Successful Staged PTCA with Drug-Eluting Stent Placement in 71-Y.O Man with CAD
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals’ expert cardiology team successfully performed a
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA)
to the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, followed by a staged PTCA to the right coronary artery (RCA) with the placement of a drug-eluting stent (Boston Scientific) in a 71-year-old male patient who presented with complaints of anginal chest pain and shortness of breath at rest. The procedure effectively restored coronary blood flow, relieved his symptoms, and is expected to improve his cardiac function while reducing the risk of future cardiac events.
Chief Complaints
A 71-year-old male patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 22 presented to the cardiology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with complaints of anginal chest pain and shortness of breath at rest.
Past Medical History
The patient had a history of diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Additionally, there was no known history of food or drug allergies.
On Examination
On clinical examination, the patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented. He appeared dyspneic at rest, exhibiting use of accessory muscles and reduced oxygen saturation. Cardiovascular examination revealed a normal heart rate. Jugular venous distension, mild pedal edema, and bilateral basal crepitations were present. These findings indicated severe left ventricular dysfunction with acute decompensated heart failure, and the nature of his symptoms raised concern, prompting further clinical evaluation.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the cardiology team, which included a detailed review of his medical history and a comprehensive clinical examination. Given his history of anginal chest pain and shortness of breath at rest, there was a strong clinical suspicion of significant coronary artery disease (CAD) with possible left ventricular dysfunction.
The patient underwent a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation to assess cardiac status. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed normal sinus rhythm. Two-dimensional echocardiography revealed severe left ventricular dysfunction. Coronary angiography confirmed critical stenosis in both the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the right coronary artery (RCA).
Based on the confirmed findings, the patient was advised to undergo
Coronary Artery Disease Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Cardiology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with Dr. Seshi Vardhan Janjirala, Interventional Cardiologist, and cross consultation with Dr. Tripti Sharma, Endocrinologist, a comprehensive evaluation was conducted. The focus was on assessing the patient’s cardiac condition in the context of his diabetes and metabolic status. Clinical and diagnostic findings confirmed significant coronary artery disease involving the LAD and RCA.
It was determined that the patient had coronary artery disease and severe LV dysfunction. Staged percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) first to the LAD, followed by PTCA to the RCA was identified as the most effective treatment to relieve symptoms, reduce the risk of further cardiac complications, and improve cardiac function.
The patient and his family were informed about his diagnosis, the planned procedures, associated risks, and the expected benefits to preserve heart function and enhance his overall prognosis.
Surgical Procedure
Following diagnosis, the patient was scheduled for a Staged Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) Procedure in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals. The treatment plan included initial PTCA to the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, followed by a second-stage PTCA with drug-eluting stent placement in the right coronary artery (RCA), under the supervision of the Cardiology Department. This approach ensured timely intervention and optimal revascularization.
- Pre-procedure Preparation: The patient was admitted to the catheterization lab after obtaining informed consent. He was positioned supine, and standard sterile precautions were maintained. Local anesthesia was administered at the vascular access site.
- Vascular Access: Vascular access was secured through the right femoral artery using the Seldinger technique. An introducer sheath was inserted to facilitate catheter passage.
- Coronary Angiography: A diagnostic coronary angiogram was first performed using a Judkins catheter. The angiogram revealed significant stenosis in both the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the right coronary artery (RCA), confirming the need for staged percutaneous coronary intervention.
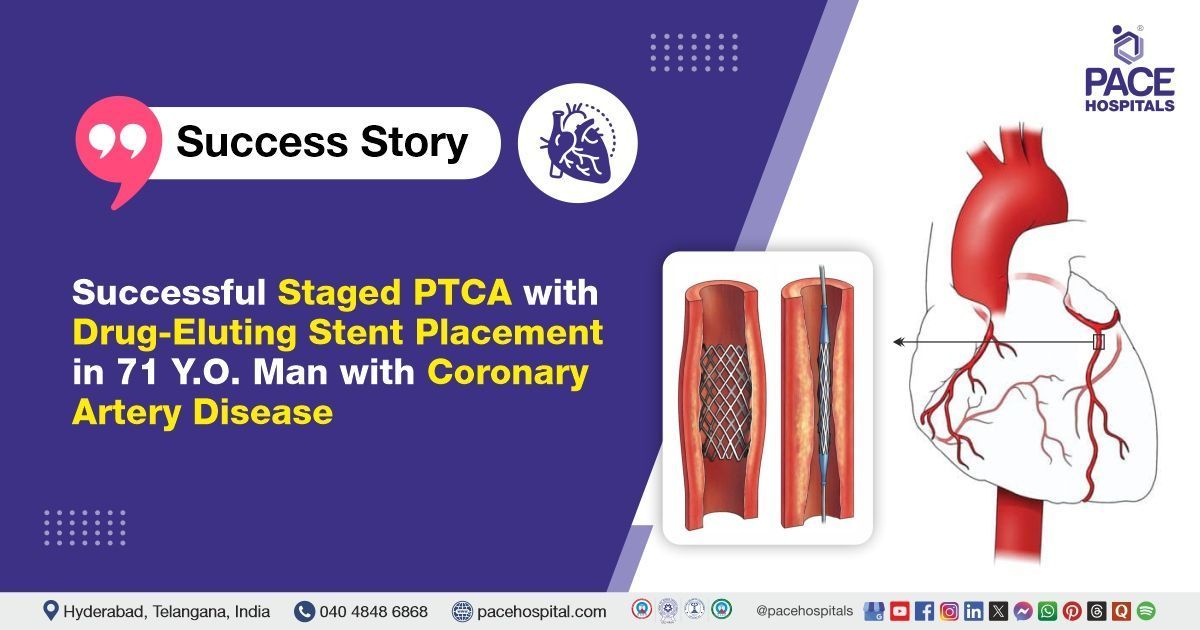
- PTCA to LAD (Initial Procedure): In the first stage, a guiding catheter was advanced to the left coronary system. A guidewire was passed across the stenotic segment of the LAD. Balloon pre-dilatation was performed, followed by the deployment of a drug-eluting stent. Post-dilatation was carried out to ensure optimal stent expansion. Final angiographic views confirmed good stent positioning with TIMI 3 flow restoration.
- Monitoring and Stabilization: Following the LAD intervention, the patient was monitored in the cardiac intensive care unit. He later developed sudden shortness of breath due to flash pulmonary edema, which was managed promptly with diuretics, oxygen therapy, and guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) in the MICU.
- Staged PTCA to RCA (Second Procedure): Once stabilized, the patient was scheduled for the second stage of revascularization. The RCA was engaged with a guiding catheter. A guidewire was navigated across the RCA lesion. Balloon angioplasty was performed, followed by the deployment of a drug-eluting stent (DES) from Boston Scientific. Post-dilatation was done to optimize stent expansion, and the final angiogram confirmed successful revascularization with no residual stenosis and good distal flow.
Completion
Hemostasis was achieved using manual compression. The patient was closely monitored in the MICU for any post-procedural complications. Dual antiplatelet therapy and other cardiac medications were continued as per protocol.
Postoperative Care
The procedure and post-procedure course were uneventful. The patient was managed with antidiabetic medication to achieve optimal glycemic control, while statins were prescribed to manage
cholesterol and reduce cardiovascular risk. Dual antiplatelet therapy was initiated to prevent thrombosis and in-stent restenosis, and other supportive therapy was given. After a stable recovery, the patient was discharged in a stable condition with detailed medical instructions for ongoing care and scheduled follow-up appointments.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed medications including antiplatelets to prevent clot formation, beta-blockers, and heart rate reducers to support cardiac function, and antihypertensives with diuretics to control blood pressure and fluid retention. Antidiabetic agents were continued for glycemic control, along with a statin for cholesterol management and an anti-inflammatory for cardiovascular protection. A gastric acid suppressant was also included to prevent gastrointestinal side effects. A strict heart-healthy diet was advised to support recovery.
Dietary Advice
The patient was advised to follow a strict cardiac-friendly and diabetic appropriate diet to support long-term heart health and recovery.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as chest pain, abdominal pain, and fever.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after 2 weeks with the cardiologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, to review his condition.
Conclusion
This case demonstrates the effectiveness of Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) in restoring coronary blood flow, stabilizing cardiac function, and preventing complications in a high-risk patient, highlighting the importance of timely intervention and multidisciplinary care.
Holistic Care Strategies for Geriatric Cardiac Patients
Holistic support for geriatric patients encompasses much more than just treating their cardiac condition. An experienced
cardiologist / heart specialist considers psychosocial factors like emotional well-being and social support, which are crucial for recovery in elderly individuals. Nutritional counselling tailored to the unique needs of older adults helps optimize healing and promote long-term heart health. Additionally, assessment and support of functional abilities—including mobility and daily self-care—are essential for maintaining independence. By adopting this geriatric-focused, multidisciplinary approach, heart specialists can improve immediate recovery, enhance overall quality of life, and help prevent future health complications in elderly cardiac patients.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868