Uterine Fibroids - Symptoms, Causes, Complications and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
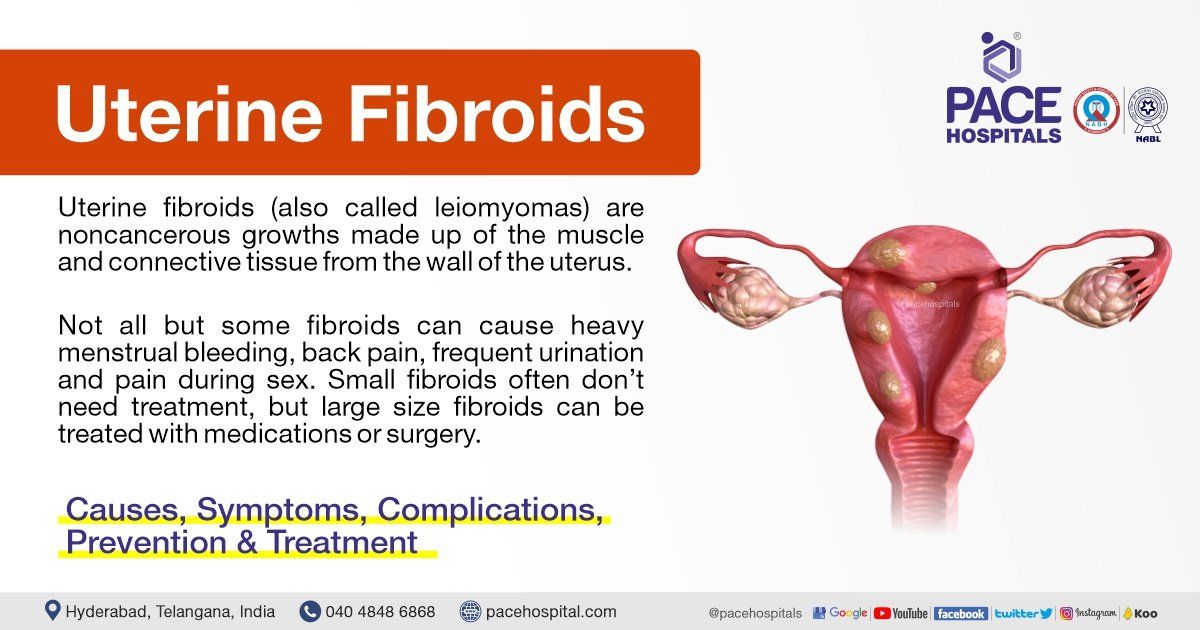
Non-cancerous growths (lumps of muscle mass) which grow from the muscle tissue of the uterus are called as uterine fibroids or leiomyomas or myomas. The precise cause of uterine fibroids is still uncertain but these are one of the most common types of growth found in a woman's uterus.
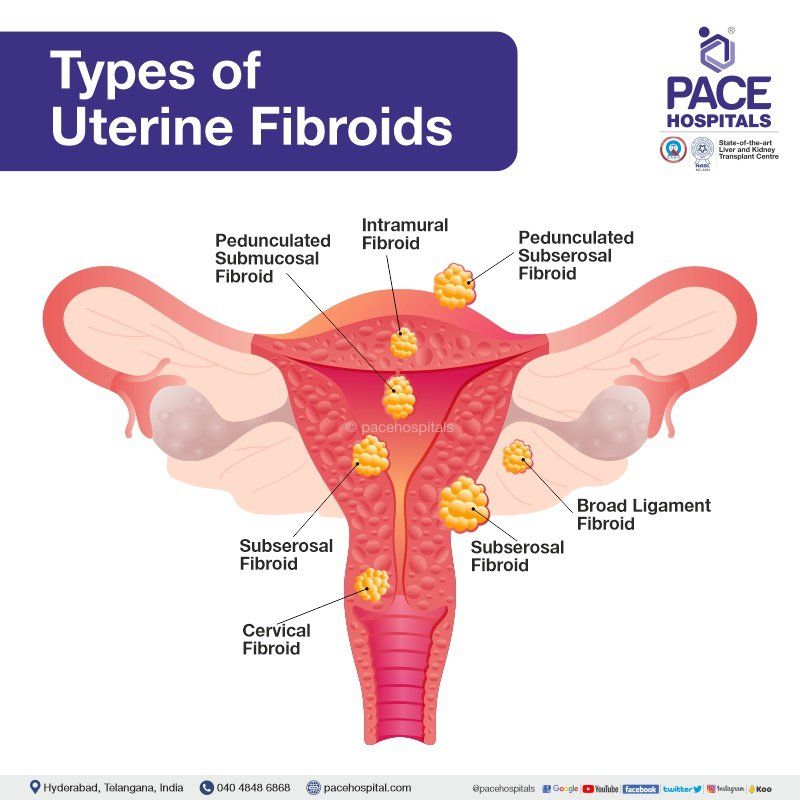
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Uterus is a pear-shaped organ which is situated in between the bladder and the rectum. Uterus is divided into three layers - (outer, middle and inner layer). Uterine fibroids can grow from any of these layers. There are six types of uterine fibroids, classified based on its location:
- Intramural fibroids
- Subserosal fibroids
- Submucosal fibroids
- Pedunculated fibroids
- Cervical fibroids
- Broad ligament fibroids
1. Intramural fibroids
Intramural fibroids are the benign growths and the most common type of uterine fibroid. These grow within the muscles of the uterus wall. It further classified based on the growth location:
- Anterior intramural fibroids - If the growth is seen within the front muscle wall of the uterus.
- Posterior intramural fibroids - If the growth is seen within the back muscle wall of the uterus.
- Fundal intramural fibroids - If the growth is seen within the top muscle wall of the uterus.
2. Subserosal fibroids
Subserosal fibroids are the benign growths and grow on the outer muscles of the uterus wall. These are also the common type of uterine fibroids. It can grow bigger as a single growth or multiple small growth and typically can cause severe pelvic pain.
3. Submucosal fibroids
Submucosal fibroids are the benign growths of the uterus and commonly seen during reproductive age of women. It grows into the uterine cavity, situated directly below the uterine inner lining. Typically, these are the least common type of uterine fibroids but can cause severe symptoms such as prolonged and heavy menstrual bleeding during or between periods, pelvic pain or lower back pain.
4. Pedunculated fibroids
Pedunculated fibroids are benign growths of the uterus. These fibroids are a stalk-like growth and a narrowed connection to the uterine wall. These can grow both outside and inside the uterus. It further classified based on the growth location:
- Pedunculated Submucosal fibroids - a stalk-like growth on the outer muscles of the uterus wall
- Pedunculated Subserosal fibroids
- a stalk-like growth into the uterine cavity, situated directly below the uterine inner lining
5. Cervical fibroids
Cervical fibroids are benign growths of the uterus. It develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. These are the rare type of uterine fibroids but can cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding during or between periods in the form of large blood clots, anaemia, pain in the pelvic area or lower back pain, frequent urination.
6. Broad ligament fibroids
Broad ligament fibroids are a benign muscle growth which develop from the broad ligament hormone-sensitive smooth muscle or the uterine smooth muscle. Typically, Broad ligament fibroid is the rare type of uterine fibroids but can cause symptoms such as chronic pain in the pelvic area, the bladder compression, and bowel dysfunction.
Smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts grow abnormally and form fibroids. Fibroids can spread superficially from the pelvis into the lower abdomen and, in a few cases, into the upper abdomen. As an alternative, they can protrude from the myometrium and enter the uterus.
It can occasionally be challenging to tell if a uterine mass is a common fibroid or a cancerous tumour, despite the fact that these fibroids are not cancerous and have very low probability of turning into one. The fibroids can range in size from the size of a pea to that of a melon. Even though uterine fibroids are usually not dangerous, they can be painful and occasionally lead to problems, such as a drop in red blood cells (anaemia), which causes tiredness because of considerable blood loss. Rarely is a transfusion necessary after blood loss.
Prevalence of Uterine Fibroids
Nearly 20-80% of females will develop fibroids by the time they become 50 years of age. The majority of women with fibroids are usually in their 40s and early 50s. Not all fibroid affected women experience symptoms. It might be difficult to deal with fibroids for those who do experience symptoms.
According to reports, 24% of Indians in cities and 37.65% of people in rural areas develop fibroids. More than ten lakhs / year incidents of uterine fibroids are seen in India. Its incidence is as follows:
| Age group | 15-25 year | 26-35 year | 36-45 years | > 45 years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence | 0.8% | 21.6% | 33.9% | 43.6% |
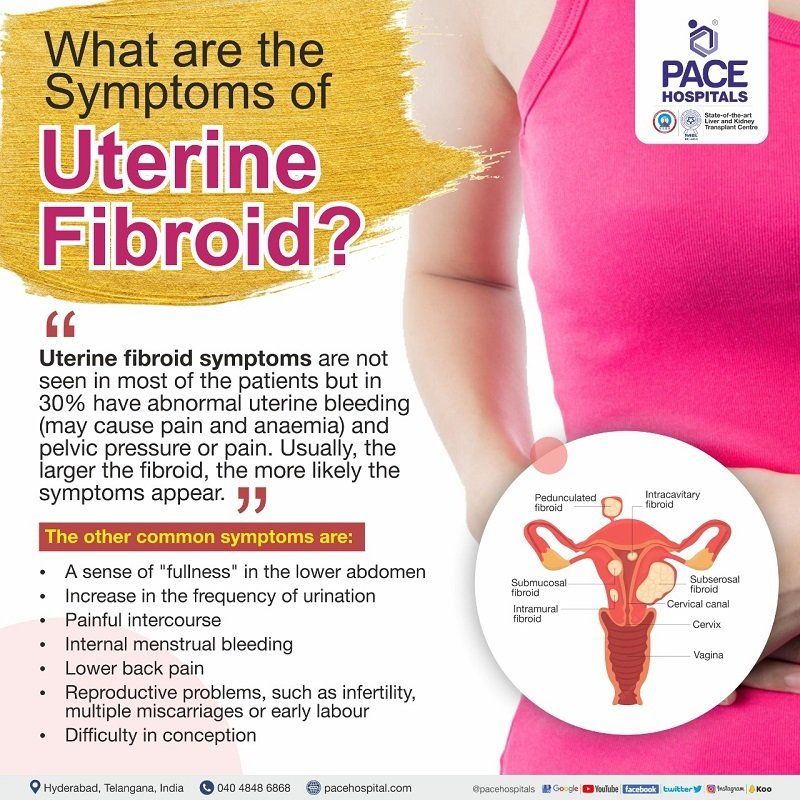
Signs and Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
The symptoms of uterine fibroids do not appear in most of the patients (asymptomatic) but usually the symptoms of the uterine fibroids include the following:
- Prolonged or heavy menstrual flow (menorrhagia) is the most common symptom
- Pelvic pressure or pain sensation – which could be suspected as large fibroids
- Pelvic discomfort or low back pain
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Urine symptoms such as urine frequency, urine urgency, urine retention
- Constipation (difficulty in emptying the bowels, usually associated with hardened stools)
- Increase in pregnancy complications such as recurrent miscarriage, premature labour, foetal malpresentation, labour complications including caesarean delivery and placental abruption
- Infertility
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
The exact causes of uterine fibroids are not known. Mostly fibroids develop in women at reproductive age, typically these are not observed in young female population who haven’t had their first menstrual period (Menarche). Based on the research and clinical data, there are some of the factors that can cause uterine fibroids to develop, such as:
- Imbalance of the estrogen and progesterone hormones
- Gene Changes (Genetic mutations)
- Other insulin-like growth factors
- Increased extracellular matrix (ECM)
Risk Factors for Uterine Fibroids
There are several factors that may affect a woman’s risk for developing uterine fibroids, that includes
- Obesity
- Early menarche (the first occurrence of menstruation)
- Nulliparity (females in whom there has been no event of pregnancy yet)
- Vitamin D deficiency (hypovitaminosis D)
- A delayed onset of menopause
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Uterine fibroids in family
Most significant risk indicators promote exposure to higher amounts of endogenous oestrogen

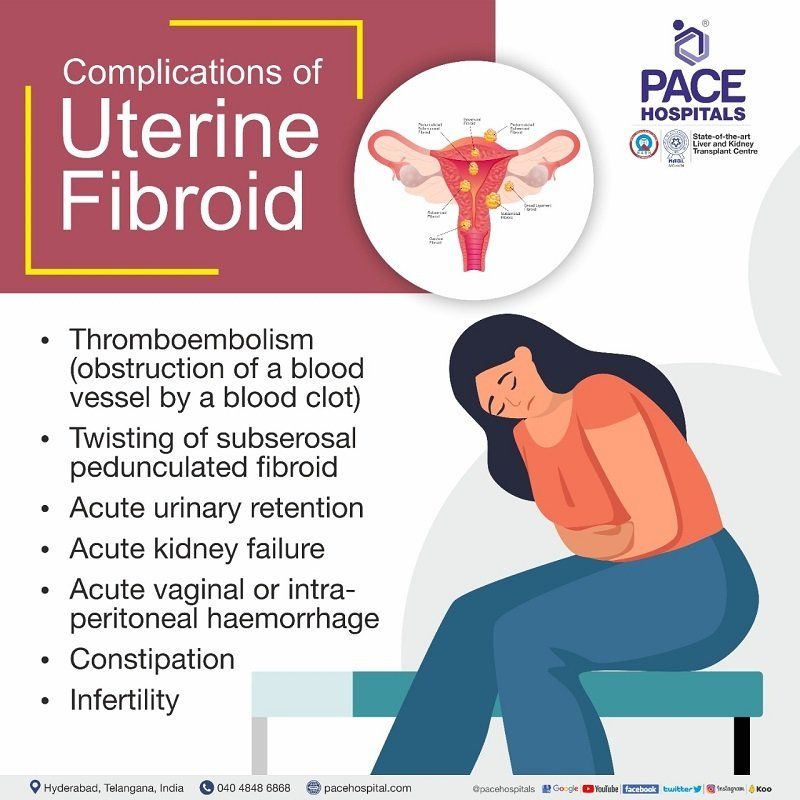
Complications of Uterine Fibroids
Although fibroids are the most prevalent tumour in women of childbearing age, acute problems from them are quite infrequent. However, when they do happen, the acute complications can have a considerable negative impact on a woman's quality of life by causing significant morbidity and, very rarely, mortality. These are the possible complications of fibroids:
- Thromboembolism (obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot)
- Constipation (difficult bowel movements)
- Female reproductive organs distortion (twisting or crushing the female organs)
- Impaired blood flow which can lead to pregnancy complications
- Infertility
- Red degeneration during pregnancy (torsion or twisting of fibroid)
Red degeneration (a hemorrhagic infarction of the uterine leiomyoma) during pregnancy is one of the severe complications, in which the subserosal pedunculated fibroid is twisted due to which further complications can arise such as:
- Acute urinary retention (difficulty in urinating)
- Acute renal failure (kidney failure)
- Acute vaginal or intra-peritoneal haemorrhage (internal bleeding at vagina)
- Mesenteric vein thrombosis (clot in the vein)
- Intestinal gangrene (obstructed blood circulation resulting in death of intestine)
Large, bulky anterior fibroids usually cause pelvic pressure and bladder symptoms, while the posterior fibroids can lead to constipation.
The adverse effects of uterine fibroids on fertility are greatly influenced by the location of the fibroid, its capacity in distorting the adnexal anatomy (the ovaries, fallopian tubes and ligaments securing female reproductive organs) and normal uterine, thus blocking the transport of spermatozoa, embryo implantation, and/or the maintenance of early pregnancy.
Impaired blood flow leading to chronic inflammation is yet another complication which can be caused by fibroids which in turn changes the endometrial receiving capacity thereby manifesting a hostile environment for intrauterine pregnancy.
During a normal pelvic exam, fibroids may be detected for the first time. Nevertheless, there are several tests which could accurately reveal further details of the fibroids. Gynaecologist may perform some of the below diagnostic procedure to know the type of fibroids before starting treatment:
- Blood tests
- Radiology examination (Ultrasound abdomen and pelvis, Transvaginal ultrasonography)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Hysteroscopy
- Hysterosalpingography
- Sonohysterography
- Laparoscopy
Prevention of Uterine Fibroids
As such there are no precisely identifiable causes of uterine fibroids, there are no exact prevention factors. Nevertheless, medical research displayed various steps in the prevention of uterine fibroids.
- A study demonstrated the correlation between the high-sugar diets with the increase of risk in some women.
- Fresh produce including broccoli, arugula, cabbage, cauliflower, and turnips may minimise the risk, according to a different study. These veggies are rich in beta-carotene, foliate, fibre, vitamins C, E, and K, as well as other nutrients and minerals.
- Uterine fibroids are less likely when regular exercise is accompanied with a stress-free lifestyle.
- Supplements such as iron, and magnesium all aid in its prevention.

In most cases, the treatment of uterine fibroid is not necessary if the symptoms are mild. Treatment is usually surgical. Pharmacological (medicine related) options are usually prescribed in case the patients want to postpone the surgery.
Medications used to treat symptoms such as abdominal pain and bleeding include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Antifibrinolytics
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) medications
- Vitamin and iron supplements
- Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD)
The surgical options for uterine fibroids include:
- Uterine artery embolization
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy
- Endometrial ablation
- Myolysis
- Myomectomy - Open, Laparoscopic or Robotic
- Abdominal Myomectomy or Laparotomy
- Total Hysterectomy - Open, Laparoscopic or Robotic
Frequently Asked Questions on Uterine Fibroids
Do fibroids eventually go away over the period of time?
Although there are some fibroids which continue to develop over the course of the reproductive years, others don't change size for many years. Post menopause, all the fibroids would usually stop expanding. Women with enlarging fibroids even after menopause should see a doctor for a diagnosis.
What types of fibroids can cause abortions?
All types of fibroids, particularly submucosal fibroids can cause abortions.
What are the other uterine diseases which are confused with fibroids?
There are various other conditions which can be mistaken for fibroids as they share the same symptoms majorly.
- Adenomyosis (the endometrium grows into the uterine wall)
- Endometriosis (inflammation of the endometrium which is the inner lining of the uterus),
- Leiomyosarcoma (a type of rare cancer that grows in the wall of uterine muscles),
- Endometrial carcinoma (cancer which originates in endometrium)
Does the condition of uterine fibroids cause thickening of endometrium?
Yes, the condition of uterine fibroids is one among the various conditions which trigger the thickening of endometrium. Thicker endometrium could cause the following ailments:
- breakthrough bleeding between periods
- extremely painful periods
- difficulty in getting pregnant
- menstrual cycles that are shorter than 24 days or longer than 38 days
- heavy bleeding during your period
Are uterine polyps and fibroids the same thing?
No, they are not the same. The prime difference between fibroids and polyps lies in the tissue they are made of - whereas fibroids are made of muscle cells and connective tissue, polyps are from the endometrial tissue which lines the uterus. The uterine polyps are more dangerous as they lead to serious health issues such as cancer, abnormal menstrual cycle, vaginal bleeding and bladder issues.
Can polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) cause uterine fibroids?
According to study which analysed 23,000 pre-menopausal African American women demonstrated that women suffering with PCOS had a 65% greater prevalence of fibroids than women without PCOS.
Can uterine fibroids cause pregnancy symptoms?
No, the symptoms of uterine fibroids and pregnancy do not majorly overlap.
How fast uterine fibroids can grow?
The median growth rate of fibroids is about 7% per 3 months which is nearly 1mm per month.
What is a calcified uterine fibroid?
As uterine fibroid enlarges in size, they outgrow blood supply triggering various degenerative changes and calcium deposition is once such rare degeneration. It is mainly seen in women from postmenopausal age group. Impaired blood supply in a fibroid causes these degenerative changes.
What causes uterine fibroids to grow after menopause?
Usually, regression of uterine fibroids is seen during the menopause phase accounting to the lack of oestrogen stimulation. However, it has been suggested that various factors can at times stimulate the growth of uterine fibroids at postmenopausal age group. This is more pronounced in obese postmenopausal woman.
How can fibroids affect pregnancy?
Uterine fibroids do not usually affect fertility but can cause complications during pregnancy, including miscarriage and postpartum haemorrhage. Fibroids may also interfere with a baby’s development, cause malpresentation of the foetus, and also cause difficulties during delivery, such as caesarean section.
Can uterine fibroids be a problem after menopause?
Uterine fibroids during menopause are very rare and are often presented as abnormal uterine bleeding. Usually, uterine fibroids regress with the onset of menopause. To-date, the most effective treatment is hysterectomy, although there are other promising therapeutic options under investigation. Intra-leiomyoma hemorrhage is one of the most common complications which may be seen among post-menopausal suffering from uterine fibroids.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles