Deep Vein Thrombosis, DVT - Symptoms, Causes, Types, Complications and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
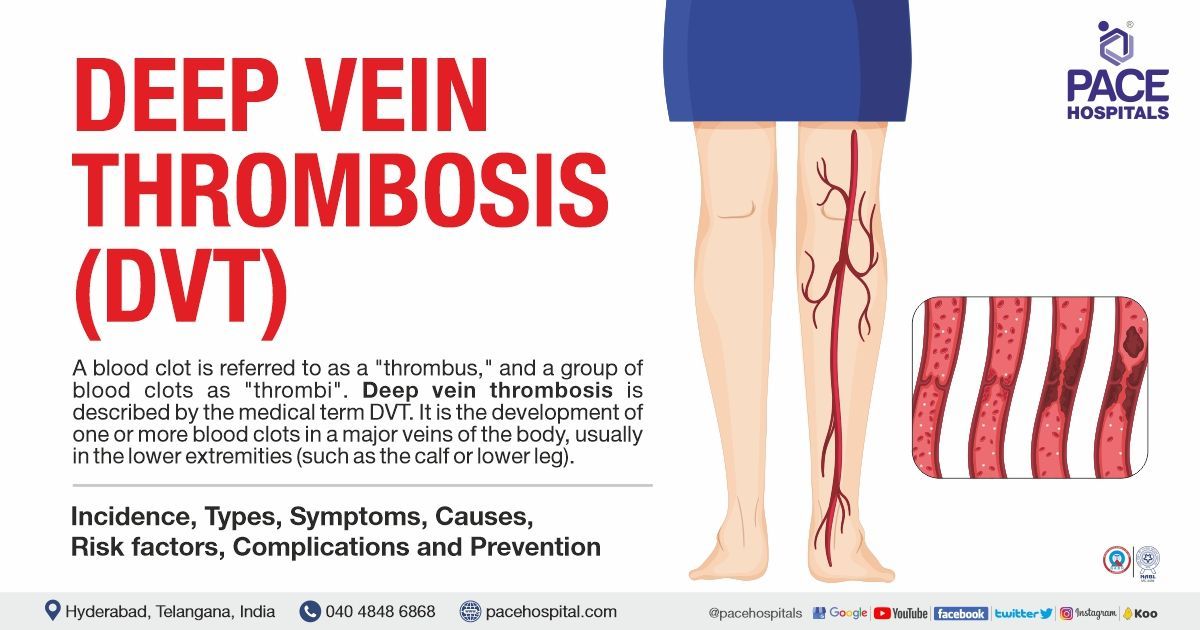
DVT full form in medical - Deep Vein Thrombosis
A blood clot is called a "thrombus," while several blood clots are called "thrombi". Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the occurrence of one or more blood clots in one of the body's principal veins, mostly in the lower limbs (such as, the lower leg or calf).
The clots may completely or partially restrict blood flow in the vein, which may cause some patients to experience pain, swelling, discomfort, discolouration, or redness in the affected area and possibly warm-to-the-touch skin. It can be dangerous if the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, where it can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE).
Incidence of DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
The lower limb is often impacted by deep vein thrombosis (DVT), with clot development occurring in a deep calf vein and spreading proximally. It is a common venous thromboembolic disorder (VTE) with an annual incidence of over 1.6 per 1000 people.
Distal veins are responsible for 40% of site involvement, followed by popliteal 16%, femoral 20%, common femoral 20%, and iliac veins 4%. Less than 10% of DVTs occur in the upper limbs, and central vein catheters are the primary risk factor.
Venocaval thromboses (clots in the vena cava) are relatively rare and connected to vascular abnormalities, compression, and cancer.
Types of DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
There are two main types of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), they are as follows::
- Acute DVT (acute deep vein thrombosis)
- Chronic DVT (chronic deep vein thrombosis)
Acute DVT: Acute deep vein thrombosis can develop in men and women of all ages, especially in the legs. It can make walking difficult, swells and hurts the legs. The number of veins injured, and the severity of the symptoms, increase with the size of the blood clot.
Chronic DVT: "Chronic" refers to more than one to two months old clots. The vein becomes scarred when the clot hardens, and it causes the vein to shrink significantly, making it difficult for blood to flow through.
There are also several other types of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including:
- Travel-Associated DVT: This type of DVT occurs in people who have been sitting for long periods of time, such as on long flights or car rides.
- Postpartum DVT: This type of DVT occurs in women within three months of giving birth.
- Immobilization DVT: This type of DVT occurs in people who are unable to move around much, such as after surgery or a major injury.
- Inherited DVT: This type of DVT is caused by a genetic disorder that makes people more likely to form blood clots.
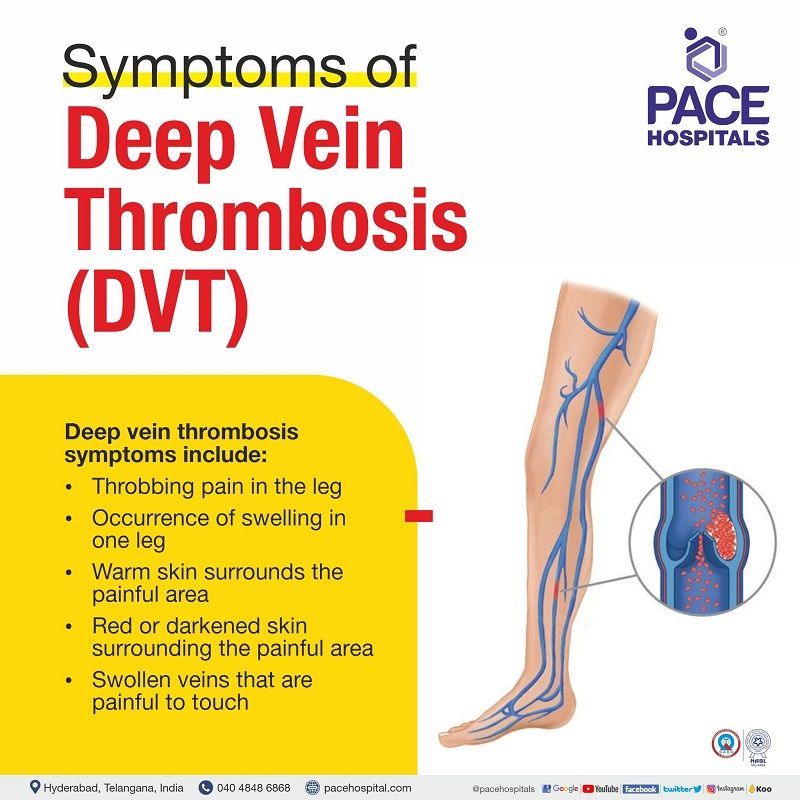
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Symptoms
DVT disease can be a serious condition, but it is usually treatable with proper medication and regular checkups. These are some of the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT):
- Throbbing (to beat or pulsate with increased force) pain in the leg
- Occurrence of swelling in one leg (rarely in both legs)
- Warm skin surrounds the painful area
- Red or darkened skin surrounding the painful area (sometimes, it may not be visible in individuals with black or brown skin)
- Swollen veins that are painful to touch
If the patient is experiencing breathlessness (dyspnoea), chest pain along with the above symptoms, then the condition is to be taken as an emergency and needs to consult the doctor immediately. This condition is called pulmonary embolism (PE).
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a condition where the portion of a blood clot in DVT passes through the bloodstream to the lungs. People can recover from this condition if the clot is small, and the proper treatment is received.
If a bigger clot dislodges and obstructs the blood from reaching the lungs, it may lead to death finally. Pulmonary embolism (PE) may cause:
- Trouble while breathing
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeats)
- Angina (chest pain when taking a deep breath)
- Haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Low blood pressure
- Dizziness (light-headedness or fainting)
Note: One-third of people who get a DVT will suffer long-term health issues called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). PTS can lead to oedema, discomfort, skin discolouration or redness, and other problems. It allows the skin more vulnerable to cellulitis, an infection that can enter the circulation and result in sepsis and death.
DVT (blood clot in a vein) typically does not cause a heart attack or stroke. Usually, the body receives oxygen-rich blood from the heart through arteries. Heart attacks and strokes can be brought on by arterial thrombosis, a blood clot in an artery.
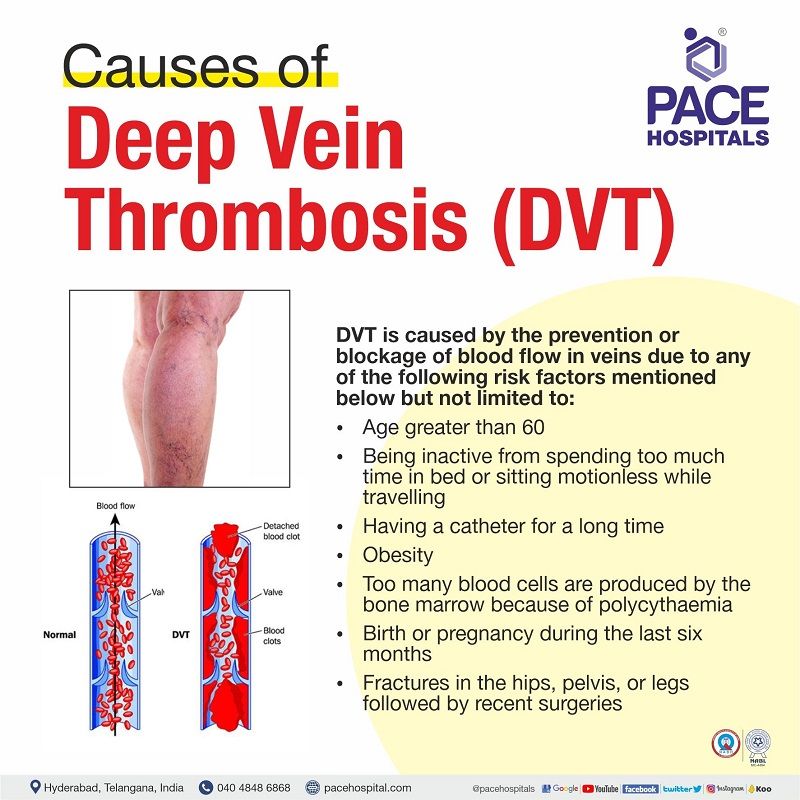
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT causes
DVT meaning
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) is caused by the prevention or blockage of blood flow in veins due to any of the following risk factors mentioned below, but not limited to:
- Age greater than 60
- Being inactive from spending too much time in bed or sitting motionless while travelling
- Having a catheter for a long time
- Obesity
- Too many blood cells are produced by the bone marrow because of polycythaemia
- Birth or pregnancy during the last six months
- Fractures in the hips, pelvis, or legs followed by recent surgeries
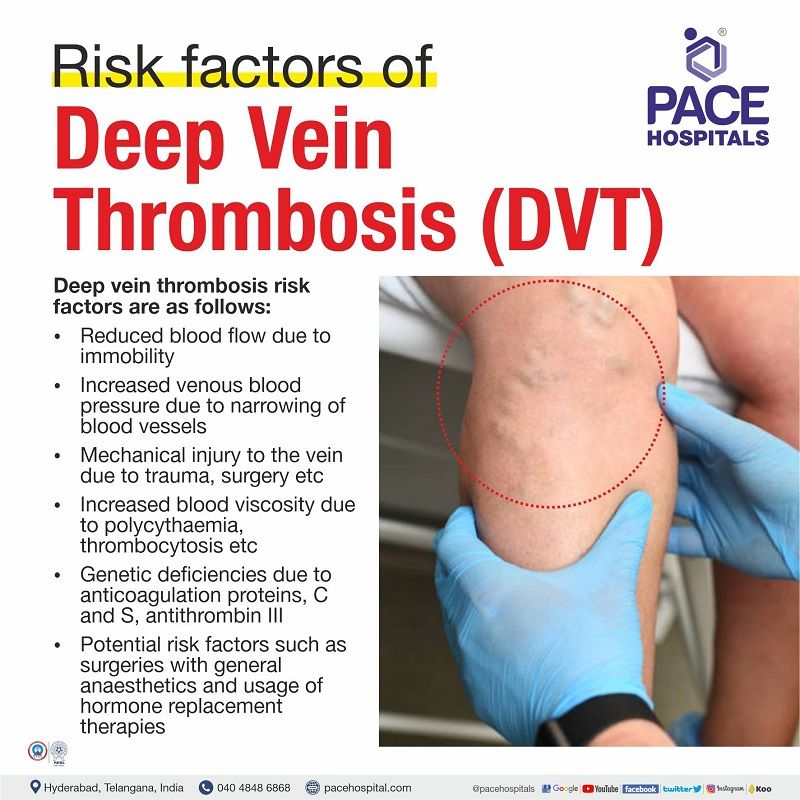
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Risk Factors
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) risk factors are classified as follows:
- General risk factors
- Risk factors associated with coagulation
- Constitutional risk factors
- Potential risk factors
General risk factors
- Reduced blood flow due to immobility because of Operations, General anaesthesia, Bed rests, Stroke or Long flights
- Increased venous blood pressure due to mechanical compression and functional impairment because of Stenosis (narrowing or constriction of the passage), Congenital anomaly (abnormal foetal changes) or Neoplasm (abnormal growth of the tissue) or Pregnancy
- Mechanical injury to the vein due to Peripherally inserted venous catheters, Trauma (injury), Surgery, Previous DVT disease or Intravenous drug abuse
- Increased blood viscosity due to Polycythaemia rubra vera (bone marrow produces too many blood cells), Thrombocytosis (producing too many platelets by the body) or Dehydration
- Anatomic changes in the veins may lead to thrombosis.
Risk factors associated with coagulation
- Genetic deficiencies due to Anticoagulation proteins C and S (glycoproteins responsible for clotting), Deficiency of Antithrombin III (clotting factor) or Factor V Leiden mutation (clotting factor)
- Acquired risks due to Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), Systemic lupus erythematosus (autoimmune inflammatory disease), Altered lupus anticoagulant (immunoglobulins), Inflammatory bowel disease (digestive tract inflammation), Nephrotic syndrome (too much protein excreted by the kidney), Cancer, Sepsis (life-threatening infection), Myocardial infarction (heart attack), Heart failure, Hypertension, Diabetes, Burns, Oral oestrogens, Smoking
Constitutional risk factors: Surgery, Critical care admission, Dehydration, Cancer, Obesity, Pregnancy, Age greater than 60
Potential risk factors: Surgery with general anaesthetics, Hospitalisation, Caesarean section (birth procedure of baby through womb), Hormone replacement therapy, Pregnancy and peripartum period (shortly before or during, or immediately after the birth), Lower extremity injury with limited mobility for more than 72 hours
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Complications
Deep vein thrombosis complications are as follows:
- Bleeding from the use of anticoagulants
- Pulmonary embolism (arteries in the lungs become blocked)
- Post-thrombotic syndrome
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Stages
The following categories describe the disease's severity:
- Provoked: As a result of acquired conditions (such as cancer, oral contraceptives, trauma, immobility, and obesity)
- Unprovoked: Due to endogenous or idiopathic (unknown) causes, there is a higher risk of recurrence if anticoagulation discontinues.
- Proximal: Over the knee, impacting the iliofemoral or femoral veins; far more prone to cause consequences such as pulmonary emboli.
- Distal: below the knee.
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Prognosis
Many DVTs will clear up without any problems.
- Two years after a DVT, 43% of patients had post-thrombotic syndrome (mild: 30%; moderate:10%; severe: 3%).
- DVT recurrence is highly probable (up to 25%).
- About 6% of DVT cases and 12% of pulmonary embolism (PE) cases end in death within a month of diagnosis.
- Early death after venous thromboembolism significantly correlates with advanced age, malignancy, underlying cardiovascular disease, and pulmonary embolism presentation.
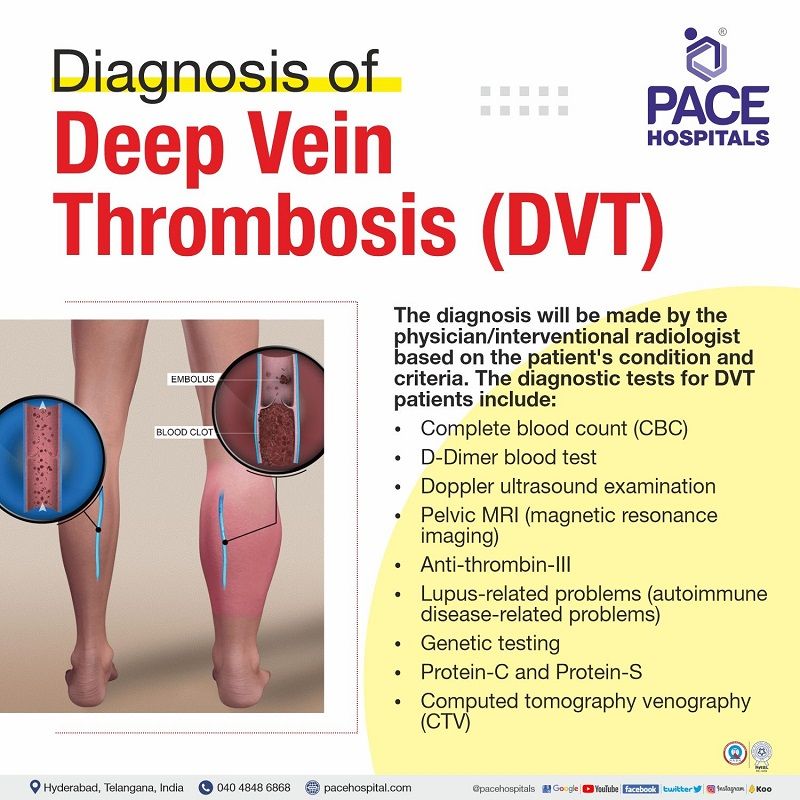
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Diagnosis
Whenever the patient visits the hospital, the interventional radiologist usually takes the patient's history and symptoms and then suggests an ultrasound exam within 24 hours.
The physician/interventional radiologist does a physical exam to know which symptoms were probably causing the DVT disease.
Physical examination
- Limb oedema may be unilateral or bilateral if the thrombus moves to the pelvic veins.
- Having dilated veins with red and hot skin.
- Tenderness (difficult to touch due to pain).
The physician/interventional radiologist takes the history regarding.
- Pain (usually seen in 50% of patients)
- Redness
- Swelling (usually seen in 70% of patients)
The diagnosis and vascular testing include
- Doppler's ultrasound exam
- Pelvic MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- D-dimer blood test (deep vein thrombosis test)
- Genetic testing
- Levels of protein C and protein S
- Antithrombin III levels
- Lupus-related problems
Deep Vein Thrombosis - DVT Treatment
The first line of treatment for DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) includes:
- Blood thinning agents
- Direct oral anticoagulants
- Ⅹa inhibitors
In rare cases, physician/interventional radiologist suggest surgeries in addition to the first-line treatment. The surgery procedures used to treat deep vein thrombosis are:
- Endovascular procedures
- Stenting
- Vena cava filter placement
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support
DVT Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Deep vein thrombosis prevention includes the following measures, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Keep moving; regular walks can help
- DVT disease is more common if dehydrated, drinking plenty of fluids is recommendable
- Stay motionless for a short time; get up and walk about every hour or so
- Avoid crossing legs while sitting
- Avoid smoking
- Don't consume alcohol; alcohol should be avoided
Deep vein thrombosis post-surgery precautions:
- When seated, keep the affected leg upwards
- Delay taking any long trips or flights for at least two weeks after you begin taking blood thinners
- If there is a must and should stay in bed for a long time, healthcare workers suggest rotating the ankles and toes in an upward and downward direction so that blood circulation will be done freely
- Using elastic or compression socks (DVT socks) improves blood circulation
- Continue the medications as prescribed by the doctor to prevent further complications
- In case of emergency or urgency, seek medical attention immediately
- Maintain regular follow-ups or appointments
Difference between DVT and Varicose Veins
Deep vein thrombosis vs varicose veins
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and varicose veins are two distinct vascular conditions that affect the veins in the body, but they have different causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
| Parameter | Varicose veins | DVT (Deep vein thrombosis) |
|---|---|---|
| Overview | In this varicose veins condition, veins are enlarged and twisted anywhere in the body but are quite common in the legs. | In DVT condition, clots are formed in the large veins, mostly in the lower limbs. |
| Causes | Increased blood pressure in the veins, Injury or damage to the veins, Being in a state of motionless for a long time | Injury or trauma to the principal veins, Inflammation or infection of the skin |
| Risk factors | Leg injury, Pregnancy, Smoking, Taking oral contraceptive pills or hormone replacement, Overweight or obesity, Older age, Being female, Being inactive | Injury, Obesity, Age greater than 60, Being motionless for a long time, Pregnancy, Dehydration, Hormone replacement therapies, Inserting venous catheters |
| Symptoms | Colour changes in the skin, Sores on the legs, Rash, A feeling of heaviness and a burning sensation in legs | Throbbing pain in legs, Swelling in one or both the legs, Swollen veins, Red or darkened skin around the infected area, Warm skin in the pain region |
| Complications | Phlebitis (inflammation or swelling of the veins), Blood clots | Pulmonary embolism, Post-thrombotic syndrome, Bleeding |
| Diagnosis | Duplex ultrasound | Complete blood count (CBC), D-dimer blood test, Doppler ultrasound exam, Pelvic MRI, Antithrombin III levels, Lupus-related problems, Genetic testing, Levels of protein C and protein S |
| Treatment | Compression stockings, Sclerotherapy, Thermal ablation, Vein stripping, Microphlebectomy | Endovascular procedures, Stenting, Vena cava filter placement, Thrombolytic agents and blood thinning agents, Direct oral anticoagulants, Ⅹa inhibitors |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles