Diet and Nutrition Goals: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. A Kishore Kumar - Consultant Nephrologist and Renal Transplant Physician
Overview
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive condition that affects how efficiently your kidneys filter waste and maintain the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. While genetics play a role, especially in younger individuals, lifestyle and dietary choices have a significant impact on both the risk and progression of CKD.
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, our nephrology and dietetics teams emphasize that nutrition is not just supportive care, it’s a frontline therapy for protecting kidney function, slowing disease progression, and improving the overall quality of life.
Understanding How CKD Affects the Kidneys
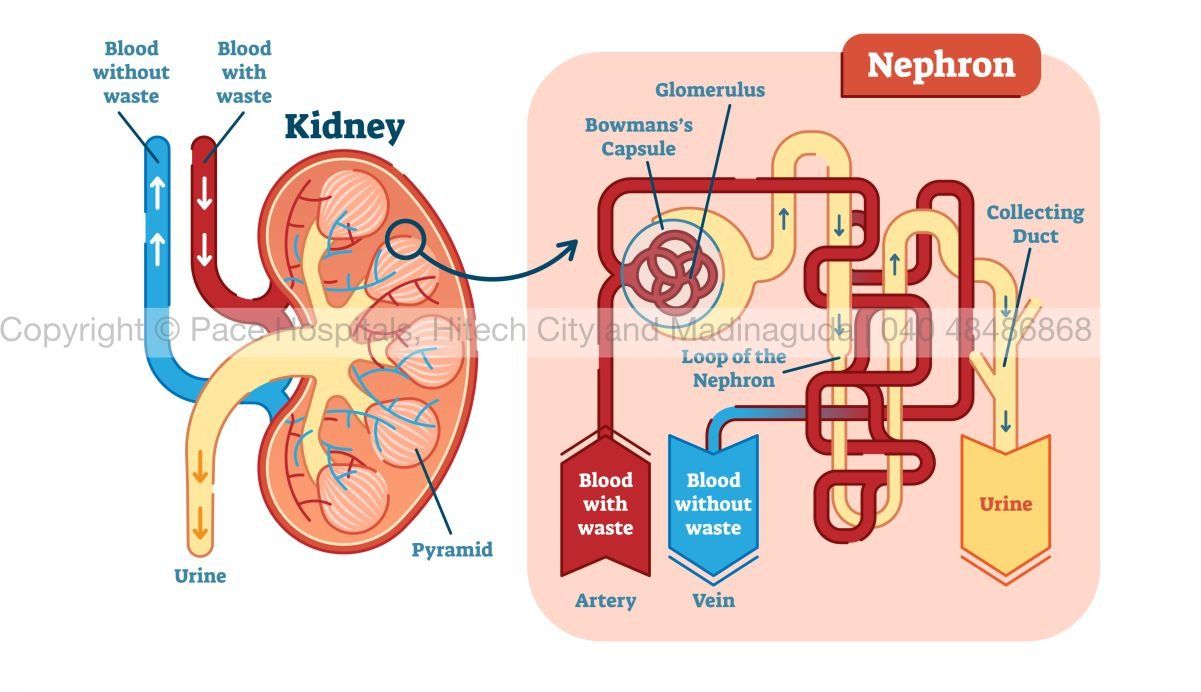
The kidney’s functional unit, the nephron, filters blood through a network of microscopic capillaries (glomeruli) and tubules that reabsorb essential substances. An average human kidney contains about one million nephrons.
When some nephrons are lost due to disease, the remaining ones work harder to maintain filtration. Over time, this increased workload causes strain and scarring, accelerating kidney damage.
Uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension, the two leading causes of CKD, intensify this damage. A Western-style diet high in red meat, processed foods, salt, and animal fat further accelerates the loss of healthy nephrons.
However, adopting a balanced, kidney-friendly diet, rich in plant foods and low in sodium and phosphorus, can reduce this burden and preserve kidney function.
Why Nutrition Matters in CKD?
For patients with CKD who are not on dialysis, dietary modification is the most effective and low-cost intervention to slow disease progression. Early dietary education at the time of diagnosis is crucial, this is when nutritional interventions are most likely to work.
Key dietary focus areas include:
- Protein type and quantity
- Salt (sodium) intake
- Phosphate management
- Fruits, vegetables, and fiber intake
Protein – Choose Wisely and Limit Intake
Protein is essential, but in CKD, too much especially animal protein, can accelerate nephron damage. After consuming meat, both renal blood flow and GFR (glomerular filtration rate) increase, forcing the remaining nephrons to filter more aggressively. This leads to intraglomerular hypertension (pressure within the nephron), resulting in micro-scarring and faster progression of CKD.
High-protein foods like red meat, cheese, and egg yolk also contain choline, phosphatidylcholine, and L-carnitine, which gut bacteria convert into uremic toxins such as trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) and p-cresyl sulfate. These toxins accumulate in CKD and contribute to inflammation, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease.
Expert Tip from PACE Hospitals
Prefer plant-based proteins such as lentils, soy, beans, and nuts in moderation. For non-vegetarians, lean meats (like fish or egg whites) over red meats.
Phosphate – The Hidden Mineral That Matters
Phosphorus is an essential mineral, generally found in many high-protein and processed foods, that can accumulate when kidney function declines.
- Plant-based phosphorus (from grains and legumes) is bound to phytic acid, which is less absorbable.
- Animal protein and processed foods contain inorganic phosphate that’s highly absorbable, increasing serum phosphorus levels.
Excess phosphorus causes calcium deposits in blood vessels and kidneys, accelerating CKD progression and increasing cardiovascular risk.
Expert Tip from PACE Hospitals
- Choose fresh, and unprocessed foods.
- Avoid packaged and highly processed meats, cheese, and bakery foods preserved with phosphates.
- Consult a kidney dietitian to balance protein and phosphorus intake effectively.
Salt (Sodium Chloride): The Hidden Risk for Kidneys
High salt intake increases the risk of high blood pressure and worsens renal damage. It raises blood volume, making it difficult for the kidneys to control fluid balance and counteracting the effects of antihypertensive drugs.
Reducing salt not only helps control blood pressure but also lowers urinary albumin excretion, an early marker of kidney stress.
Expert Tip from PACE Hospitals
- Avoid pickles, chips, canned soups, and processed foods.
- Limit daily salt intake to <5 grams (one teaspoon).
- Use lemon, herbs, and spices as natural flavor substitutes.
Fruits and Vegetables – Nature’s Renal Protectors
Fruits and vegetables are natural buffers that help neutralize acid load in the body. When metabolism generates acid, the kidneys use bicarbonate to neutralize it. In CKD, limited bicarbonate regeneration leads to metabolic acidosis, worsening kidney function.
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables:
- Lowers acid production
- Reduces tubular stress on remaining nephrons
- Slows CKD progression
Expert Tip from PACE Hospitals
Increase intake of alkali-producing foods, like apples, oranges, bananas, and leafy greens—under dietitian supervision. In advanced CKD, potassium-rich fruits may need moderation.
Fiber – The Forgotten Hero
Dietary fiber has many benefits for CKD patients:
- Reduces cardiovascular risk
- Improves gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria (Bifidobacterium)
- Reduces toxin absorption by strengthening the intestinal barrier
- Promotes excretion of urea and potassium through stool
- Prevents constipation, which is common in CKD
Expert Tip from PACE Hospitals
Ensure 25–30 grams of fiber per day from sources like oats, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
The Balance of Fluids
In early stages of CKD, adequate hydration helps flush toxins, but in advanced stages, excess fluid can lead to swelling, hypertension, and breathlessness. Fluid restriction should always be individualized based on urine output, edema, and blood pressure readings.
Lifestyle Integration with Nutrition
Nutrition alone isn’t enough, integrating lifestyle habits makes a difference.
- Maintain blood sugar in diabetic CKD.
- Exercise moderately to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Monitor weight regularly.
- Follow up with nephrologists for GFR and electrolyte monitoring.
At PACE Hospitals in Hyderabad, nutritionists work closely with nephrologists to develop individual renal diet plans. This helps ensure that the patients receive the right nutrients without stressing their kidneys.
Key Takeaways
- Limiting intake of animal protein, salt, and phosphorus-rich foods to reduce kidney strain.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich plant foods.
- Avoid processed and packaged items.
- Stay active and maintain hydration balance.
- Consult a renal dietitian for tailored advice.
With the right diet and medical supervision, the progression of CKD can be slowed, delaying the need for dialysis and improving long-term outcomes.
FAQs on Diet and Nutrition Goals in CKD
Why is diet important in chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Diet plays a key role in slowing CKD progression by reducing strain on nephrons, managing blood pressure, and lowering toxin buildup in the body.
What foods should CKD patients avoid?
Avoid red meat, processed foods, high-salt items, and phosphate-preserved foods. These increase kidney workload and worsen kidney damage.
Can plant-based diets help in CKD?
Yes. Plant-based diets reduce acid load, uremic toxins, and inflammation while improving heart and gut health in CKD patients.
Which fruits and vegetables are best for CKD patients?
Low-potassium options like apples, cabbage, carrots, and berries are ideal. High-potassium fruits like bananas may need limitation in advanced CKD.
How much water should CKD patients drink daily?
Fluid needs vary by disease stage. In early CKD, moderate hydration is beneficial, but in advanced CKD, fluid intake must be individualized by a doctor.
How does high protein intake affect kidney function?
Excess protein increases intraglomerular pressure, causing nephron damage and faster decline in kidney function, especially from animal protein sources.
What is the role of salt restriction in CKD?
Reducing salt intake helps control blood pressure, reduce fluid retention, and lower urinary albumin loss, protecting kidney function.
How does phosphate harm kidneys?
High phosphate leads to calcium deposits in kidneys and blood vessels, worsening kidney and heart function. Limiting phosphate-rich foods is essential.
Can dietary fiber help kidney health?
Yes. A high-fiber diets improve gut health, reduce toxin absorption, and support cardiovascular protection in CKD patients.
Why choose PACE Hospitals for CKD nutrition management?
PACE Hospitals offers complete CKD care through expert nephrology care, renal diet planning, and personalized lifestyle counseling to slow CKD progression and improve quality of life.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868