treating their health issues and leading educated lifestyles. Erectile dysfunction can be prevented by following the below mentioned preventive strategies:
Smoking cessation: If patients have a habit of smoking it is highly recommended to quit smoking. Because smoking has been linked to heart and blood vessel damage, which can contribute to erectile dysfunction. Even after accounting for heart and blood vessel problems and other potential causes of erectile dysfunction, smoking increases the likelihood of developing erectile dysfunction.
Following a healthy diet: Whole grains, low-fat dairy products, fruits and vegetables, and lean meats are all good choices for maintaining erectile function. Avoiding eating foods heavy in fat, particularly saturated fat, and sodium. Following a healthy eating plan for healthy weight gain and managing blood pressure and diabetes. Controlling blood pressure and diabetes may help to prevent erectile dysfunction.
Alcohol abstinence: Excessive alcohol usage can disturb testicular function and production of male hormones, resulting in erectile dysfunction and infertility.
So, avoiding consuming too much alcohol is helpful. In case of problems, cut down on alcohol, consult with a counsellor who specializes in helping people who drink excessively.
Maintaining healthy weight to tackle diabetes (high blood glucose) and hypertension (increased blood pressure): Maintaining a healthy weight can also assist to delay the onset of diabetes and lower the blood pressure. Seek help from a healthcare professional to know about how to prevent diabetes or manage an existing diagnosis. Getting the blood pressure checked regularly.
Losing weight can help reduce inflammation, enhance testosterone (male sex hormone) levels, and boost self-esteem, all of which can help prevent erectile dysfunction (ED).
Indulging in physical exercise: Physical activity improves blood circulation throughout the body, including the penis. Beginners are suggested to begin slowly, with simple activities like walking at a normal pace. Then gradually progress to more strenuous activities, such as brisk walking or swimming. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity every day.
Staying away from illegal drugs:
Illegal drug use may make it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. Some illegal drugs may inhibit the ability to become aroused or experience other sensations. Illegal drug use may conceal further psychological, emotional, or physiological issues that could be the source of erectile dysfunction.
Difference between Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation
Erectile dysfunction vs Premature ejaculation
Both premature ejaculation (PE) and erectile dysfunction (ED) are prevalent sexual dysfunctions that can impact men at any stage of life. The primary distinction between these two disorders is that premature ejaculation (PE) occurs when a person ejaculates too soon during sexual activity, but erectile dysfunction (ED)occurs when a person cannot achieve or sustain an erection. The primary differences between premature ejaculation and erectile dysfunction are mentioned below
| Aspect | Premature ejaculation | Erectile dysfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ejaculation that occurs sooner than desired, often with minimal sexual stimulation. | The inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance |
| Symptoms | Ejaculation occurs within minutes of penetration or before.Involuntary ejaculation Often accompanied by frustration or embarrassment. | Difficulty in achieving erection, Difficulty in maintaining erection, Reduced sexual desire or satisfaction |
| Duration | Typically happens within 1-2 minutes of penetration or before it. | Can be occasional or persistent with symptoms lasting for at least a few months |
| Causes | Psychological factors (anxiety, stress, guilt), Hormonal imbalances, Neurological factors, Relationship issues. | Physical factors (heart disease, diabetes, hypertension), Psychological factors(stress, anxiety, depression), Medication side effects, Hormonal imbalances |
| Diagnosis | Sexual history and partner’s input, Physical examination, Psychological evaluation if needed. | Medical history and physical exam, Blood tests to check for underlying health conditions, Psychological evaluation if needed |
| Treatment | Behavioural techniques (e.g., start-stop method, squeeze technique), Medications (e.g., SSRIs, topical anesthetics), Counselling or sex therapy, Lifestyle changes (e.g., stress management) | Medications (e.g., PDE5 inhibitors like Viagra, Cialis), Lifestyle changes (e.g., exercise, diet), Counselling or therapy, Medical devices (e.g., vacuum pumps), Surgery in severe cases |
| Impact on relationships | Can cause frustration, reduced sexual satisfaction, and strain in relationships | Can lead to embarrassment, reduced sexual confidence, and strain in relationships |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Erectile dysfunction
What is the latest treatment for erectile dysfunction?
Men now have a new alternative for treating erectile dysfunction (ED) that is said to work faster than traditional erectile dysfunction medications and is available without a prescription. The FDA (food and drug administration) has authorised the over-the-counter sale of a topical gel to treat erectile dysfunction. It is packaged in single-use tubes. The contents are applied on the head of the penis just before sexual intercourse.
Does diabetes affect erectile dysfunction?
Yes. Diabetes (high blood glucose) affects erectile dysfunction. The reasons why diabetic men are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction are not well understood. However, we do know that men with diabetes are more prone to develop erectile dysfunction when their diabetes is poorly controlled.
Over time, poor diabetes control may cause more damage to the nerves and circulation that control blood flow to the penis. Keeping blood glucose levels within the usual range will help lessen the likelihood of these problems arising.
Does covid cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes. Research demonstrates that the prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men aged over 40 is high after recovery from coronavirus disease due to cardiovascular problems, mental illness, and poor overall health developed due to coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Can erectile dysfunction be cured?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a curable condition, although not all causes can be cured. Many people can benefit from treatment to achieve and sustain an erection, as well as improve their physical and emotional health and intimacy in relationships.
Does erectile dysfunction cause infertility?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) does not directly affect sperm quality or induce infertility. However, it can make conception more difficult because of the inability to sustain an erection during intercourse and ejaculation. Erectile dysfunction can also induce stress and a bad body image, leading men to avoid sexual engagement. This can decrease the frequency of sex, further affecting fertility.
What is the main cause of erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can have several causes, both physical and psychological. The primary causes that can cause the erectile dysfunction include, cardiovascular (heart related) issues, diabetes (increased blood glucose) hormonal imbalances, neurological disorders lifestyle factors.
What is the best food for erectile dysfunction?
According to research, following a balanced diet not only lowers the risk of developing erectile dysfunction but also helps ease the symptoms of erectile dysfunction to some extent. The diet includes plenty of vegetables, fruits, fish, whole grains, and oils that contain healthy fats such as olive oil.
Who treats erectile dysfunction (whom to consult for erectile dysfunction)?
A general physician or urologist can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). A urologist is a specialist in the urinary and reproductive systems who can help determine the cause of ED and propose treatment options.
How to cure erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation naturally?
If a man is currently suffering from erectile dysfunction or wants to avoid developing the illness, the recommendations that can help him overcome it for greater health and a better sex life include, walking, eating nutritious diet, improving vascular (blood vessels) health and exercise.
What habits cause erectile dysfunction?
Erection issues might develop when men are scared, concerned, frustrated, or weak. Consuming alcohol and/or taking substances can also have an impact. It may also be caused by another medical condition or as a side effect of some medications or cancer treatments.
How common is erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a highly prevalent illness that affects about 30% of males aged 40 to 70 years. According to some estimates, half of all males in this age group suffer from erectile dysfunction. However, the true figures may be higher because many men do not seek help due to embarrassment or humiliation.
Is erectile dysfunction (ED) just a normal part of getting older?
No, erectile dysfunction (ED) is not a natural consequence of ageing. While ED is more common in older men, it can strike men of any age and is not unavoidable. In reality, almost one-third of men in their seventies do not have erectile dysfunction (ED).
Can low testosterone cause erectile dysfunction (ED)?
Yes, low testosterone levels can lead to erectile dysfunction (ED), which affects sexual desire, mood, and muscle and fat changes. Testosterone treatment may help to alleviate symptoms.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868