Kidney Biopsy : Indications, Preparation and Procedure
Pace Hospitals
Indications for kidney biopsy
- Blood in the urine (called haematuria)
- Protein in the urine (called proteinuria)
- Problems with kidney function (if the kidneys function declines slowly or suddenly and the cause is not clear)
Uses of kidney biopsy
- Diagnosing a kidney problem which cannot be identified by any other way
- Helps is developing treatment plan
- Determines the extent of kidney damage
- Can tell us how well the treatment is working
- Can tell us if any treatment is going to work or not based on the damage already occurred
Preparation for kidney biopsy
- Adequate blood pressure control in patients who are already hypertensive preferably below 140/90mmHg
- Blood tests are done to check if the patient has adequate haemoglobin and clotting capacity
- Tests done are- complete blood count, PT-INR, APTT, Bleeding and clotting time
- Urine tests are done to rule out any infection
- Ultrasound kidneys to see if the kidneys are in normal position and size of kidneys are checked
- Medications are reviewed to see if the patient is on blood thinners like Aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, heparin etc
- Blood thinners like aspirin and clopidogrel are stopped 7 days before procedure
Procedure for kidney biopsy
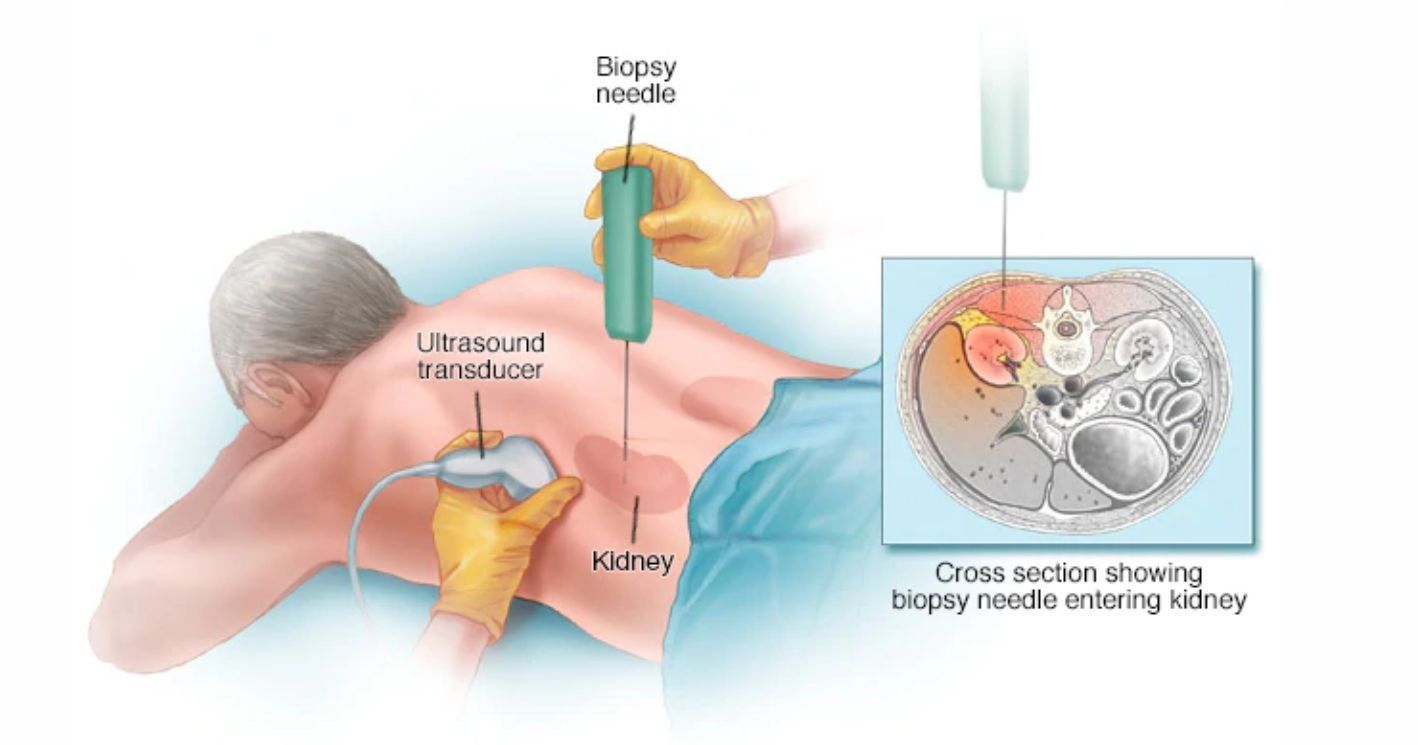
- Using an ultrasound machine probe, size of the kidneys and position of the kidneys are assessed first and then a site is identified to insert the kidney biopsy needle
- Skin over the back where the site of entry is marked is cleaned with antiseptic
- A local anaesthetic medication is injected with a syringe with needle at the site of entry to numb the area
- Using the ultrasound probe as a guide, a biopsy needle (a spring-loaded instrument) is inserted and sample of kidney is collected
- Patient is asked to hold the breath while collecting the sample and patient hears a pop sound or sharp clicking sound or feel some pressure
- Biopsy needle maybe inserted few times to get adequate sample
- Once the procedure is completed a bandage is placed over the biopsy site
Post procedure care
Contraindications of kidney biopsy
- Skin infection over site of needle insertion
- Infection of kidney (pyelonephritis)
- Uncontrolled hypertension (systolic BP > 140 mmHg)
- Small hyperechoic kidneys (suggestive of advanced irreversible chronic kidney disease)
- Patients with increased bleeding risk
- Low platelet counts, elevated INR
- On blood thinners and anti-blood clotting medications (need to be stopped before procedure)
- Horse shoe kidney
- Multiple cysts in kidneys
- Hydronephrosis (obstruction to urine outflow from kidney)
Possible complications of kidney biopsy
- Bleeding is the most common complication of renal biopsy.
- Many people may notice blood in their urine after biopsy which resolves spontaneously
- Some times blood may clot in urinary bladder and requires Foleys catheter insertion to clear the clot
- Severe bleeding into the kidney or urine requiring blood transfusion is uncommon
- Very rarely, it may become life threatening and possibly require a procedure or surgery to stop the bleeding.
- Pain can occur after a renal biopsy
- Pain generally responds to pain killers and resolves
- The biopsy needle can rarely injure the walls of a nearby artery and vein, and this can lead to the development of a fistula (a connection between the two blood vessels).
- These are benign and generally intervened only when they cause bleeding which is persistent, resistant hypertension and heart failure or kidney dysfunction
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868