Vertigo - Symptoms, Types, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Vertigo definition
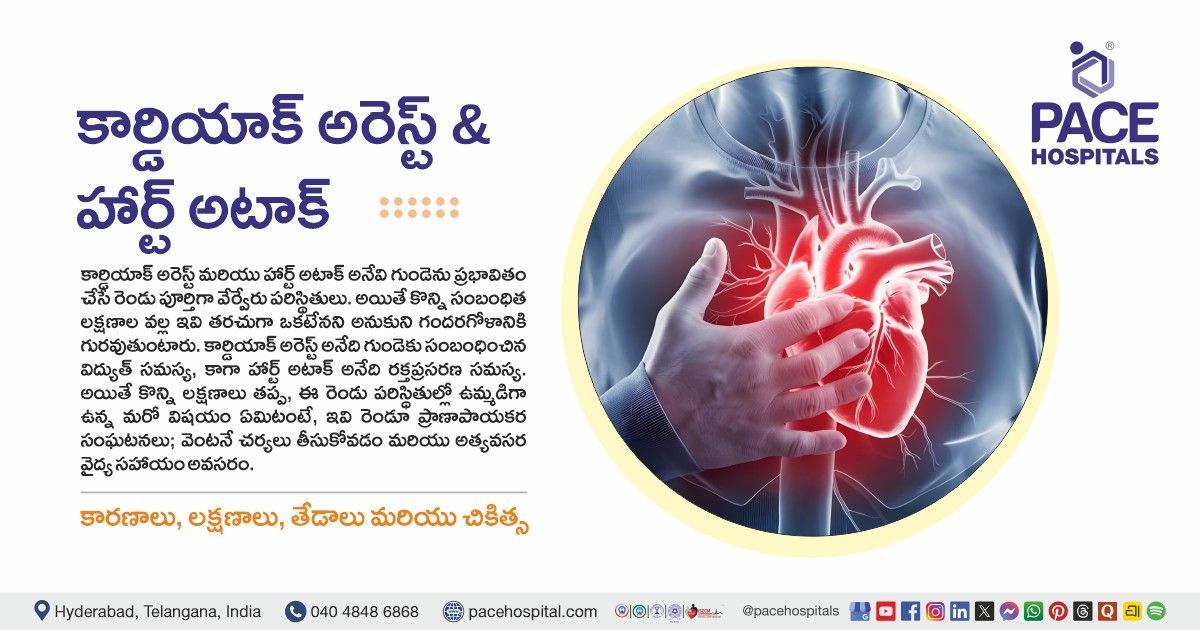
Vertigo, rather than a condition, is a symptom of vestibular dysfunction, a disturbance in the body's balance system, and a type of dizziness characterized by an abnormal sensation of motion (mainly rotational motion). People with vertigo may experience a feeling of spinning or moving in the environment around them. It can last for a few seconds to hours; however, people with severe vertigo may suffer for many days to months.
Vertigo is commonly caused by a disturbance of the semicircular canals (three tiny fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that help in balance), vestibular system (which provides information about balance, motion, and the location of head and body to the brain concerning surroundings), or vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). Vertigo can affect individuals of all ages and cause weakness, loss of balance, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
The treatment of vertigo includes medical management, physical therapy, psychotherapy, and, in some rare cases, surgical treatment may be preferred. Neurologists, ENT specialists (ear, nose, and throat) , or balance physiotherapists are essential healthcare personnel who effectively handle vertigo cases.
Vertigo meaning
The vertigo term is derived from the Latin word “vertigo” in the early 15th century, which means the sensation of whirling or dizziness.
Vertigo prevalence
Vertigo incidence worldwide
It is estimated that globally, about 1 in every 10 individuals suffers from vertigo. The prevalence of vestibular vertigo increases with age and is nearly two to three times more prevalent in women than men. It makes up approximately 25% of reported cases of dizziness, with a 12-month prevalence (existing cases) of 5% and a yearly incidence (new cases) of 1.4%.
Vertigo incidence in India
The prevalence of vertigo in the Indian rural population is 0.71%, which accounts for over ninety lakh people.

Types of vertigo
Nearly 80% of vertigo is peripheral, whereas 20% is central in origin .Based on its etiology, vertigo is divided into two types: central and peripheral.
- Central vertigo
- Peripheral vertigo
Central vertigo: The underlying pathology (disease process) in the brain stem or cerebellum (responsible for processing sensory information and controlling balance) generally causes central vertigo. The more gradual onset of symptoms usually describes central vertigo and may be associated with other neurological symptoms such as difficulty in speaking or double vision.
Peripheral vertigo
Peripheral vertigo: The pathology of the inner ear (that is responsible for spatial orientation and maintaining balance) causes peripheral vertigo. The typical characteristics of peripheral vertigo include sudden intense dizziness episodes along with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.

Vertigo symptoms
People with severe vertigo may experience constant symptoms that last for several days, thus making their daily life challenging, Its common symptoms include:
- Being sick or feeling sick
- Moving or spinning sensation
- Loss of balance (making it difficult to walk or stand)
- Dizziness (feeling of light-headedness, weak or unsteady)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Sweating
- Looking pale
- Nystagmus (rhythmic jerking eye movements) during a vertigo episode
Other symptoms of vertigo:
Depending upon the condition that causes vertigo, other symptoms may be experienced, including:
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- High temperature
- Hearing loss
Vertigo risk factors
Some factors may increase the risk of developing vertigo. Individuals having these factors do not mean they will develop vertigo, they just increase the risk for vertigo. Below are some of the risk factors of vertigo:
- Gender: According to the 2003 report of the German National Telephone Health Interview Survey (GNT-HIS), a higher lifetime prevalence of severe or moderate vertigo was seen in women (36%) compared to men (22%).
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to experience severe symptoms of vertigo compared with normal individuals.
- Hypertension: Both central and peripheral parts of balance may be affected by hypertension (high blood pressure)
Other risk factors include:
- Body mass index
- Hyperlipidaemia (high levels of cholesterol in the blood)
- Migraine
- Age
- Cervical spondylosis (a type of degenerative disease that affects the neck)
- Head trauma
- Long use of computers
- Otitis media (inflammation or infection in the middle ear)
- Osteoporosis (a disease that thins and weakens the bones)
- Smoking history
- Vitamin D deficiency

Vertigo causes
The following are the most common causes of vertigo, which mainly occurs when disturbance happens in the structures that are responsible for maintaining balance include inner ear, brain parts including the brain stem and cerebellum, and the nerve parts that connect the inner ear to the brain stem and cerebellum:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): It is characterized by brief, intense dizziness episodes that move the head and occurs when the tiny(small) crystals in the inner ear that control balance move out of place, affecting the signals from the inner ear to the brain.
- Vestibular neuronitis: This is a condition of inflammation of the inner ear that causes sudden intense vertigo lasting several days, accompanied by vomiting and nausea. It usually gets back to normal on its own.
- Meniere disease: This includes the buildup of fluid pressure in the inner ear that causes repeated sudden vertigo episodes lasting 20 minutes or more. Meniere disease is often associated with hearing loss, feeling of fullness in the ear, and tinnitus (ringing in the ear)
- Vestibular migraine headache: This type of migraine headache is seen mainly in individuals having a history or family history of migraine. Though it is an uncommon symptom, hearing loss may be experienced in these people.
- Labyrinthitis: This is an inner ear infection caused by a flu virus or cold.
The below-mentioned conditions may cause vertigo less commonly to a person:
- Brain tumor: The growth of abnormal cells in the areas of the brain
- Stroke and Transient ischemic attack: A medical emergency condition that occurs when the blood flow is blocked (stopped) to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts
- Head injury: Any trauma to the brain, skull, or scalp
- Infection: Growth of germs in the body
- Pregnancy: The time when a foetus develops inside a woman's uterus, usually about nine months
- Multiple sclerosis: A chronic autoimmune disease condition that affects the central nervous system)
- Acoustic neuroma: A noncancerous tumour that grows on the vestibulocochlear nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain).
Complications of vertigo
Patients suffering from vertigo may experience the following complications:
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
- Collision: Sudden head movements while riding a bike or driving may trigger BPPV increasing the risk of accidents
- Secondary injury: Risk of injuring themselves by falling.
Vertigo vs dizziness
Both vertigo and dizziness are common conditions that affect the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation. Although they may appear similar, they have the following differences.
| Parameters | Vertigo | Dizziness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a symptom of vestibular dysfunction and a type of dizziness characterized by an abnormal sensation of motion. | It is a general, non-specific term used to indicate a sense of disorientation. |
| Symptoms | Feeling sick, moving or spinning sensation, loss of balance, dizziness (feeling of light-headedness, weak or unsteady), nausea, vomiting, sweating, looking pale | Loss of consciousness, walking difficulty, headache, neck pain, |
| Causes | The disorders of the ear (inner ear) and brain (brain stem, cerebellum) parts and the nerve tracts that connect the inner ear with the brain stem and cerebellum, which are responsible for maintaining balance, generally cause vertigo. | Dizziness may be caused by hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), dehydration, anaemia, low blood pressure, migraine, anxiety, or stress. |
| Treatment | Includes medical management, physiotherapy, psychotherapy, vestibular rehabilitation exercise, and surgical treatment in rare cases | Treatment of dizziness depends on the cause. Generally, medicines and balancing exercises can treat dizziness. |
Difference between central vertigo and Peripheral vertigo
Central vs peripheral vertigo
Based on its etiology, vertigo is divided into two types: central and peripheral. Nearly 80% of vertigo is peripheral, whereas 20% is central in origin. The parameters below differentiate central vertigo and peripheral vertigo.
| Parameters | Central vertigo | Peripheral vertigo |
|---|---|---|
| Causes | The underlying pathology in the brain stem or cerebellum (which is responsible for processing sensory information and controlling balance) generally causes central vertigo. | The pathology of the inner ear (that is responsible for spatial orientation and maintaining balance) causes peripheral vertigo. |
| Symptoms | The more gradual onset of symptoms usually describes central vertigo and may be associated with other neurological symptoms (difficulty speaking or double vision) | The typical characteristics of peripheral vertigo include sudden intense dizziness episodes along with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. |
| Onset | Gradual (minutes to hours) | Acute (seconds) |
| Intensity | Severe | Mild-moderate |
Vertigo prevention
The prevention of vertigo depends upon the cause of its occurrence. The following measures help in the prevention of vertigo in individuals:
- Taking an adequate amount of water to stay hydrated.
- Taking rest as much as possible
- Avoiding sudden, fast head movements such as moving around too quickly or looking up suddenly.
- People need to change positions slowly while standing up after lying down. They need to sit for a couple of minutes before standing up.
- People need to hold onto the railing while climbing the stairs.
- Walking aids need to be used while walking.
- When experiencing vertigo, operating hazardous equipment or machinery, or driving, they must be avoided to protect themselves.
Vertigo diagnosis
Diagnosing vertigo usually includes a combination of the patient's medical history, neurological examination, symptoms, and diagnostic tests. Here's an overview of the steps involved in diagnosing a vertigo:
- Complete detailed history of the patient
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Brainstem auditory evoked potential studies and audiogram (formal hearing test)
- Caloric stimulation
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) and Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Comprehensive vestibular testing: Electronystagmography (computerized recording and analysis of abnormal eye movements), vestibular-evoked myogenic potential testing, and rotary chair testing (looking for abnormal eye movements while sitting in a chair which is rotated)
- Walking (gait) testing like the Romberg test
- Diagnostic testing includes computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) scans of the brain and inner ear, and the Dix-Hallpike maneuver (that is used to diagnose benign paroxysmal positional vertigo), gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Vertigo treatment
Most of the individuals with vertigo get better without any treatment. The treatment of vertigo generally depends on its cause, and it includes the following:
- Medical management: Benzodiazepines, antihistamines, and antiemetics
- Physiotherapy
- Psychotherapy
- Vestibular rehabilitation exercises
- Surgical treatment in rare cases such as transection of the posterior ampullary nerve, occlusion of the posterior canal with bony plugs
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Vertigo
What triggers vertigo attacks?
Stress (general life stress), improper nutrition, irregular menstrual cycle, fatigue (lack of energy), alcohol consumption, head movements, inadequate physical activity, and lack of sleep are some of the triggering factors of vertigo attacks.
Can allergies cause vertigo?
Yes, allergies can cause vertigo. Deposits of IgE in the vestibular end organs indicate the inner ear's ability to participate in immune reactions. In some cases, allergic challenges can induce vertigo in humans and animals.
Can an ear infection cause vertigo?
Yes, labyrinthitis (an inflammatory condition of the inner ear) can cause vertigo. The labyrinth is a delicate structure that is located deep inside the human ear and becomes inflamed in labyrinthitis conditions, which affects people's hearing and balance.
How to cure vertigo permanently?
There is no permanent cure for vertigo, but following some of the measures, such as lifestyle changes, chiropractic care, physical therapy techniques, and even some supplements, may reduce the occurrence of vertigo attacks.
Does vertigo go away on its own?
Yes, most cases of vertigo go away on their own without any medication usage. In some cases, vertigo patients may need medication. The treatment of vertigo mainly depends on the cause of the symptoms.
What is vertigo?
Vertigo, rather than a condition, is a symptom of vestibular dysfunction and a type of dizziness characterized by an abnormal sensation of motion (mainly rotational motion) and can affect people of all ages.
What causes vertigo?
The disorders of the ear (inner ear) and brain (brain stem, cerebellum) parts and the nerve tracts that connect the inner ear with the brain stem and cerebellum, which are responsible for maintaining balance, generally cause vertigo.
Can a chiropractor help with vertigo?
Interestingly, many chiropractic studies have shown improvement in patients with vertigo symptoms when treated for temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction and upper cervical spine. Chiropractic care may enhance the quality of life of vertigo patients.
Can dehydration cause vertigo?
Water is an important nutrient for health. Dehydration (inadequate water intake) may promote vestibular disorders such as vertigo that affect people's quality of life and may increase the risk of falls.
What is BPPV vertigo?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a problem in the inner ear. It includes brief, intense dizziness episodes that move the head. BPPV occurs when the tiny (small) crystals in the inner ear that control balance move out of place, affecting the signals from the inner ear to the brain.
How long does vertigo last?
People with vertigo may experience a feeling of spinning or moving in the environment around them, which can last for a few seconds to hours, and people with severe vertigo can suffer for many days to months.
Can tinnitus cause vertigo?
Tinnitus is characterized by a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears and is often associated with sensorineural hearing loss and sometimes with dizziness or vertigo. They are both caused by the condition called Meniere’s disease which is a disorder of the inner ear that causes severe dizziness (vertigo), ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and is often associated with hearing loss and feeling of fullness in the ear.
How to prevent vertigo?
By drinking adequate water to stay hydrated, resting as much as possible, and avoiding sudden, fast head movements such as moving around too quickly or looking up suddenly, vertigo can be prevented.
Does vertigo make you tired?
Yes, during an attack of vertigo, patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) may experience the symptoms of fatigue (a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy), which can make people tired.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868