Diabetic Neuropathy – Causes, Symptoms, Complications & Treatment
PACE Hospitals
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is a progressive disease and a serious complication of diabetes that occurs due to nerve damage. Uncontrolled high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) mainly affects the nervous system. Depending on nerves damage in the body symptoms may vary.
Nervous system are very essential in the human body that send messages or signal to organs and body parts to perform normal function such as breathing, walking, bodily functions, sense of touch and feel etc.
Prevalence of Diabetic Neuropathy
According to the International Diabetes Federation 2017 estimates, 425 million people are living with diabetes mellitus (DM) in the world. By 2045, the number is predicted to rise to 629 million people. India, in 2017, had 72,946,400 patients, the second-largest number of people living with diabetes. The current prevalence in India is 8.8%
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is the most common complication among diabetes mellitus patients, with a prevalence ranging from 18.8 to 61.9% in India. Early diagnosis of DPN can reduce associated complications.
DSPN (Distal symmetric polyneuropathy) constitutes the most common type seen in 50% of patients with Diabetic Neuropathy, CTS (Carpal tunnel syndrome seen) in 25%, Autonomic neuropathy in 7% and other types seen in 3% of patients that include Polyradiculopathies (Diabetic amyotrophy, Thoracic polyradiculopathy), Mononeuropathies (Cranial mononeuropathy, Peripheral mononeuropathy), Small fiber neuropathy, Treatment induced insulin neuritis, Diabetic cachexic neuropathy.

Types and Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
The symptoms commonly seen in diabetic neuropathy are numbness or pain in legs or feet, tingling, burning pains and cramps, distal weakness of limbs, problems related to blood vessels, urinary tract, digestive system and heart. Symptoms like lightheadedness, excessive sweating, urinary incontinence, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and sensation of fullness are observed in autonomic neuropathy.
Symptoms may vary based on the nerve damage in your body, you may not notice the symptoms till the considerable damage. There are mainly four types of Diabetic neuropathy:
1. Distal symmetric peripheral neuropathy
It is the most common type of diabetic neuropathy. Nerve damage usually affects the toes and feet first. Some people do not feel any symptoms, but other people can have symptoms which include:
- Numbness or loss of feeling.
- Burning or pain, which is often worse at rest or at night.
- Tingling
- Feeling light touches as bothersome or painful
- Sharp pains or jabs.
Diabetic neuropathy usually affects both sides of the body. Symptoms are often noticed in the toes. If the disease progresses, symptoms may gradually move up the legs; if the mid-calves are affected, symptoms may develop in the hands. This is called glove and stocking pattern of symptoms. Over time, the ability to sense pain may be lost, which greatly increases the risk of injury.
2. Autonomic neuropathy
The autonomic nervous system controls the eyes, heart, stomach, intestines, bladder, and sex organs. Diabetes can affect nerves in any of these areas, possibly causing:
- Bladder problems, including urinary incontinence or urinary retention.
- Constipation, uncontrolled diarrhea or both.
- Slow stomach emptying leading to nausea, vomiting, sensation of fullness and loss of appetite.
- Increased or decreased sweating. Sudden drop in BP when rise from sitting or lying down that may cause feeling light-headedness (orthostatic hypotension).
- Erectile dysfunction in men, vaginal dryness in women.
- Changes in the way eyes adjust from light to dark.
- Problems regulating body temperature.
3. Proximal neuropathy (Diabetic polyradiculopathy)
It is also called Diabetic amyotrophy, often affecting nerves in thighs, hips or buttocks or legs. It can also affect chest and abdominal area. Generally symptoms are on one side, but it may spread to the other side as well. Symptoms include:
- Severe pain in hip, thigh or buttock.
- Eventually weak and shrinking thigh muscles.
- Difficulty rising from a sitting position.
- Severe stomach pain
4. Mononeuropathy (Focal neuropathy)
It is of two types’ - cranial nerve mononeuropathy and peripheral nerve mononeuropathy.
Cranial mononeuropathy: affecting cranial nerves leading to symptoms like double vision due to 3rd or 6th nerve involvement or paralysis on one side of the face (bell’s palsy) due to 7th cranial nerve involvement.
Peripheral mononeuropathy: In this nerve involvement leads to entrapment neuropathy like carpal tunnel syndrome leading to symptoms like numbness or tingling in hand or fingers involving thumb, index and middle fingers and weakness in the hands causing things to drop.
Other types include:
- Small fiber neuropathy which involves severe burning paraesthesia in feet
- Treatment induced Insulin neuritis associated with paraesthesia with the initiation of insulin treatment
- Diabetic cachexic neuropathy commonly seen in men with weight loss and paraesthesia.
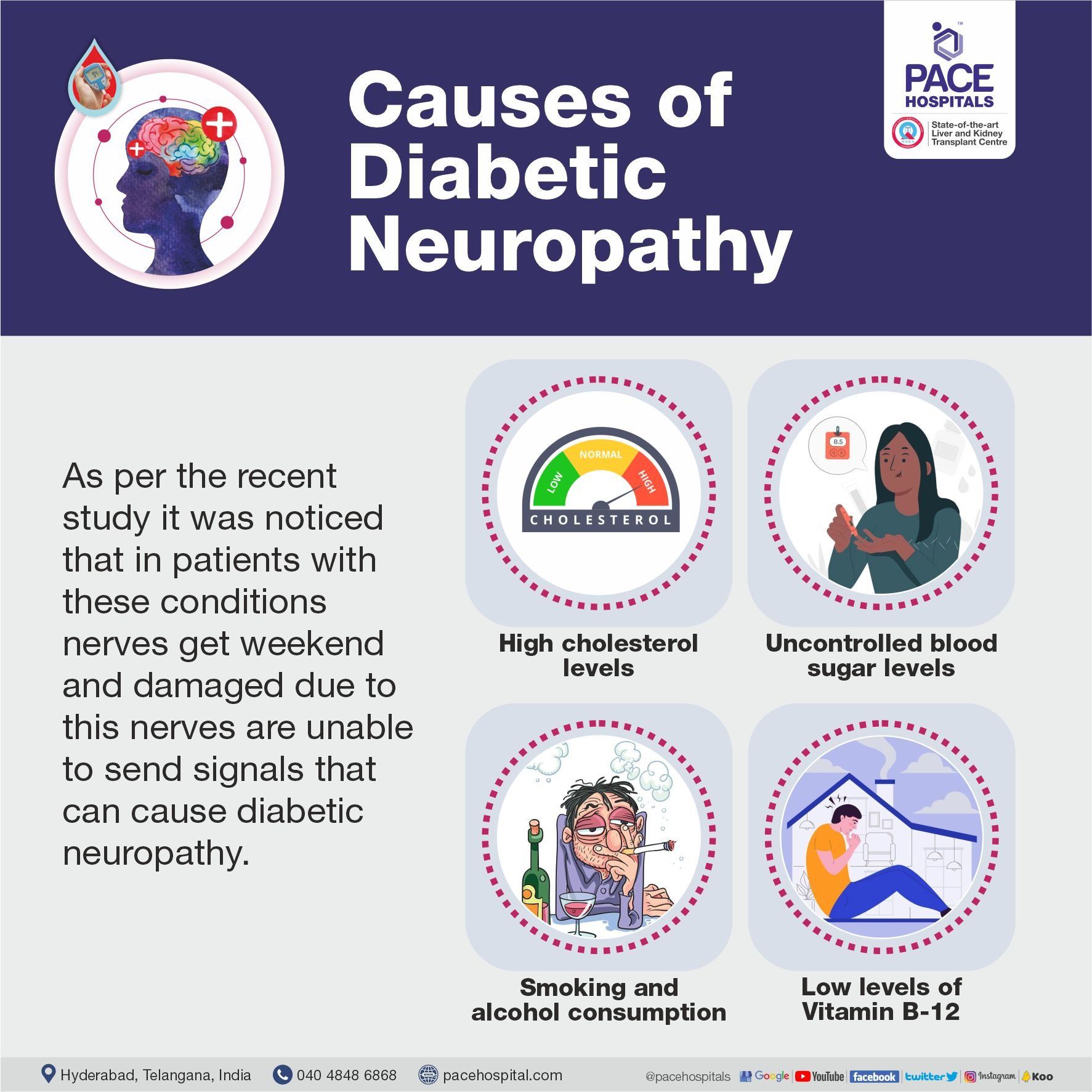
Causes of Diabetic Neuropathy
As per the recent study it was noticed that in patients with uncontrolled blood sugar levels nerves get weekend and damaged due to this nerves are unable to send signals that can cause diabetic neuropathy. Apart from hyperglycemia, these factors can also damage nerves:
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Low levels of Vitamin B-12
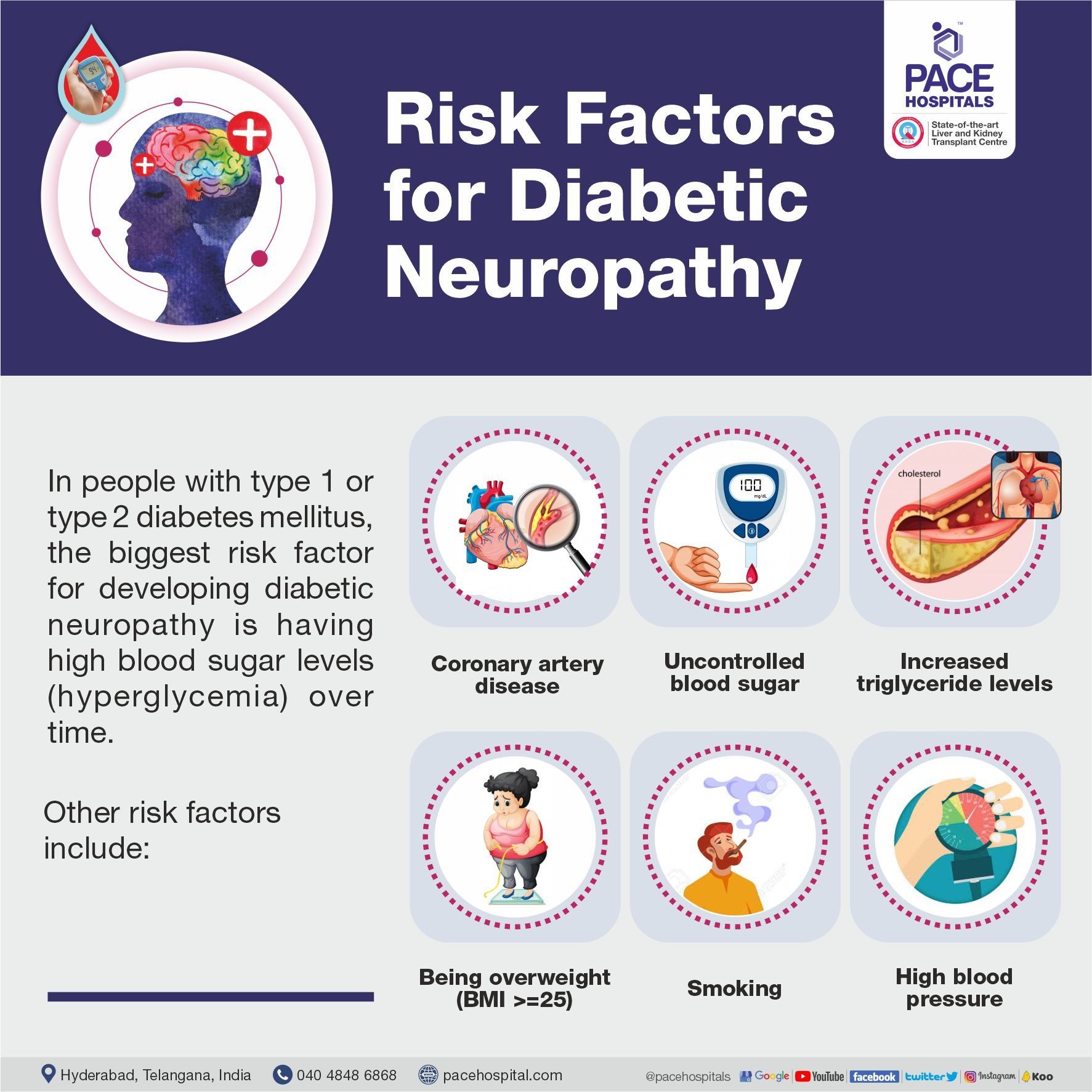
Risk Factors for Diabetic Neuropathy
In people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus, the biggest risk factor for developing diabetic neuropathy is having high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) over time.
Other risk factors include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Uncontrolled blood sugar
- Increased triglyceride levels
- Being overweight (BMI >=25)
- Smoking
- High blood pressure

Complications of Diabetic Neuropathy
Foot ulcers and amputation: There is loss of ability to sense pain or hot and cold, which increases the risk of injury to the feet. A small injury has the potential to develop into a large ulcer. In severe cases, infection spreads to bone or lead to tissue damage and can lead to dreadful complication of amputation of toe or foot or even the entire leg.
Other complications like
- Hypoglycemic (low blood sugar (glucose) level) unawareness
- Urinary tract infections, urinary incontinence
- Sudden blood pressure drop
- Digestive problems
- Sexual dysfunction
- Damage to the joints leading to charcot arthropathy are commonly seen.
Tests to Diagnose Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is diagnosed based on medical history and physical examination of the feet. Examination findings like loss of the ability to sense vibration and movement in the toes or feet, loss of the ability to sense pain, light touch, and temperature in toes or feet, loss or reduction of reflexes are observed.
Other tests include:
- Nerve conduction studies
- Autonomic function tests
- Nerve biopsy and imaging
- Skin biopsy and quantification of intraepidermal nerve fiber density for evaluating small fiber neuropathy.
- Corneal confocal microscopy for assessment of retinal nerve fibers acts as early marker in DSPN.
What are The Preventive Measures and Treatment for Diabetic Neuropathy?
- Control of blood sugar levels: Symptoms of pain and burning may improve when blood glucose levels improve. If blood sugar levels are not controlled with the current treatment regimen, a different regimen is recommended.
- Lifestyle interventions, specifically diet and exercise: The goal is to achieve and maintain normal body weight with a nutrient dense diet low in saturated fats and high in whole grains, vegetables, fruits and lean meats. Exercise should consist of atleast 150 moderate to vigorous physical activity, such as brisk walking, atleast three times per week.
- Care of the feet: Checking feet every day, keeping feet clean and dry, moisturising feet, wearing clean dry socks and wearing cushioned shoes that fit well.
- Pain and paresthesias management: Neuropathic pain is often hard to manage and can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life. It commonly becomes more intense at night and may interfere with sleep. Various medicines are used to treat diabetic neuropathy, including certain anticonvulsant drugs and monoamine reuptake inhibitors.
Diabetic neuropathy is the most common complication associated with diabetes. Early identification of symptoms and early evaluation helps in the prevention of disabling complications like distal weakness, foot deformities and weakness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Diabetic Neuropathy
What is diabetic neuropathy and why does it develop?
Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage caused by long-standing Diabetes, particularly when blood sugar levels remain poorly controlled. High glucose levels damage nerve fibers and reduce blood supply to nerves over time. This leads to gradual loss of sensation and nerve function.
Does diabetic neuropathy affect only the feet and hands?
No. While peripheral nerves are commonly affected, diabetic neuropathy can also involve autonomic nerves. This may impact other metabolic processes such as bladder control, digestion, sexual function, and cardiovascular regulation.
Can diabetic neuropathy occur even with mild diabetes?
Yes. Neuropathy can develop even in people with relatively mild Diabetes if glucose control fluctuates frequently. Duration of diabetes and consistency of control play an important role.
How does diabetic neuropathy impact digestion?
When digestive nerves are damaged, the intestines may move slowly or sporadically. This may result in symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, bloating, or irregular bowel habits.
Can diabetic neuropathy affect bladder function?
Autonomic nerve involvement can interfere with bladder emptying or control, resulting in urinary incontinence or retention.
Can diabetic neuropathy cause sexual health problems?
Yes. Nerve damage may interfere with sexual response, leading to erectile dysfunction in men and reduced sensation in women. These symptoms are frequently under-reported but treatable.
Are foot problems linked to diabetic neuropathy?
Yes, decreased sensation increases the likelihood of undetected injuries (like cuts, blisters, and burns), pressure sores, and infections. Regular foot care is necessary for prevention.
When should someone with diabetes seek evaluation for neuropathy?
Evaluation is advised if symptoms such as numbness, pain, bowel changes, bladder issues, or sexual dysfunction appear. Early assessment supports timely care and prevention of further miserable condition.
Why is early detection of diabetic neuropathy important?
Early nerve damage may be reversible or stabilized with proper treatment. Delayed diagnosis increases the risk of complications such as ulcers, infections, and functional disability.
How does diabetic neuropathy affect daily activities?
Nerve damage may reduce sensation, balance, and coordination. This raises the possibility of falls, undiscovered injuries, and difficulties doing normal duties.
Is pain always present in diabetic neuropathy?
No, not always. Some people report tingling, pain, or burning sensations, while others may only feel numbness. Loss of sensation might be equally alarming.
Can diabetic neuropathy progress over time?
Yes, nerve damage can worsen over time if not treated properly. Progression increases the possibility of complications such as foot ulcers and infections.
Does vitamin deficiency play a role in neuropathy?
Yes, certain deficiencies, particularly Vitamin B-12, may worsen nerve damage or mimic neuropathy symptoms. Identifying the exact cause responsible and fixing inadequacies can dramatically enhance nerve health.
Can lifestyle changes help manage diabetic neuropathy?
Yes, lifestyle measures such as blood sugar control, physical activity, and foot care management play an important and major role. These steps help slow progression and reduce symptom severity.
Is diabetic neuropathy reversible?
While total reversal is unlikely and rare, early intervention can limit progression and alleviate symptoms. Consistent glucose control remains the primary goal of managing the existing condition.
How does PACE Hospitals evaluate diabetic neuropathy?
PACE Hospitals conducts a comprehensive assessment that includes:
- Review of Diabetes duration and the way to control (diet, lifestyle changes, medications)
- Detailed nerve function evaluation
- Screening for autonomic symptoms such as urinary incontinence and bowel changes
- Identification of contributing factors like Vitamin B-12 deficiency
When should a patient with diabetes consult PACE Hospitals for neuropathy?
Consultation is recommended when:
- Persistent numbness, pain, or tingling develops
- Digestive symptoms such as constipation or diarrhea occur
- Sexual health concerns like erectile dysfunction arise
- Daily activities are affected by nerve symptoms
How does PACE Hospitals manage complications of diabetic neuropathy?
At PACE Hospitals, the management of complications include:
- Optimizing blood sugar control
- Treating pain and sensory symptoms
- Addressing autonomic issues affecting bladder and bowel function
- Preventing secondary complications such as foot ulcers
Does PACE Hospitals check nutritional factors in neuropathy care?
Yes. Care includes:
- Screening for deficiencies, including Vitamin B-12
- Nutritional counseling when needed
- Correcting deficiencies that may worsen nerve damage
- Monitoring response to supplementation
Why choose PACE Hospitals for diabetic neuropathy care?
PACE Hospitals gives ample choices for providing:
- Experienced specialists in diabetes and for nerve disorders treatment (neurologist) - single roof
- Integrated evaluation of sensory and autonomic symptoms
- Patient-centered treatment planning
- Focus on long-term nerve health and quality of life
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868