Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) - Procedure & Cost
PACE Hospitals is recognized as the best hospital for EMR in Hyderabad, India, delivering advanced care for GI conditions.
Our specialists focus on treating precancerous and cancerous gastrointestinal disorders with precision. The team includes top gastroenterologists with extensive expertise in Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR). EMR allows safe, minimally invasive removal of abnormal or early-stage cancerous tissue. The SpyGlass® system enhances visualization for accurate diagnosis and targeted EMR treatment. Modern laparoscopic support ensures safe management of related complex GI cases.
Request an Appointment for EMR Test
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection - appointment
What is Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Procedure?
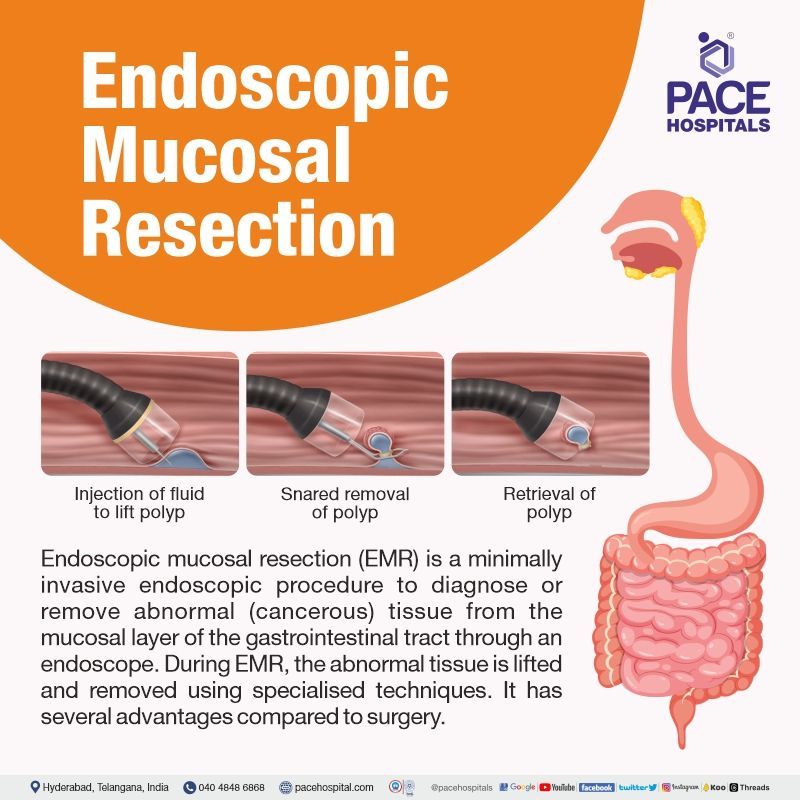
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is a type of third space endoscopy technique treating cancerous tumours or precancerous lesions. This procedure is performed by an interventional gastroenterologist with an endoscope (flexible tube with a camera) equipped with an electrical snare (thin wire forming a loop) at the end.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) can perform both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Since this is a minimally invasive procedure, patient can experience a faster recovery with less pain when compared to open surgery. EMR is usually prescribed in patients suspected or confirmed cancerous tumours or precancerous lesions originated in the gut mucosa (mucous membrane lining the alimentary canal).
When the interventional gastroenterologists want to remove any tumour, they just tighten the electrical snare around it, which not only separates the tumour but also cauterises the wound.
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is a natural evolution of endoscopy, which has been developing since 1995. EMR procedure is developed to not only observe the gut but also to remove any neoplasms (new cancer growths) seen on the superficial layers such as mucosa and submucosa of the gastrointestinal tract.
Endoscopic mucosal resection technique uses
Endoscopic mucosal resection is currently used for the removal of various tumours which originate within the mucosa layer. The mucosa layer is a thin mucus membrane which runs the entirety of the gastrointestinal tract lines, covering the insides of the organs.
The mucosa layer is one of the largest protective barriers involved in protection and absorption, especially in the gastrointestinal tract, where it plays a role in digestion.
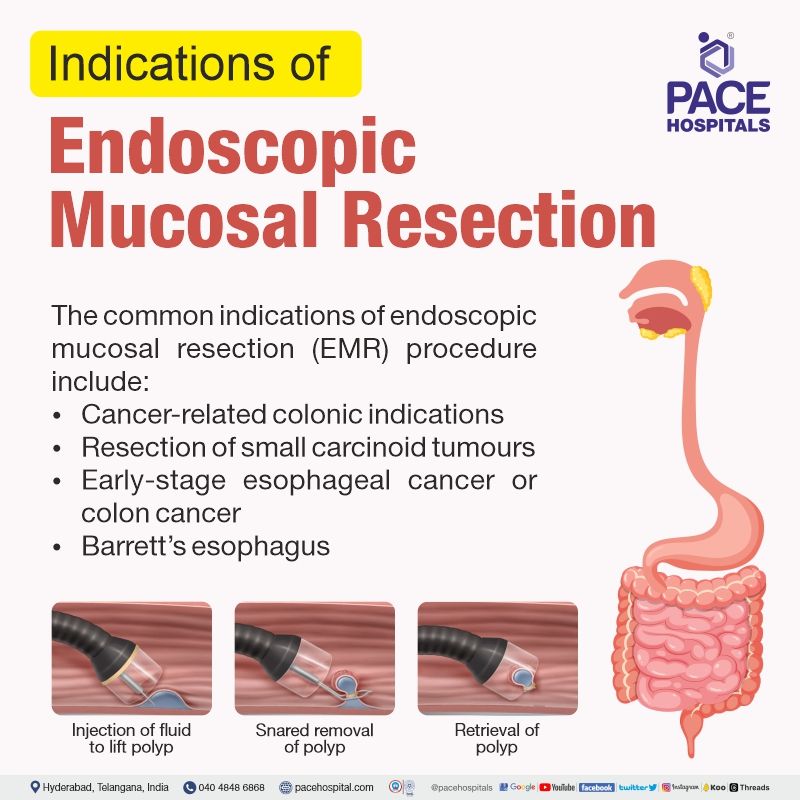
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Indications
Since the endoscopic mucosal resection technique was initially developed for rigid sigmoidoscopy and later for flexible colonoscopy, the colonic indications for endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) procedure are usually common with the former.
The common indications for endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) procedure include:
- Colonic indications are primarily cancer-related in adults (especially colorectal cancer).
- Resection of small carcinoid tumours which were found incidentally.
- Resection of tumour with diameters less than 2 cm and didn’t reach deeper layers of the gastrointestinal wall.
- Early-stage esophageal cancer or colon cancer
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Unique paediatric indications for this procedure are yet to be established.
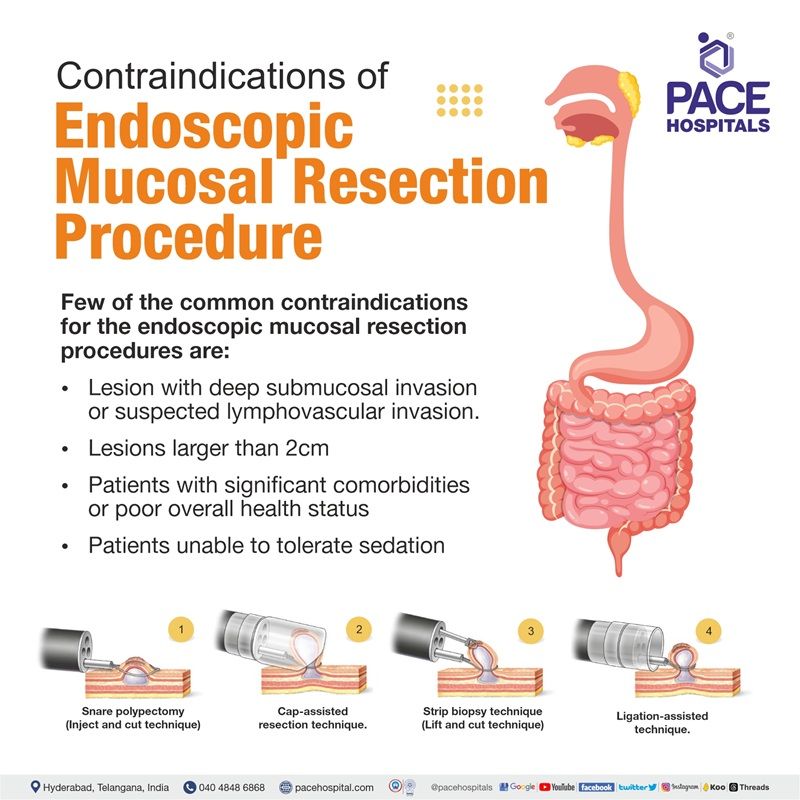
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Contraindications
There are several contraindications to consider for the endoscopic mucosal resection procedure. These include:
- Lesion characteristics: The endoscopic mucosal resection technique may not be suitable for lesions with deep submucosal invasion or suspected lymphovascular invasion. These factors may increase the risk of incomplete resection and potential recurrence.
- Lesion size: The endoscopic mucosal resection technique is generally done for lesions smaller than 2 cm in diameter. Larger lesions could resort to alternative approaches, such as endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) or surgical resection.
- Location: Lesions in difficult anatomical positions, such as the appendix or diverticulum, may be challenging to resect using conventional endoscopic mucosal resection techniques.
- Patient factors: Certain patient factors may also contraindicate EMR. For example, patients with significant comorbidities or poor overall health status may not be suitable candidates for the procedure. Additionally, patients who are unable to tolerate sedation or anaesthesia may not be able to undergo an EMR procedure .
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Doctors
Gastroenterologists who are also skilled in interventional endoscopy are usually the first preferred choice for endoscopic mucosal resection doctors. Nevertheless, interventional gastroenterologists and endoscopists with experience in interventional endoscopy could also be consulted.
Need for specialised training and the learning curve
Advanced techniques, such as colorectal EMR, demand higher technical skills than basic colonoscopy; hence, the patients to whom EMR is prescribed must approach endoscopists who have completed standard endoscopy training with documented competence in basic colonoscopy and polypectomy.
A 2017 study demonstrated that to achieve competency in endoscopic mucosal resection procedures, the endoscopist must perform at least 100 EMR procedures.
Cost Efficacy of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Over Surgery
Cost efficacy of endoscopic mucosal resection over surgery for large laterally spreading colorectal lesions (Endoscopic mucosal resection colon polyps)
A 2016 study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology demonstrated that endoscopic mucosal resection cost estimates could vary depending on various factors, such as the site and size of the lesion, the healthcare facility, and the country.
When compared with surgical resection, the inpatient hospitalisation, anaesthesiologist costs, and risk of complications such as anastomotic breakdown, sepsis, cardiopulmonary events, etc, were reduced when endoscopic mucosal resection was opted to treat the laterally spreading colorectal lesions ≥20 mm in size.
The study reported that the median procedure time for an endoscopic mucosal resection technique was about 20 minutes. The remainder of the colonoscopy was conservatively estimated to take 20 minutes. The anaesthesiologist assessment and the endoscopic mucosal resection colon recovery time was estimated at 20 minutes.
Nevertheless, it must be understood that the endoscopic mucosal resection technique provides substantial outcomes only when appropriately experienced gastroenterologists/endoscopists perform the procedure in adequately resourced tertiary and quaternary healthcare centres.
Considerations of gastroenterologists/endoscopists before planning an endoscopic mucosal resection procedure
A widely accepted procedure, the endoscopic mucosal resection technique was first developed in 1955 for neoplasms removal, which laterally spread across the superficial layers, i.e., the mucosal and submucosal layers of the gastrointestinal tract.
In rigid sigmoidoscopy and flexible colonoscopy, the endoscopic mucosal resection technique was introduced in 1955 and 1973, respectively. Gradually, the list of indications has been extended to include the entirety of the gastrointestinal tract. Through this technique, resection of large polyps can be done endoscopically, which would otherwise require radical surgery.
Before commencing any endoscopic mucosal resection procedure, the endoscopist takes meticulous care to inspect the lesion according to endoscopic mucosal resection guidelines published by the Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society in collaboration with the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association.
Leision inspection is necessary to understand and distinguish resectable lesions from those potentially affected by submucosal invasion. The common factors which an endoscopist may look for when inspecting a lesion before resection:
- Size and location of the lesion
- Type of lesion
- Ulceration
- Hardening
- Lymphadenopathy etc
The distinction is necessary as, depending on the lesion types, they could require either another endoscopic approach or a referral for surgical treatment. Close visual inspection is necessary to delineate the margins of lesions. By carefully inspecting the lesion and delineating the margins, the endoscopist can increase the chances of a successful and curative resection.
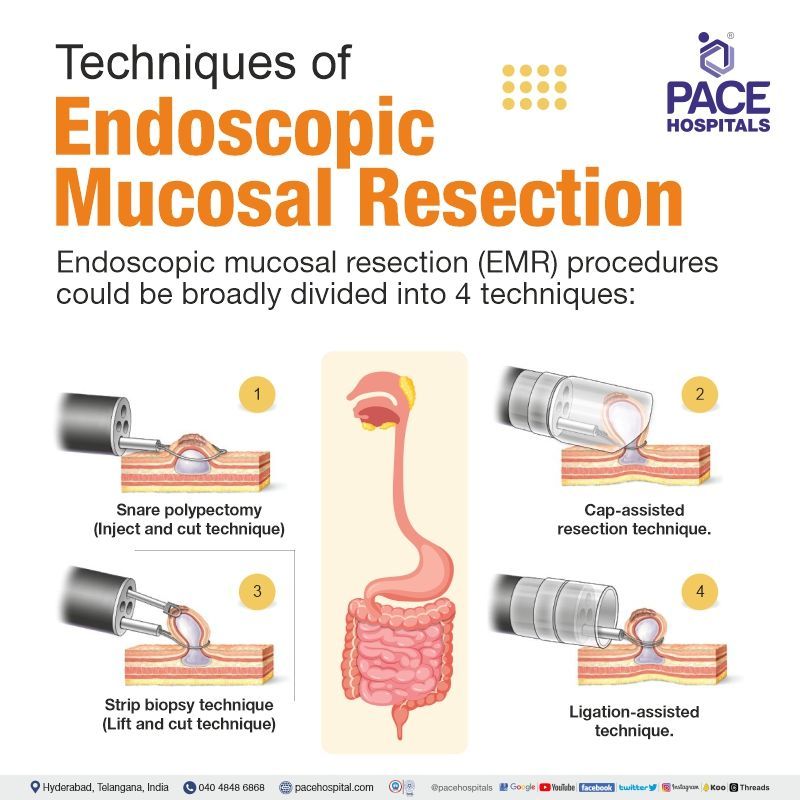
Techniques of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
Endoscopic mucosal resection procedures could be broadly divided into 4 techniques:
- Snare polypectomy (Inject and cut technique)
- Cap-assisted resection technique
- Ligation-assisted technique
- Strip biopsy technique (Lift and cut technique)
- Snare polypectomy (Inject and cut technique) : The most applicable in the colon. This technique involves injecting a solution into or around the lesion to provide a ‘‘submucosal lift’’ and then subsequently resecting (cutting) the elevated lesion with a standard snare with electrocautery. Although this technique has been widely utilised in the Far East, particularly in Japan, only a few centres in the West have reported their experience with inject and cut EMR in the colon.
- Strip biopsy technique (Lift and cut technique): The lift-and-cut EMR method has been developed for resection of early gastric cancer. Chromoendoscopy (Endoscopy that uses stains to highlight differences in mucosa) is utilised to highlight the area of malignant cancer. Normal saline or glucose solution can be injected into the submucosal layer, raising the flat mucosal lesions. The procedure is performed with a polypectomy snare.
- Cap-assisted resection technique: The cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection technique has a specialised, transparent cap at the tip of an endoscope. Once the periphery of the lesion is marked, saline solution is injected into the submucosal layer. The crescent-shaped snare is then prelooped into the rim of the cap by suctioning the normal mucosa, thus sealing the cap outlet. With suction being released, the cap then sucks the lesion with a medium to high vacuum. Then, the lesion is strangulated by closing the snare, with the suction again released. Blend electrosurgical current is typically used to resect the lesion.
- Ligation-assisted resection technique: In ligation-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection, a band ligation device is attached at the end of the endoscope. By positioning over the target lesion, the banding cap creates suction which retracts the lesion. Through a band, the lesion is captured, creating a pseudopolyp, which can be resected with an electrocautery snare. The EMR band ligator handle allows snare device insertion through the endoscope without removing the banding apparatus.
- Multiband mucosectomy (MBM): A type of modified ligation-assisted EMR, this band endoscopic mucosal resection procedure is the cornerstone for the staging and treatment of early cancer arising in Barrett’s esophagus. MBM in endoscopic mucosal resection Barrett's esophagus helps in retracting mucosa into a cap without the necessity for prior submucosal lifting. With the released rubbed band, the created pseudopolyp is resected with a snare.
How is an endoscopic mucosal resection performed?
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is performed to remove flat neoplasms (abnormal cell growth) of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal generally by injecting saline solution into the submucosal space facilitating a complete and safe removal of the lesion minimising the damage to deeper layers.
Before the Endoscopic Mucosal Resection procedure
Once the gastroenterology team decides to perform an endoscopic mucosal resection in a patient, detailed instructions will be provided to prepare the patient for the same. A few of the steps could include:
- Laxative or enema to cleanse the bowel and take only liquid diet, especially if EMR procedure is to be done in the lower gastrointestinal tract.
- In the case of an endoscopic mucosal resection technique to be done in the upper gastrointestinal tract, the patient is refrained from either eating or drinking for 12 hours before the procedure. This clears the oesophagus off food.
- The patient must explicitly state about any known allergies.
- An accomplice must be accompanied to drive the patient home after the procedure, as the medication could make the patient sleepy.
During the Endoscopic Mucosal Resection procedure
An intravenous sedative is delivered to avoid pain.
- A high-definition endoscope is placed either through the mouth or anus, depending on tumour location.
- The gastroenterologists and endoscopists observe the imagery appearing on the screen and navigate the endoscope to avoid damage to surrounding tissue during the procedure.
- Employing either of the 4 techniques explained earlier, the tumour is resected (separated) from surrounding tissues.
- An electrical current in the wire slices away the tumour, cauterising the cut simultaneously.
- Either through a specialised retrieval tool or through the endoscope, the tumour is removed. In the case of a large tumour, it is often retrieved piece by piece.
- The retrieved tissue could be sampled for laboratory examination by a pathologist.
After Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) procedure
Post-EMR procedure, the patient will be reeled into a recovery room for monitoring while the sedative wears off. The gastroenterologist discusses the results with the patient before discharge.
The pathologist’s examination confirms if the procedure has completely removed the tumour. The patient may experience the following side effects:
- Sore throat if the endoscope had been passed through the mouth.
- Vomiting or upset stomach if the procedure occurred in the stomach or intestine.
- Bloating or excessive gas or cramping may be seen, especially if the abdomen was inflated during the treatment.
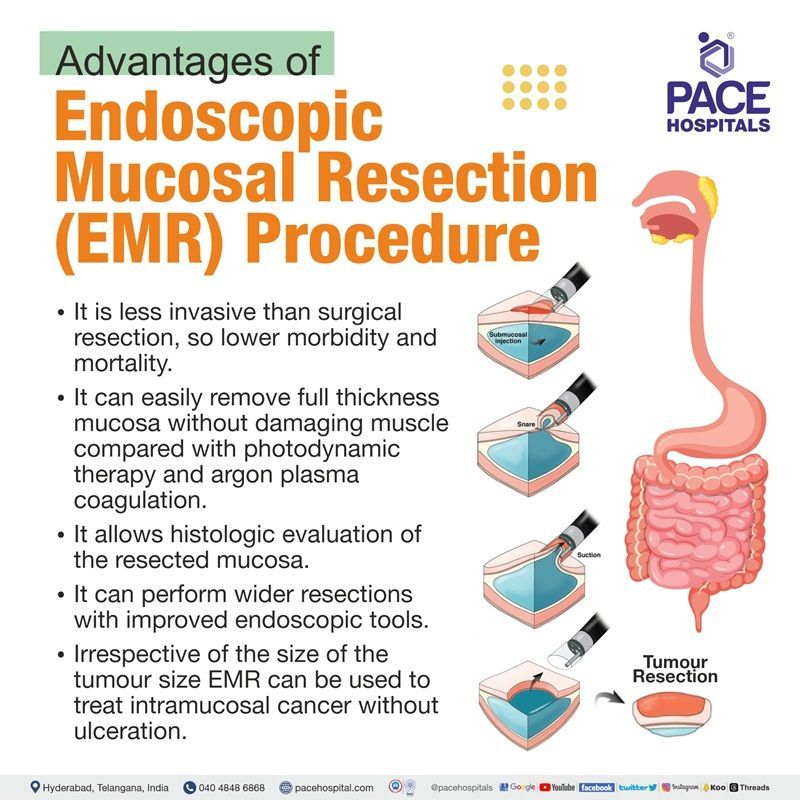
Advantages of Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)
- EMR procedure is less invasive than surgical resection, so lower morbidity and mortality.
- EMR can easily remove full thickness mucosa without damaging muscle compared with photodynamic therapy and argon plasma coagulation.
- EMR procedure allows histologic evaluation of the resected mucosa.
- EMR procedure can perform wider resections with improved endoscopic tools.
- Irrespective of the size of the tumour size EMR can be used to treat intramucosal cancer without ulceration.
The common questions the patients may ask after endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)
- When can I go home?
- What kind of pain can I expect?
- What are the side effects of EMR?
- What can I eat and drink after EMR?
- When can I go back to work?
- When can I start exercising again?
- When do I need to see my doctor again?
- What are the results of the biopsy?
- Do I need any further treatment?
- What is my risk of developing cancer in the future?
- How can I reduce my risk of developing cancer in the future? etc.
Endoscopic mucosal resection recovery and follow-up
Following the endoscopic mucosal resection procedure, the patient may rarely complain about mild chest discomfort for a few days.
- Liquid diet must be taken for 1-2 days if an endoscopic mucosal resection procedure is performed in the esophageal region.
- After that, only soft or pureed food must be taken for at least 2 days, along with proton pump inhibitor medications.
- The entire removal of the diseased tissue may need several endoscopic visits.
Endoscopic mucosal resection vs polypectomy
Difference between Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and Polypectomy
Endoscopic mucosal resection procedure (EMR) and polypectomy are the techniques used for the removal of colorectal polyps. There are a few differences between them, which are highlighted in a 2022 study enlisting end-stage renal disease patients suffering from 3-10-mm colorectal polyps.
| Elements | Polypectomy procedure | Endoscopic Mucosal Resection procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A minimally invasive operation to remove a polyp (tissue growth in the body could be cancerous). Usually done in colon. | A minimally invasive endoscopic procedure developed to not only observe but also to remove any neoplasms (new cancer growths) seen on the superficial layers, such as mucosa and submucosa of the gastrointestinal tract . |
| Types | Cold forceps polypectomy, Snare polypectomy, Electrocautery etc | Inject and cut, Lift and cut, Cap-assisted EMR; and Ligation-assisted EMR |
| Delayed bleeding | Lesser or nothing at all | Cases of delayed bleeding seen |
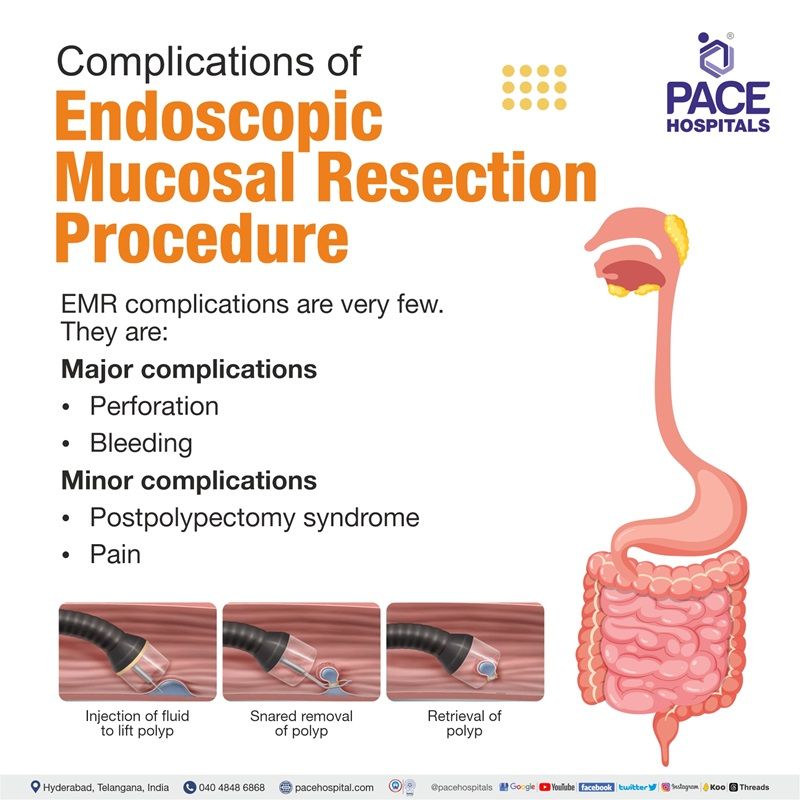
Endoscopic mucosal resection complications
The major complications associated with endoscopic mucosal resection are perforation and bleeding. Nevertheless, it must be understood that the rate of complications was very low, that only 2 cases of minor bleeding and no perforations were seen in 100 cases of endoscopic mucosal resection techniques.
Usually, high doses of proton pump inhibitors are prescribed for 4–8 weeks, which facilitate mucosal healing after an upper gastrointestinal EMR procedure. Frequently occurring minor complications include post polypectomy syndrome and pain.
Major complications of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR):
- Perforation
- Bleeding
Minor complications of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR):
- Postpolypectomy coagulation syndrome (PPCS) (also referred as postpolypectomy syndrome (PPS), postpolypectomy electrocoagulation syndrome (PPES), and transmural burn syndrome)
- Pain
Endoscopic mucosal resection risk factors
The risk factors for post-procedural bleeding could vary depending on the location and other factors of the procedure.
- The possibility of post-procedural bleeding after an endoscopic mucosal resection stomach procedure could increase if the patient is a male suffering from any of cardiopathy or, cirrhosis or chronic kidney disease.
- Lack of sufficient amount of submucosal saline injection in endoscopic mucosal resection esophagus is potentially the largest risk factor for causing perforation in the management of esophageal and gastric cancers.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Cost in Hyderabad, India
The
cost of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹1,10,000 to ₹1,62,000 (approximately US $1,330 – US $1,960).
The exact EMR price varies depending on several factors such as the size and location of the lesion, whether the growth is premalignant or early malignant, the technique used (standard EMR or advanced EMR), patient comorbidities, surgeon expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Procedure
- Small lesion (<2 cm) – ₹1,10,000 – ₹1,25,000 (US $1,330 – US $1,515)
- Medium lesion (2–4 cm) – Standard EMR – ₹1,25,000 – ₹1,40,000 (US $1,515 – US $1,700)
- Large or flat lesion (>4 cm) – Advanced EMR technique – ₹1,40,000 – ₹1,62,000 (US $1,700 – US $1,960)
Frequently Asked Questions on Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
How much does Endoscopic Mucosal Resection cost in India?
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection cost in India, ranges vary from ₹ 1,25,000 to ₹ 1,75,000 (Rupees one lakh twenty-five thousand to one lakh seventy-five thousand). However, cost of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Procedure in India vary in different private hospitals in different cities.