Arthroscopy Procedure | Benefits, Recovery time & Cost
PACE Hospitals is one of the best hospitals for arthroscopy in Hyderabad, India. Our expert orthopedic team offers advanced minimally invasive procedures, including knee arthroscopy, shoulder arthroscopy, ankle arthroscopy, and hip arthroscopy, with personalized treatment plans that encompass surgical intervention, pain management, and post-operative physiotherapy—designed to restore joint function, relieve pain, and support faster recovery and care at every stage of your arthroscopy journey.
Book an Appointment for Arthroscopy Procedure
Arthroscopy Procedure Online Appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
WhatsApp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
HITEC City and Madeenaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
WhatsApp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
HITEC City and Madeenaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Arthroscopy Procedure?
State-of-the-Art Operation Theatres & HD Arthroscopy Systems
Team of the Best Orthopedic & Sports Injury Surgeons in Hyderabad
Post-surgery care tailored physiotherapy and rehabilitation
Affordable arthroscopy surgery cost in Hyderabad with Insurance & Cashless Options
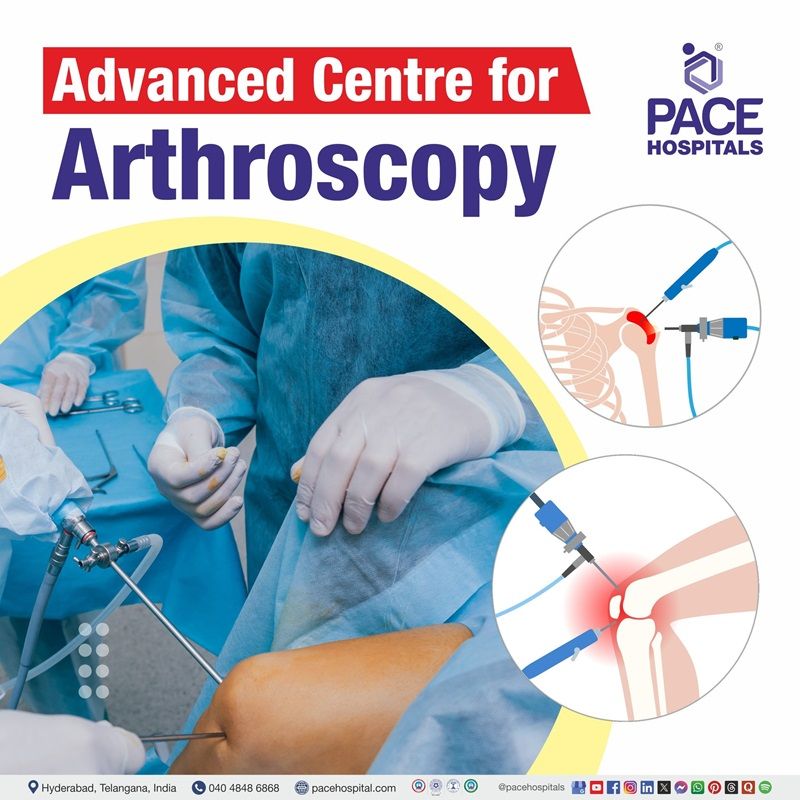
What is Arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy definition
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure which orthopedic surgeons use to diagnose and treat joint problems, most commonly in the knee, shoulder, and other large joints. During an arthroscopy, the joints are examined using a device known as an arthroscope. This is a thin, drinking straw-sized metal tube. It has a camera and a light source. The orthopedic surgeon can see inside the joint by sending images from the arthroscope to an eyepiece or a video screen.
Arthroscopy meaning
"Arthroscopy" is derived from the Greek words "arthro" and "skopein".
Arthro means “joint”, and skopein means “to look”. Hence, the term arthroscopy means "to look within the joint."
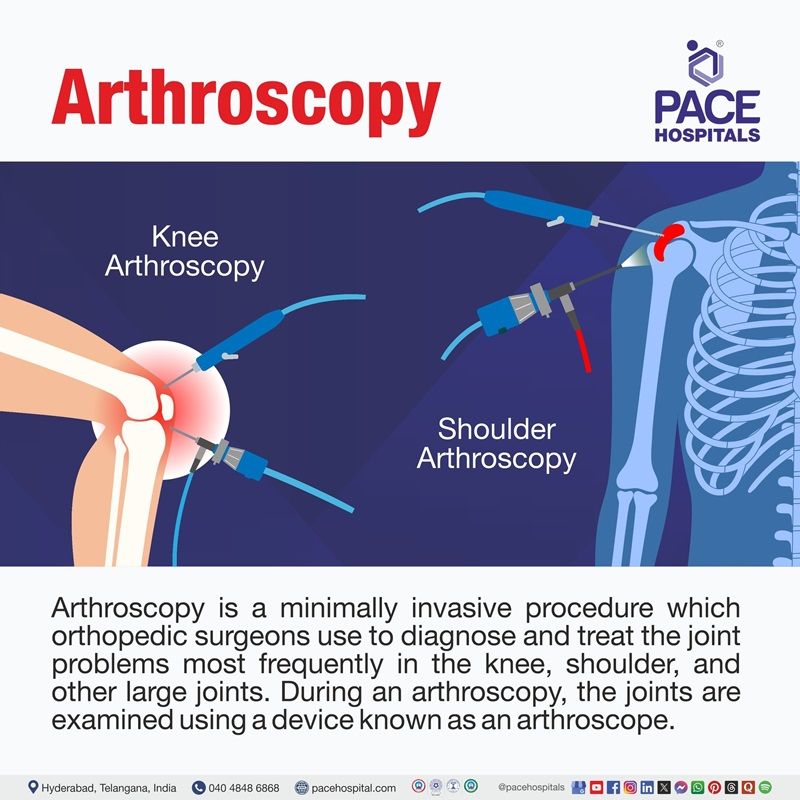
Arthroscopy Types
A minimally invasive surgical procedure called an arthroscopy is used to identify and treat joint problems. Based on the joint being involved, the arthroscopy types are categorized as below:
Knee arthroscopy
A minimally invasive technique that involves inserting an arthroscope into the knee joint to assess and treat problems like meniscal tears, cartilage damage, ligament injuries (such as the ACL or PCL), and loose body removal. Across the world, it is among the most frequently performed arthroscopic procedures.
Hip arthroscopy
A minimally invasive method for diagnosing and treating conditions of the hip joint, such as cartilage damage, loose bodies, femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), and labral tears Small incisions are made to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments into the hip.
Shoulder arthroscopy
In order to examine, diagnose, and treat issues like rotator cuff tears, labral tears, impingement syndrome, recurrent dislocations, and loose body removal, an arthroscope is inserted into the shoulder joint during this procedure. It is frequently carried out for conditions like rotator cuff repair and subacromial impingement.
Ankle arthroscopy
Through this procedure, the surgeon can identify and treat disorders that affect the ankle joint, including loose bodies, persistent ankle pain, ankle impingement, and cartilage damage. It is frequently employed for both therapeutic and diagnostic reasons.
Wrist arthroscopy
A minimally invasive procedure to assess and manage wrist issues, such as ganglion cysts, fractures, ligament damage, and persistent wrist pain. The arthroscope is inserted through tiny incisions to view and fix the wrist joint.
Elbow arthroscopy
This type of arthroscopy is used to identify and treat stiffness, tennis elbow, arthritis, and loose bodies in the elbow. This procedure assists in eliminating inflammatory tissue or fixing damaged elbow structures.
Spine arthroscopy
A less popular but growingly popular less invasive method for treating tumors, spinal deformities, degenerative disc disease, and spinal disc herniation. Compared to open spine surgery, the method speeds recovery and minimizes tissue damage.

Arthroscopy Indications
When imaging tests or physical examinations cannot accurately identify the cause of joint symptoms, arthroscopy is used. It assists doctors in closely examining the meniscus, ligaments, cartilage, and synovial membrane to determine the exact problem. Below are some of the indications for arthroscopy:
- Removal of loose bodies: Arthroscopy is recommended when loose bone or cartilage fragments in joints cause pain, locking, or limited mobility.
- Management of inflamed joint linings (Synovitis): When inflammatory or infectious synovitis affects the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, or ankle, a synovectomy may be recommended.
- Treatment of damaged or torn cartilage: Arthroscopy is used to treat cartilage injuries in other joints, including the ankle, hip, and shoulder, or to repair or remove a torn meniscus in the knee.
- Treatment of scarring and joint stiffness: Removal of scar tissue (arthrofibrosis) that limits joint movement, particularly following surgery or injury, can be done with arthroscopy.
- Repair of torn ligaments and tendons: It is often used to repair rotator cuff or labral tears in the shoulder and to reconstruct torn ligaments (such as the ACL in the knee).
- Diagnosis and management of joint disorders: It is used to visualize intra-articular pathology directly and treat it specifically when non-invasive imaging is inconclusive.
- Selected cases of arthritis: Arthroscopy can be used to treat some arthritis-related issues, such as removing loose bodies or inflammatory tissue, to help relieve symptoms.
Specific joint indications
- Knee: Meniscal tears, cartilage defects, ligament injuries, patellar problems, and infection.
- Shoulder: Rotator cuff tears, instability, labral tears, impingement, and AC joint pathology.
- Ankle: Synovitis, osteochondral lesions, impingement, and loose bodies.
- Hip, Wrist, Elbow: Labral tears, loose bodies, synovitis, and ligament injuries.
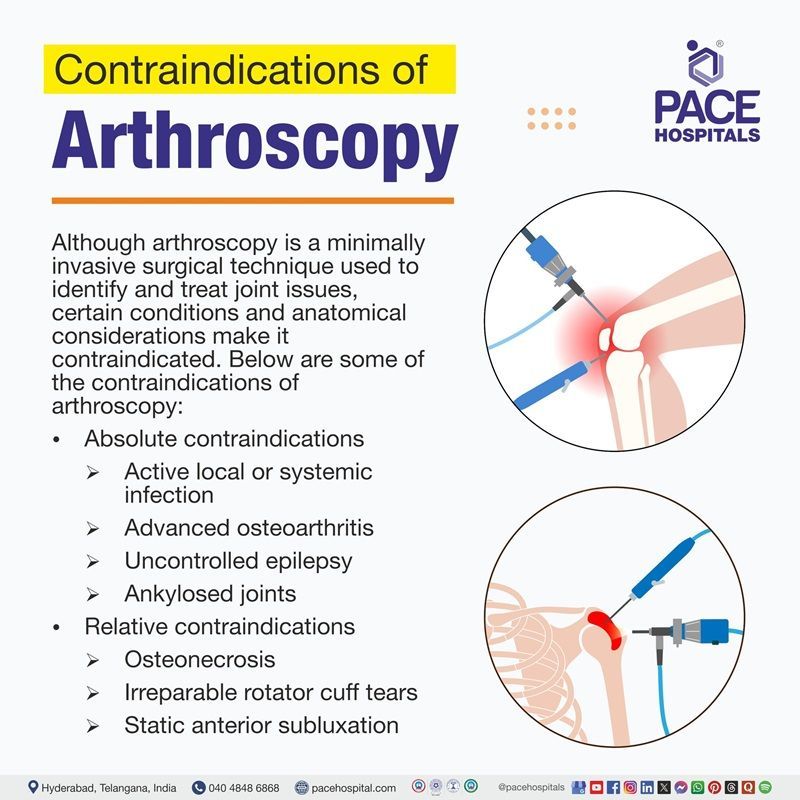
Contraindications of Arthroscopy
Although arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to identify and treat joint issues, certain conditions and anatomical considerations make it contraindicated. Below are some of the contraindications of arthroscopy:
Absolute contraindications
- Active local or systemic infection: When there are active infections, arthroscopy is contraindicated due to the risk of septic arthritis.
- Advanced osteoarthritis: Due to its limited therapeutic benefits, arthroscopy is not advised for joints with severe degenerative changes (Outerbridge grade III/IV). This includes osteoarthritis in the knee with significant cartilage loss and advanced hip osteoarthritis with femoral head collapse.
- Uncontrolled epilepsy: Seizures increase the risk of postoperative complications, such as coracoid graft fracture, in cases of shoulder instability.
- Ankylosed joints: Joint fusion, such as hip ankylosis, impairs arthroscopic access and mobility.
- Voluntary dislocators: Surgical results are poor for patients who have a history of shoulder dislocation or subluxation.
Relative contraindications
- Osteonecrosis: Hip arthroscopy is contraindicated in cases of osteonecrosis with femoral head collapse; however, it may be helpful in the early stages.
- Irreparable rotator cuff tears: Because of the risk of instability, shoulder arthroscopy (such as the Latarjet procedure) is avoided if it is related to massive, irreparable tears.
- Protrusio acetabuli: Hip arthroscopy has traditionally been contraindicated, but newer methods allow for correction in some circumstances.
- Symptomatic Os Acromiale: Arthroscopic acromioplasty is contraindicated because of a compromised deltoid attachment.
- Static anterior subluxation: In shoulders with subscapularis insufficiency, arthroscopy may worsen anterior humeral head subluxation.
Special considerations
- Older patients: Complication risks are higher in older patients (e.g., bone block non-union in Latarjet procedures).
- Poor bone quality: This may restrict the integration of grafts in unstable surgeries.
- Failed conservative treatment: Unless mechanical symptoms continue after non-surgical treatment, arthroscopy is not recommended.

Benefits of Arthroscopy
Compared to open surgery, arthroscopic surgery has several important advantages, such as smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and a lower likelihood of complications. Below are some of the advantages of arthroscopy:
- Minimally invasive approach: Compared to open surgery, arthroscopy requires fewer incisions, which greatly reduces soft tissue damage and lowers postoperative pain and swelling.
- Lower risk of complications: In comparison to open procedures, arthroscopy's minimally invasive nature lowers the risk of complications like infection, joint stiffness (arthrofibrosis), and postoperative morbidity.
- Faster recovery and rehabilitation: After an arthroscopy, patients usually recover more quickly, have shorter hospital stays, and can start rehabilitation earlier, which allows them to return to their regular activities and jobs sooner.
- Outpatient and cost-effective: The majority of arthroscopic procedures are done as outpatient procedures, which lowers hospital expenses and provides more options for anesthesia.
- Enhanced quality of life: Compared to open surgery, patients frequently report better functional outcomes and quality of life following arthroscopic procedures, with fewer complications and higher postoperative scores.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy: Compared to imaging techniques like CT Scan, ultrasound, or arthrography, arthroscopy provides a more accurate diagnosis because it allows direct visualization of the joint's interior, particularly for complex joint lesions.
- Simultaneous diagnosis and treatment: In the same session, this procedure allows for both diagnosis and treatment, allowing for prompt management of detected pathologies (e.g., meniscus repair, removal of loose bodies).
Arthroscopy Procedure Steps
Arthroscopy procedure steps include the following:
Before the arthroscopy procedure
- To make sure the patient is a good candidate for arthroscopy, the surgeon performs a comprehensive medical evaluation that includes a thorough history and physical examination. This may include further diagnostic imaging or blood tests.
- Patients are advised to disclose any allergies to medications, latex, or anaesthetics, current medications, including over the counter and herbal supplements; and any history of bleeding disorders or anticoagulant use. Before surgery, certain medications may need to be stopped.
- It is recommended to cut down on alcohol consumption and quit smoking in order to promote healing and lower the risk of surgery complication.
- If a woman is pregnant or suspects she is pregnant, she must inform the doctor.
- Informed consent is obtained after providing the patient with a thorough explanation of the procedure. Patients are advised to carefully review the consent form and ask questions.
- Before the procedure, patients are advised to fast (not eat or drink anything) starting at midnight.
- Since mobility may be temporarily restricted following surgery, arrangements should be made for postoperative assistance at home.
During the arthroscopy procedure
- The patient is taken to the operating room and properly positioned (lateral or supine, depending on the joint) after their identity is confirmed, and safety procedures have been verified.
- Anaesthesia is given; options include local, regional, or general anesthesia; additional nerve blocks are occasionally used to manage pain.
- The surgical site is sterilized, and anatomical landmarks are marked. Small incisions called portals are made, usually using a No. 15 or 11 blade, being careful not to damage cartilage or ligaments.
- Saline solution is infused to distend the joint and enhance visualization after the arthroscopic cannula is placed through the primary portal, which is generally anterolateral for the knee.
- After introducing the arthroscope, a careful diagnostic examination is carried out, looking at ligaments, menisci, and cartilage. The surgeon can move and rotate the arthroscope to view all relevant compartments.
- Additional portals for the insertion of specialised instruments are made under direct visualization if therapeutic intervention is required. When necessary, procedures like synovectomy, loose body removal, and meniscal debridement are carried out.
- After concluding, the instruments are removed, and the joint is irrigated. A sterile dressing is applied after the incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips.
After the arthroscopy procedure
- As the anesthesia wears off, patients are monitored in the recovery area. When necessary, pain management is given.
- Physical therapy may be started to regain joint strength and function, and early mobilization is advised to avoid stiffness.
- The length of recovery and return to regular activities is determined by the particular procedure carried out as well as patient-specific factors.
- Follow-up appointments are planned to evaluate the progress of recovery and wound healing. Usually, stitches are taken out 7–10 days after surgery.
- Patients are advised to be on the lookout for and report any symptoms of complications, such as infection, severe swelling, or ongoing pain, as soon as they appear.
Arthroscopy Complications
After an arthroscopy, complications are usually rare; for the majority of joints, reported rates are about 1%. Careful patient selection and perioperative management are essential because the risk of complications is influenced by surgical complexity, operative time, and patient-related factors (such as age, obesity, diabetes, smoking, and comorbidities). Below are some of the complications of the arthroscopy procedure:
- Bleeding and hemarthrosis: One of the most common complications is hemarthrosis, or bleeding into the joint, which occasionally necessitates joint aspiration.
- Infection: After an arthroscopy, infection is uncommon but can happen; deep infections are especially rare. Infection rates are typically less than 1%.
- Thromboembolic events: Although uncommon, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism can occur, particularly during lower limb arthroscopy.
- Nerve injury: Nerve damage can be either temporary or permanent, and it is frequently associated with portal placement or traction. The incidence varies by joint, ranging from 0.9% in the hip to up to 7.5% in the elbow.
- Persistent pain and frozen joint: Notable complications, especially after shoulder arthroscopy, include persistent pain and frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis).
- Stiffness and adhesions: Adhesions or postoperative joint stiffness may form, sometimes necessitating further procedures to resolve.
- Instrument breakage: Although rare, arthroscopic instrument breakage is a known complication that occasionally requires additional care.
- Wound and skin complications: Ecchymosis and superficial infections are examples of minor wound-healing problems that can occur but usually go away without significant intervention.
- Soft tissue and cartilage injury: The procedure may result in iatrogenic damage to the labrum, cartilage, or other soft tissues, particularly in technically demanding joints like the hip.
- Anesthetic and cardiovascular complications: There have been rare reports of anesthesia-related or cardiovascular complications, especially in elderly or high-risk patients.
Arthroscopy Recovery Time
Depending on the joint and procedure, the recovery time following an arthroscopy varies, but most patients report a significant improvement in their functional abilities within three to six months. Approximately 30% of patients recover from arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in three months, 40% in three to six months, and the remaining patients may require more time. Age, the size of the tear, and preoperative stiffness all affect how quickly patients recover. Most patients who have knee arthroscopy get back to their regular activities in four weeks. In general, quicker recovery following arthroscopic procedures is related to smaller injuries and younger ages.
Questions that the patients can ask the healthcare team about the arthroscopy procedure?
- When can I go home?
- When do I need to see my doctor again?
- What kind of pain can I expect?
- What is the expected recovery time?
- What precautions should I take?
- Will I require physical therapy after surgery, and for how long?
- What problems can occur after arthroscopy?
- Are there any specific exercises I should avoid while recovering?
- When can I go back to my regular activities?
- How long will my recovery take, and what kind of assistance will I require throughout that time?
- Do I need any further treatment?
Difference between Arthroplasty and Arthroscopy
Arthroplasty vs arthroscopy
Arthroplasty and arthroscopy are two different surgical techniques that are frequently used in the treatment of joint disorders. Below are the parameters that help in differentiating arthroplasty and arthroscopy:
| Parameters | Arthroplasty | Arthroscopy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An arthroplasty is a procedure used to repair a joint. Resurfacing the bones can help restore a joint. It's also possible to use a prosthesis or artificial joint. | It is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a scope to diagnose or treat intra-articular pathology. |
| Common indications | Severe joint damage, end-stage arthritis, and unsuccessful conservative treatments | Meniscal tears, mild to moderate cartilage lesions, ligament damage, and diagnostic requirements |
| Invasiveness | It is more invasive and includes open surgery and prosthesis implantation | It is less invasive and uses tiny incisions and specialized instruments |
| Recovery time | It has a longer recovery, and extensive rehabilitation is needed | It has a shorter recovery and can return to activities faster |
| Complications | Increased risk: cardiac events, thromboembolism, infection, and prosthesis failure | The overall risk is lower, but complications like infection, stiffness, and neurovascular injury could occur. |
Difference between Shoulder Arthroscopy and Arthroplasty
Shoulder Arthroscopy vs Arthroplasty
The functions of shoulder arthroscopy and arthroplasty in the treatment of shoulder pathology are distinct. In comparison with arthroplasty, arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that is frequently used for rotator cuff repair, treatment of impingement, and for diagnostic purposes. It offers significant improvements in pain and function, even in elderly patients, and is less expensive and requires a quicker recovery.
Although arthroplasty, which includes anatomic and reverse total shoulder replacement, offers dependable pain relief and functional improvements, it is usually saved for patients with advanced joint diseases like severe osteoarthritis or irreparable rotator cuff tears. However, it is more invasive and has a higher risk of complications.
Comparative studies show that arthroplasty is preferred for patients with advanced degenerative changes or to those whose previous repairs have failed, while arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is typically more cost-effective and should be considered first when feasible.
Arthroscopy Cost in Hyderabad, India
The cost of arthroscopy in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹35,000 to ₹1,80,000 (approximately US $420 – US $2,165).
The exact arthroscopy price varies depending on several factors such as the type of joint involved (knee, shoulder, ankle, hip, wrist), the complexity of the injury, whether ligament or cartilage repair is required, the use of implants or anchors, surgeon expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Arthroscopy / Procedure
- Knee Arthroscopy (Diagnostic / Basic Procedure) – ₹35,000 – ₹55,000 (US $420 – US $660)
- Knee Arthroscopy with Meniscus Repair / Debridement – ₹55,000 – ₹1,10,000 (US $660 – US $1,325)
- Shoulder Arthroscopy (Diagnostic / Basic) – ₹50,000 – ₹90,000 (US $600 – US $1,080)
- Shoulder Arthroscopy with Rotator Cuff Repair / Stabilization – ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,80,000 (US $1,205 – US $2,165)
- Ankle / Wrist Arthroscopy – ₹40,000 – ₹90,000 (US $480 – US $1,080)
- Hip Arthroscopy (Labral Tear / FAI Correction) – ₹1,20,000 – ₹1,80,000 (US $1,445 – US $2,165)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Arthroscopy Procedure
Do you need crutches after a knee arthroscopy?
After a knee arthroscopy, crutches are frequently required for a short duration, particularly after surgical inventions. However, many patients can walk without assistance within a few days, and by four weeks, the majority can resume their normal activities. Crutches can help with walking during the starting stages of recovery, especially if there is pain or weakness. However, how long they are needed last depends on the patient's recovery and the extent of the surgery.
Which Is the Best Hospital for Arthroscopy in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is considered one of the leading centres for arthroscopy and advanced sports injury management.
Our team of expert orthopaedic and sports medicine surgeons perform minimally invasive joint procedures using high-definition arthroscopic cameras, precision-guided instruments, and rapid-recovery protocols.
With advanced operating theatres, modern rehabilitation facilities, and comprehensive injury management programs, PACE Hospitals ensures safe, accurate, and highly successful arthroscopy outcomes — supported by cashless facility options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and complete assistance with medical insurance processing for eligible patients.
Is arthroscopy safe?
Depending on the joint and patient characteristics, arthroscopy is usually regarded as a minimally invasive, safe procedure with low complication rates, which typically range from 1% to 8%. While rare but serious risks like infection, nerve damage, or thromboembolism can occur and should be taken into consideration when choosing surgery, the majority of complications are generally minor and temporary.
What is the success rate of arthroscopy surgery?
Although arthroscopy surgery success rates vary by joint and indication, long-term studies show high patient satisfaction and survival rates. Hip arthroscopy satisfaction rates are approximately 90%, and 10-year survivorship rates range from 72.6% to 91.6%. The 10-year survival rate for arthroscopic bone marrow stimulation procedures is nearly 82%.
What Is the Cost of Arthroscopy in Hyderabad, India?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of arthroscopy typically ranges from ₹35,000 to ₹1,60,000 and above (approximately US $420 – US $1,925), depending on:
- Type of joint involved (knee, shoulder, ankle, hip, wrist)
- Extent of ligament, cartilage, or tendon damage
- Whether repair, reconstruction, or debridement is required
- Need for implants/anchors or biological augmentation
- Duration of hospital stay and post-operative physiotherapy
- Surgeon expertise and advanced arthroscopic instrumentation
Basic diagnostic arthroscopy falls at the lower end, while complex repair or reconstruction procedures fall toward the higher range.
After a detailed evaluation, imaging review (MRI/X-ray), and joint assessment, our orthopaedic team provides a personalised treatment plan and an accurate cost estimate based on your joint condition and clinical requirements.
How long does it take to recover from wrist arthroscopy?
Most patients recover from wrist arthroscopy in 2 to 8 weeks, based on the procedure and individual factors. After two weeks, it's usually possible to resume light activities or sedentary work, but if tissue repair was done, manual work or full recovery could take up to six weeks or more.
Is hip arthroscopy worth it?
At mid- to long-term follow-up, hip arthroscopy typically results in high rates of patient satisfaction and return to activity, as well as notable improvements in pain, function, and quality of life, particularly for conditions like femoroacetabular impingement and labral tears. However, after one to two years, the advantages over non-operative care might diminish, and older patients or those with osteoarthritis tend to have worse results. When all factors are considered, hip arthroscopy is thought to be beneficial for patients who are carefully selected.
Is arthroscopy painful?
Arthroscopy usually results in mild to moderate pain, which typically peaks in the first 8 to 24 hours following the procedure and then subsides over time. Most patients only need very little additional analgesia. Several factors can influence postoperative pain intensity, including preoperative pain levels, procedure type, and individual characteristics.
Is hip arthroscopy a major surgery?
Compared to traditional open procedures, hip arthroscopy is regarded as a minimally invasive surgery because it treats joint issues with small incisions and specialized tools, resulting in less tissue damage, less pain after surgery, and a quicker recovery. Nevertheless, it should not be considered a minor or insignificant procedure because it is still a surgical intervention that requires anesthesia and carries some risks.
Is arthroscopy a diagnostic?
Arthroscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that can be used to treat joint issues while also allowing direct visualization of the inside of a joint to diagnose conditions when non-invasive imaging is inconclusive. When other tests fail to provide correct answers, diagnostic arthroscopy is especially helpful in determining the causes of joint pain, swelling, or instability. Thus, in orthopedic practice, arthroscopy plays an essential diagnostic role.
How long is hip arthroscopy surgery?
Depending on patient-specific factors and the procedure's complexity, hip arthroscopy surgery usually takes 45 to 150 minutes. Large studies have shown that the average operating time is between 99 and 115 minutes.
Is arthroscopy advisable at the 70 years age?
Studies have shown that arthroscopy is generally safe and can improve function and relieve symptoms, so it may be recommended for some patients at age 70, especially those without significant underlying degenerative changes. However, comorbidities and older age may raise the chance of complications and the need for additional surgery, so risk assessment and patient selection are important.
Is it hard to lift the thigh after an arthroscopy?
After an arthroscopy, postoperative quadriceps weakness and reflex inhibition of muscle function frequently result in difficulty lifting the thigh. Since this weakness may last for weeks or even months, focused rehabilitation is crucial to regaining muscle strength and restoring regular movement patterns
What happens if knee arthroscopy fails?
Patients may suffer from chronic pain, poor functional results, or osteoarthritis if knee arthroscopy is unsuccessful, particularly if a meniscal repair is unsuccessful. Infection, thrombosis, or the requirement for additional surgery are some of the additional complications.
When to start physical therapy after knee arthroscopy?
Unless the surgeon specifies otherwise, physical therapy usually starts within the first week following knee arthroscopy, sometimes even the day after the procedure. It focuses on mild range-of-motion and quadriceps activation exercises. Early initiation aids in preventing stiffness, reducing swelling, and restoring mobility; however, the course of treatment needs to be adjusted depending on the patient's pain, swelling, and specific surgical procedures.
What is the difference between hip arthroscopy and total hip replacement?
For patients without advanced arthritis, hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive treatment option for femoroacetabular impingement and labral tears. It provides a quicker recovery but has limited benefits in cases of severe degeneration. Total hip replacement, which is more invasive and typically used for severe joint disease, offers consistent pain relief and enhanced function, particularly for elderly patients or those with severe osteoarthritis. The decision is based on the degree of joint damage as well as patient-specific parameters.
What are the dos and Don'ts for patients after arthroscopy surgery?
Do’s
- To lessen swelling, patients need to elevate the joint and take rest.
- Patients need to apply ice packs to reduce pain and swelling as directed.
- Patients need to adhere to any weight-bearing or mobility restrictions (if recommended, they need to use braces, slings, or crutches).
- To regain strength and range of motion, patients need to begin physical therapy as directed.
- Patients need to watch for signs of infection. They should keep wounds clean and dry.
- Patients need to attend all follow-up visits.
Don’ts
- Until the doctor gives the all-clear, patients need to avoid putting weight or strain on the operated joint.
- Patients should not skip advised exercises or therapy.
- Until allowed, avoid getting the incision wet (no soaking or swimming).
- Patients should not neglect infection symptoms, such as fever, discharge, swelling, or redness.
- Patients should not return to heavy activity or sports too early.




