Dyssynergic Defecation - Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Mysore Sudhir - Senior Consultant Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist
Constipation is one of the most frequent gastrointestinal problems worldwide. Although it is not a disease itself, it is often a symptom of an underlying disorder affecting the digestive or nervous system. Among the different forms of chronic constipation, Dyssynergic Defecation (DD) stands out as a functional problem involving poor coordination of pelvic floor muscles during bowel movements.
Dyssynergic Defecation is both underdiagnosed and undertreated, primarily because people tend to dismiss constipation as a minor inconvenience rather than a complex, chronic issue. Understanding its causes, identifying the symptoms, and accessing effective therapies such as biofeedback can dramatically improve quality of life.
What is Constipation?
Constipation is defined by the infrequent or difficult passage of stool and affects up to 20–30% of the population, especially women and the elderly. According to standard clinical criteria, constipation is present if a person experiences two or more of the following symptoms in the past 12 months (without laxative use):
- Fewer than three bowel movements per week
- Excessive straining during at least 25% of bowel movements
- A feeling of partial evacuation in 25% or more of attempts
- Passage of hard or pellet-like stools in at least 25% of cases
While constipation can be caused by dietary habits, lifestyle, medications, or structural abnormalities, it often results from functional problems in bowel movement coordination, this is where Dyssynergic Defecation comes in.
What is Dyssynergic Defecation (DD)?
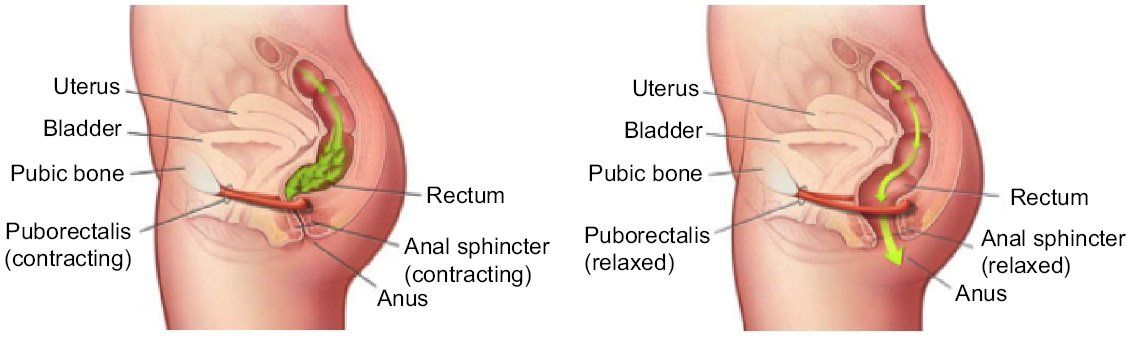
Dyssynergic Defecation (also called pelvic floor dyssynergia or anismus) occurs when the pelvic floor muscles and anal sphincter fail to coordinate properly during defecation. Normally, to pass stool, the rectal muscles contract (to push stool out), while the anal sphincter muscles relax. In DD, this coordination is disrupted. Instead of relaxing, the pelvic floor muscles or anal sphincter may paradoxically tighten, blocking stool passage and leading to chronic constipation.
Common Symptoms of Dyssynergic Defecation:
- Severe straining during bowel movements
- A sensation of “blockage” or incomplete evacuation
- The need for digital manipulation (using fingers to help stool pass)
- Hard, dry, or pellet-like stools
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating
- Reduced frequency of bowel movements
This condition is a functional disorder, meaning there is no structural blockage in the colon, but rather a problem with muscle coordination.
The Dynamics of Defecation
Effective defecation requires coordinated activity between the rectum, abdominal wall muscles, and pelvic floor muscles (including the puborectalis and anal sphincters).
During a normal bowel movement:
- The rectum contracts, pushing stool downward.
- The internal and external anal sphincters relax.
- The puborectalis muscle (which loops around the rectum) also relaxes, straightening the rectoanal angle for stool passage.
In Dyssynergic Defecation, this coordination is lost. Patients may show:
- Inadequate abdominal pressure during defecation,
- Paradoxical contraction of the external anal sphincter, or
- Failure of anal relaxation, increasing outlet resistance.
The result: stool becomes trapped in the rectum despite normal or increased effort.
Psychological Distress and Quality of Life
DD doesn’t just affect the gut, it significantly impacts mental health and daily well-being. Chronic constipation and the embarrassment associated with bowel difficulties can lead to:
- Anxiety and depression
- Social withdrawal
- Fear of eating or travel
- Decreased productivity
Recent studies show a strong correlation between dyssynergic defecation and psychological stress. Patients often describe their condition as frustrating, exhausting, and socially isolating.
Diagnosis of Dyssynergic Defecation
Dyssynergic Defecation needs to be diagnosed using both clinical and specialized tests in order to differentiate from slow-transit constipation or structural bowel abnormalities.
Clinical History and Examination
A detailed history is the first step. The doctor will ask about:
- Bowel frequency, stool consistency, and straining
- Use of laxatives or enemas
- History of childbirth, pelvic surgery, or trauma
A digital rectal examination (DRE) is often the first test. The doctor assesses:
- The resting tone of the anal sphincter
- The ability to squeeze and relax
- The angle and coordination of the pelvic muscles during simulated defecation
Anorectal Manometry
This is the gold standard for diagnosing Dyssynergic Defecation.
It measures:
- Rectal pressure (pushing effort)
- Anal sphincter pressure (relaxation/contraction)
- Rectal sensation and reflexes
During this test, patients attempt to “push” as if defecating. Normally, rectal pressure increases while anal pressure decreases. In DD, there may be:
- Inadequate push
- Paradoxical contraction
- No relaxation of the anal muscles
Based on these findings, four subtypes of DD are recognized, each with a distinct pattern of muscle dysfunction.
MRI Defecography
This imaging technique visualises pelvic floor structures in real time during defecation. It identifies:
- Rectocele (rectal wall bulge)
- Intussusception (rectal folding)
- Rectal prolapse
- Pelvic floor descent
Balloon Expulsion Test
In a simple, non-invasive test, a small water-filled balloon is inserted into the rectum. The patient is then instructed to expel it, and failure to do so within one to two minutes shows the presence of DD. Although slow-transit constipation can coexist with DD, tests like marker studies or scintigraphy can be used to evaluate total intestinal motility.
Treatment of Dyssynergic Defecation
Treatment must be individualised, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. Common management strategies include:
Standard Medical Therapy
Traditional constipation treatments (like fiber supplements, stool softeners, osmotic or stimulant laxatives) may provide mild relief but are often ineffective for DD because the underlying issue is muscle coordination, not stool consistency.
Still, doctors may recommend:
- High-fiber diet (25–30 g/day)
- Adequate hydration
- Regular toilet training
- Timed bowel movements after meals
Biofeedback Therapy – The Mainstay of Treatment
Biofeedback therapy is the most effective, evidence-based treatment for Dyssynergic Defecation. It is a non-invasive, instrument-guided training program that teaches patients to:
- Coordinate their abdominal and pelvic muscles properly
- Increase rectal pressure effectively during defecation
- Relax the anal sphincter and puborectalis muscle
How Biofeedback Works:
Patients learn to control muscle action consciously by receiving visual or auditory feedback from sensors implanted in the anal canal. They "retrain" their defecation reflex over the course of several sessions.
Benefits:
- 70–80% success rate in improving bowel movement
- Non-surgical and safe
- Reduces laxative dependency
- Enhances confidence and quality of life
Most patients require only 6-8 training sessions.
Psychological and Behavioural Therapy
Since stress and anxiety can worsen symptoms, cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and relaxation training are valuable adjuncts. Encouraging a positive outlook and addressing emotional distress significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Surgery (Rare Cases)
Surgery is rarely needed unless there are structural abnormalities (like rectal prolapse or severe outlet obstruction). Procedures such as colectomy or ileostomy are reserved for patients unresponsive to all conservative measures.
Lifestyle and Home Management Tips
- Establish a fixed toilet routine, ideally after breakfast when colonic movement is strongest.
- To straighten the rectoanal angle, squat (with feet elevated on a footstool).
- Avoid suppressing your urge to defecate.
- Practice in pelvic floor exercises for relaxation and deep breathing.
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or counselling.
Summary: Dyssynergic Defecation at a Glance
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Cause | Loss of coordination between the rectum, pelvic floor, and anal sphincter |
| Symptoms | Common signs include straining, feeling like the bowel isn't fully emptied, and a blocked sensation while passing stool, often related to constipation. |
| Diagnosis | Evaluation usually involves a digital rectal exam, anorectal manometry to check muscle function, and MRI defecography to look at pelvic floor and rectal movement. |
| Treatment | Management includes biofeedback therapy to improve muscle coordination, lifestyle changes such as increased fiber intake and hydration, and psychological support when necessary. |
| Prognosis | With proper treatment, the prognosis is excellent, and most individuals regain normal bowel function. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Dyssynergic Defecation
What is Dyssynergic Defecation?
It is a condition in which the pelvic floor and anal muscles do not function properly during bowel movements. This lack of coordination makes bowel movement difficult and frequently incomplete.
What causes Dyssynergic Defecation?
Causes include learned behavioural patterns, chronic straining, pelvic injury, childbirth trauma, neurological issues, or stress affecting muscle coordination.
How is DD diagnosed?
Through clinical evaluation, digital rectal exam, anorectal manometry, MRI defecography, and balloon expulsion tests.
Can Dyssynergic Defecation be cured?
Yes. With biofeedback therapy, proper training, and lifestyle changes, most patients achieve complete recovery.
What happens if Dyssynergic Defecation is left untreated?
It can cause chronic(long term) constipation, anal fissures, rectal prolapse, and a decreased quality of life.
Can exercise help for Dyssynergic Defecation?
Yes. Gentle core strengthening, yoga, and pelvic floor relaxation exercises may assist in recovery.
How is Dyssynergic Defecation different from regular constipation?
In regular constipation, stool is hard or slow to pass. In DD, stool reaches the rectum but cannot be expelled due to muscle dysfunction.
What is biofeedback therapy, and how does it work?
It’s a non-surgical method using sensors to help retrain bowel muscles for proper coordination during defecation.
Are laxatives effective for DD?
Laxatives may provide temporary relief, but do not treat the root cause. Biofeedback therapy addresses the underlying muscle dysfunction.
Is DD linked to psychological stress?
Yes. Chronic stress and anxiety can disrupt pelvic muscle coordination and worsen symptoms.
How long does biofeedback therapy take to show results?
Most patients see improvement after 4-6 sessions, although complete healing may take many weeks.
Who is more likely to develop DD?
It is most common in women, older adults, and individuals with a history of chronic constipation or pelvic surgery. These factors can weaken pelvic floor muscles and elevates the risk of developing related conditions.
Conclusion
Dyssynergic Defecation is a treatable functional disorder, not a lifelong condition. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis through anorectal manometry, and biofeedback therapy can help restore normal bowel function and quality of life.
If you have chronic constipation, heavy straining, or incomplete evacuation, you need to see a gastroenterologist or colorectal specialist. Addressing the condition early alleviates complications and allows you to naturally regain digestive harmony.
Remember that bowel health reflects overall well-being, and restoring correct coordination is the key to lasting relief.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868