Brain Stroke: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Overview | Prevalence | Types | Causes | Symptoms | Risk Factors | Complications | Diagnosis | Treatment | Prevention | Brain stroke vs Paralysis | Brain aneurysm vs Stroke | FAQs | When to consult a Doctor
What is a Brain Stroke?
A brain stroke is also known as a cerebrovascular disorder as it affects the cerebro (brain) and the vascular (blood vessels) that supply blood to the brain. While the term cerebrovascular disease is relatively new, the medical conditions which are included under this term (and which are generally linked by the familiar term “stroke”) have attracted medical attention since time and memorial. Since ancient times, stroke has been recognised within a complex syndrome known as apoplexy.
Hippocrates defined apoplexy solely by its presentation: a sudden loss of consciousness, motion, and sensation, and not by any presumed common vascular aetiology, as stroke is currently defined in contemporary practice.
The term apoplexia was employed by the Greeks, to denote a disease in which the patient falls to the ground, often suddenly, and lies without sense or voluntary motion. Persons suffering from this disease were instantly affected as if they were struck by lightning. The ancient’s doctors thus termed “attoniti aut, syderati” [struck by lightning; tempest] an alternative term, “cerebrovascular accident,” which is colloquially abbreviated as “CVA,” was introduced in the much recent early-20th century.
Brain stroke definition
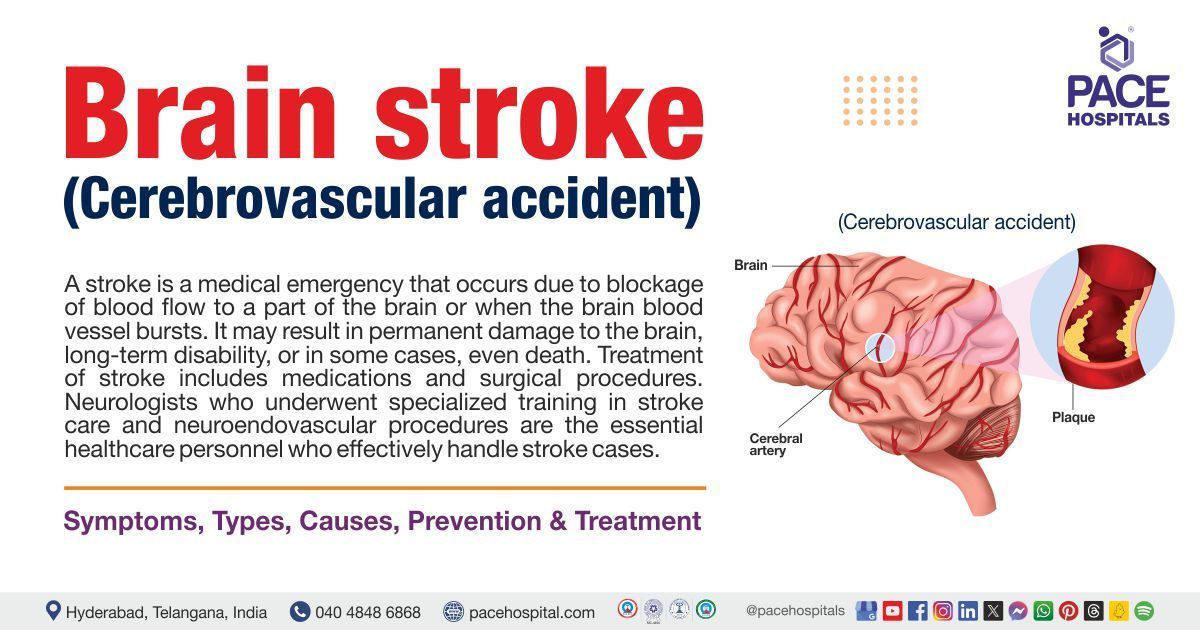
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident, is a medical emergency condition that occurs when the blood flow is blocked to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts. A stroke may result in permanent damage to the brain, long-term disability, or in some cases, even death. Treatment of stroke includes medications and surgical procedures. Neurologists who underwent specialized training in stroke care and neuroendovascular procedures are the essential healthcare personnel who effectively handle stroke cases.
One in four people may have a stroke in their lifetime. Reduced blood supply to the brain occurs mainly because of two reasons: one is a blood clot (ischemic stroke), and the other is bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke)
A constant oxygen and nutrient supply is essential for the brain to work properly and may create problems if the blood supply is interrupted, even briefly. Just a few minutes without a supply of oxygen or blood is enough to dysfunction and eventually degenerate the brain cells. In such cases, people may not effectively perform the things, controlled by the affected part of the brain.
Prevalence of Brain Stroke
Brain stroke cases in the world
Worldwide, every year, 1.5 crore people suffer from stroke. among these, 50 lakh meet their demise, while another 50 lakh are left permanently disabled. Worldwide, the second most common cause of death is stroke. Strokes are more frequent in older people compared to younger adults. Over two-thirds of all strokes occur in people more than 65 years age. Women may experience more compared to men and 60% of deaths due to stroke occur in women.
Brain stroke cases in India
From 1970-1979 to 2000-2008, more than 100% increase in the incidence of stroke cases has been recorded in low- and middle-income countries including India. A study published in 2017 calculated the cumulative incidence of stroke cases which ranged from 105-152 per lakh Indians annually, while the crude prevalence of stroke cases ranged from 44.29-559 per lakh Indians in different parts of the country from 2007 to 2016 past decade. These values were comparatively higher than those of high-income countries.

Types of Brain Stroke
Brain stroke is mainly two types.
- Ischemic stroke: It is the most common type and contributes to 80% of brain strokes.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: It contributes to 20% of brain strokes.
Ischemic stroke can be either thrombotic or embolic.
- Thrombotic stroke is the most common type of ischemic stroke. A blood clot forms inside a diseased or damaged artery in the brain resulting from atherosclerosis (cholesterol containing deposits called plaque), blocking blood flow.
- Embolic stroke is caused when a clot or small piece of plaque formed in one of the arteries leading to the brain or in the heart, is pushed through the blood stream and lodges in narrower brain arteries. The blood supply is cut off from the brain due to the clogged vessel.
Haemorrhagic stroke can be due to Intracerebral haemorrhage or Subarachnoid haemorrhage.
- Intracerebral haemorrhage is the bleeding that occurs within the brain tissue, most common cause is due to changes in the arteries caused by long-term
Hypertension.
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage is bleeding that occurs between the surface of the brain and skull. Common causes being cerebral aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation (AVM).
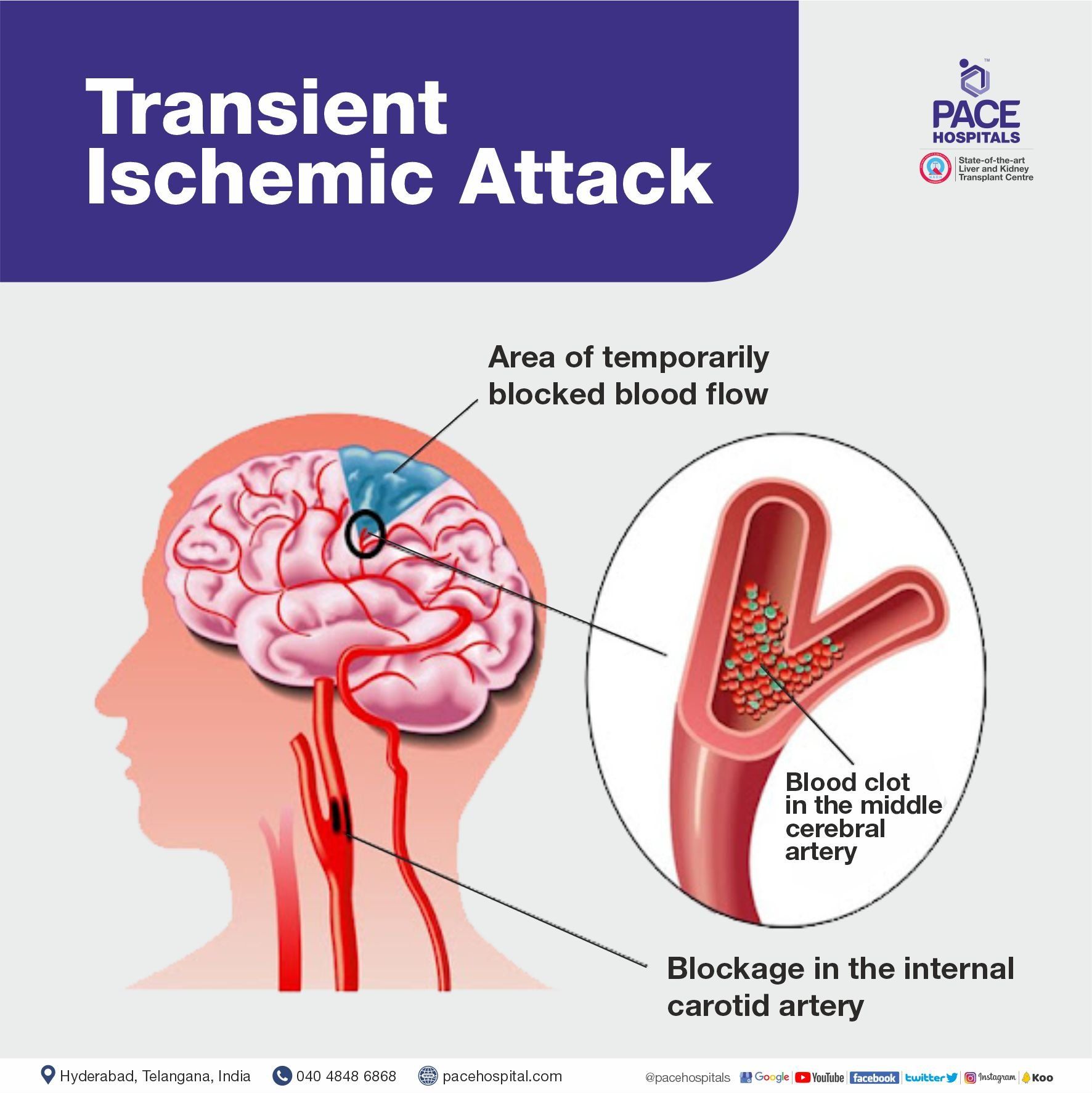
What is a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)?
Transient ischemic attack is a warning sign of a possible future stroke and is treated as a neurological emergency. Common temporary symptoms include difficulty speaking or understanding others, loss or blurring of vision in one eye and loss of strength or numbness in an arm or leg.
Usually these symptoms resolve in less than 10 to 20 minutes and almost always within one hour. Even if all the symptoms resolve, it is important that anyone experiencing these symptoms have to be immediately evaluated.
History of transient ischemic attack (TIAs): About 30 percent of strokes are preceded by one or more TIAs that can occur days, weeks or even months before a stroke.

Brain Stroke Causes
The cerebrovascular accident pathophysiology mainly includes blocked or interrupted blood flow to the brain. Physical injury to the brain can cause severe bleeding which also decreases blood flow to the brain. The other causes of brain stroke are:
- Chronic inflammation: Long-term inflammation) can damage the blood vessels and the brain cells, leading to ischemic stroke.
- Aneurysm: A balloon-like bulge in an artery that can stretch and burst can cause blood loss and, eventually, a stroke
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs): Tangles of poorly formed arteries and veins can rupture in the brain.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure puts pressure on the inner walls of the arteries and can lead to brain stroke.
- Atherosclerosis: Accumulation of plaques inside the arteries reduces blood flow causing stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation: The atrium's blood flow slows down when atrial fibrillation occurs. Blood clots may form when the blood pools, gets slow, and stagnates. A clot that escapes from the heart and makes its way to the brain has the potential to cause a stroke by obstructing the blood supply to the brain's arteries.
- Sickle cell disease: Sickled cells can stick together causing the blockage of blood vessels which may lead to brain stroke.
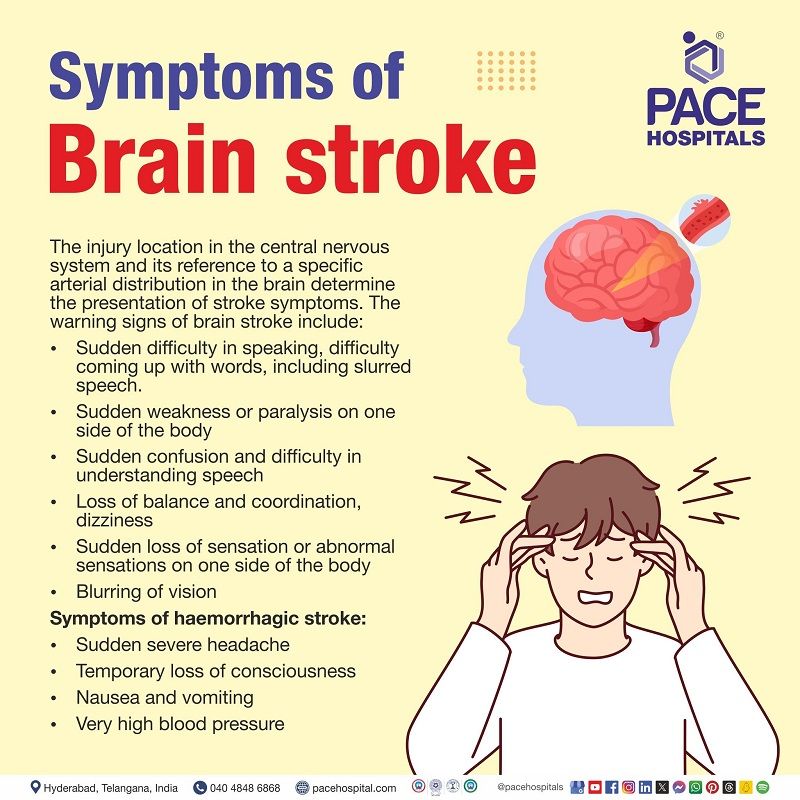
What are the Symptoms of a Brain Stroke?
The range and severity of early stroke symptoms vary considerably, but they share the common characteristic symptom of sudden onset. Common signs and symptoms of a brain stroke include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Sudden confusion
- Trouble in speaking
- Difficulty in understanding speech
- Sudden trouble in seeing with one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble in walking, dizziness
- Loss of balance or lack of coordination
- Sudden severe headache with vomiting or unconsciousness
Brain Stroke Risk Factors
Many common medical conditions can increase the chances of having a brain stroke. Some risk factors of brain stroke can be modified, known as modifiable risk factors, while others cannot be changed, called as non-modifiable risk factors.
Modifiable risk factors for stroke
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): High levels of blood pressure can lead to the damage to the arteries (blood vessels) that supply blood to the brain leading to increase in the risk of brain stroke.
- Heart diseases: People with heart disease can have increased risk of stroke occurrence.
- Diabetes (high blood sugar): Diabetes can cause pathologic changes in blood vessels at various locations, thereby increasing the risk of stroke occurrence.
- Smoking: The risk of ischemic stroke occurrence in smokers is almost doubled when compared with nonsmoking people.
- High blood cholesterol: Higher cholesterol levels can cause atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries by lipid buildup), which can decrease the blood supply to the brain.
- Excessive intake of alcohol: Having more amounts of alcohol can cause high blood pressure, leading to stroke.
- Illegal drugs: The use of illicit drugs can increase the risk of stroke.
Non-modifiable risk factors for stroke
- Age: People of all ages, including children, have strokes but older the age, the more significant the risk of stroke.
- Gender: Stroke can occur more often in men than women, but more women die from stroke.
- Family history of stroke: People with a history of stroke in their family may have higher chances of occurrence of stroke.
- Prior stroke history: People who had a stroke in the past may have a higher chance of another stroke occurrence.
- Other risk factors:
- Hyperhomocysteinemia (when homocysteine levels are greater than normal limits
(<15 micromol/L) o Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA, a disorder of frequent cessation of breathing during his or her sleep, few infections)
- Covid being in recent times, and a history of TIAs can also increase the risk of stroke.

When to call emergency?
TIME IS BRAIN. WITH A STROKE TIME LOST IS BRAIN LOST.
The estimated pace of neurons lost in acute ischemic stroke per minute is 1.9 million neurons, per hour is 120 million and per stroke around 1.2 billion cells are lost. This is the reason for early identification of stroke symptoms and early intervention to prevent long-term disability.
Act FAST at the first sign of stroke. We can use these letters F.A.S.T. to spot the signs of stroke and know when to call emergency.
F: Facial weakness
A: Arm weakness
S: Speech difficulty
T: Time to call emergency
Complications of Brain Stroke
Stroke sufferers may have difficulty speaking, swallowing, and understanding, and they may have long-term disability. Below are some of the most common complications of the brain stroke:
- Cerebral edema : Swelling of the brain.
- Seizures: Neurological disorder that may cause brief episodical unconsciousness and convulsions, during which the body shakes uncontrollably due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- Urinary tract infections (UTI) or bladder control problems: People with stroke may need a urinary catheter to collect the urine as they cannot control bladder function.
- Pneumonia: Swallowing problems can be seen in people who suffer from stroke. Food may be inhaled into the lungs, thus causing lung infection.
- Pressure ulcers: Sores on the skin may be formed due to the continuous pressure on body areas as stroke patients may not move freely or change their body position.
- Clinical depression: Mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest.
- Deep venous thrombosis (DVT): Because of the lack of movement from stroke, people may experience blood clots in the veins of the legs.
- Undernutrition and dehydration: Stroke patients may suffer from difficulty swallowing, resulting in dehydration and undernutrition.
- Contractures: Permanent shortening of muscles.
- Paralysis: Lack of movement or weakness in the limbs.
Brain Stroke Diagnosis
The nursing diagnosis for cerebrovascular accident usually includes a combination of medical history of the patient, physical examination, symptoms, and diagnostic tests. Here's an overview of the steps involved in diagnosing brain stroke:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Arterial blood gases (ABGs)
- Blood and urine culture and routine toxicology
- Imaging studies: Computed tomography (CT) scan, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),
- Other imaging tests: Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomographic angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), Doppler sonography (carotid ultrasound)
- Heart tests: Electrocardiogram (ECG), Echocardiography
- Lumbar puncture (also called a spinal tap)
Brain Stroke Treatment
Brain stroke patient requires emergency treatment. The earlier the treatment, the better the recovery of the patient from brain stroke. For successful treatment of brain stroke, rapid and correct diagnosis of the kind of stroke and the exact location of its damage are essential. The treatment for a brain stroke typically involves:
Treatment for ischemic brain stroke:
- Medicine: Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA); anticoagulant or blood thinning medicines.
- Surgical procedures:
- Angioplasty and stenting procedures,
- Thrombectomy
- Carotid endarterectomy
Treatment for haemorrhagic brain stroke:
- Medicine: Antihypertensives and IV fluids are often used to help control or minimize brain swelling.
- Surgical procedures: Aneurysm clipping, coil embolization, blood transfusion, draining excess fluid, surgery, or radiation may be used to remove or shrink an arteriovenous malformation (AVM), craniotomy surgery may be performed to temporarily remove part of the skull to reduce swelling, surgery to remove pooled blood may also be used.
Brain stroke rehabilitation: Rehabilitation plays a main role in the brain stroke recovery and includes:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy ,Speech therapy and Psychiatric therapy.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support

Brain Stroke Prevention
People may prevent stroke by maintaining healthy choices and managing any existing health conditions. The following measures help in the prevention of cerebrovascular accident:
- Taking a healthy diet: Having foods low in cholesterol, saturated fats, trans fats, and high in fiber can help prevent brain stroke.
- Regular physical activity: Generally, two and half hours of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, like brisk walk, weekly once is recommended to keep the body fit, reducing the risk of stroke.
- Avoiding alcoholism: Drinking too much alcohol can result in hypertension (increase in blood pressure), which increases the chances of stroke. Avoiding alcoholism can reduce stroke risk.
- Smoking cessation: The chance of having a stroke is less in non-smokers. Quitting smoking or avoiding second-hand smoke may reduce the occurrence of stroke in people.
- Being overweight or obese: The chance of having a stroke is higher in people who are overweight or obese.
- Controlling cholesterol: Maintaining good cholesterol levels helps reduce the occurrence of stroke.
- Controlling blood sugar and blood pressure: Maintaining regular and normal blood sugar reduces the risk of stroke. A low intake of salt can manage high blood pressure.
Brain stroke vs Paralysis
Difference between brain stroke and paralysis
Brain stroke and paralysis are often used interchangeably, but they are different medical conditions. Below are some of the parameters that differentiate brain stroke and paralysis.
| Parameters | Brain stroke | Paralysis |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Brain stroke is a medical emergency condition and occurs when the blood flow is blocked to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts. | Inability to move some or all of the body. It can be a symptom of many conditions affecting the muscles and nerves. It is a complication of brain stroke. |
| Symptoms | Sudden difficulty in speaking , Sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the body , Sudden confusion and difficulty in understanding speech , Loss of balance and coordination , Dizziness , Sudden loss of sensation , Abnormal sensations on one side of the body , Blurring of vision(dimness) | Muscle weakness , Numbness , Weakness in the face or body, Loss of sensation |
| Onset | Sudden onset and symptoms develop rapidly | Gradual onset |
| Recovery | Some people may recover fully, but others may have long-term or lifelong disabilities. | Recovery of the patients depends on the severity of nerve damage. |
Brain aneurysm vs Stroke
Both aneurysm and stroke are neurovascular disorders which may appear suddenly without warning signals, but below are some critical differences between aneurysm and stroke.
| Parameters | Aneurysm | Stroke |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Aneurysm is a weakened, ballooned area on wall of artery. | Brain stroke is a medical emergency condition and occurs when the blood flow is interrupted to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts |
| Symptoms | Sudden severe headache, Nausea and vomiting , Loss of consciousness, Loss of balance and coordination in walking , Blurred or double vision, Confusion, Drowsiness | Sudden difficulty in speaking, Sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, Sudden confusion and difficulty in understanding speech, Loss of balance and coordination, Dizziness,Sudden loss of sensation, Abnormal sensations on one side of the body and Blurring of vision(dimness) |
| Onset | Sudden onset | Sudden onset and symptoms develop rapidly |
| Recovery | Based on the size, location, and type of aneurysm | Some people may recover fully, but others may have long-term or lifelong disabilities. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Brain Stroke
Is brain stroke dangerous?
Yes, brain stroke is one of the most dangerous and life-threatening diseases. It is a medical emergency condition, and without prompt treatment, it may lead to permanent brain damage, long-term disability, or, in some cases, even death.
Can brain stroke repeat?
Yes, brain stroke can repeat. People who had a stroke in the past may have a higher chance of another stroke occurrence. Uncontrolled diabetes (increase glucose in blood), hypertension (increased blood pressure), missing the prescribed stroke medication, and smoking may cause recurrent strokes.
How does a stroke damage the brain?
A constant oxygen and nutrients supply is essential for the brain to work correctly. It can create problems if the blood supply to the brain is stopped, even temporarily.
After just a few minutes without a supply of oxygen or blood, the brain cells begin to die, and their function is lost, and people may not do the things controlled by that part of the brain.
Are brain stroke and paralysis the same?
No, brain stroke and paralysis are not the same. Paralysis (loss of muscle function in a body part) is one of the common outcomes of stroke (happens when the blood flow is blocked to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts)
How do you improve brain function after a stroke?
Brain function after a stroke is generally improved by practicing rehabilitation activities. Rehabilitation centers can include speech therapy, physical therapy, and occupational therapy as they improve cognitive function in brain-stroke patients.
What is brain stroke?
Brain stroke is a medical emergency condition and occurs when the blood flow is blocked or stopped to the part of the brain or when the brain blood vessel bursts. A stroke can result in permanent damage to the brain, long-term disability, or, in some cases, even death.
Can blood thinners cause strokes and bleeding in the brain?
Yes, blood thinners can cause bleeding in the brain more than usual. Usually, blood thinners protect from stroke and heart attacks, but they also may have the risk of bleeding. Nevertheless, the benefits of blood thinners often outweigh the risks.
What causes brain swelling after a stroke?
Cerebral oedema also known as swelling in the brain, is a serious complication of ischemic stroke, and it is caused by an increase in the intracranial pressure, leading to the worsening of the neurological symptoms.
How long does brain swelling last after a stroke?
Cerebral oedema (swelling in the brain) generally starts to develop during the initial 24 to 48 hours and reaches a maximum extent of 3 to 5 days from the occurrence of acute ischaemic stroke. Osmotherapy and osmotic diuretics has been the mainstay of pharmacologic therapy in reducing cerebral oedema.
Can a brain stroke patient recover fully?
Brain stroke patient recovery time is different from one individual to the other. Some may recover for weeks, months, or even years. Some individuals may recover fully, but some of them may suffer from long-term disabilities.
Is a brain aneurysm a stroke?
No, brain aneurysm is not a stroke; both are two different medical conditions. A stroke is caused when the blood flow is blocked or interrupted to the part of the brain (ischemic stroke) or when the brain blood vessel bursts (hemorrhagic stroke). An aneurysm is a weakened, ballooned like area on an artery wall. Nevertheless, if an aneurysm bursts and bleeds, it may be thought of as a hemorrhagic stroke.
What causes a stroke in the brain stem?
Hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes (high blood glucose), smoking, heart diseases, and atrial fibrillation (irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm) may cause stroke in the brain stem. Injury to an artery because of sudden head or neck movement is one of the rare causes of brain stem stroke.
Which side of the brain affects speech in a stroke?
In most people, the left side of the brain affects speech in a stroke because the brain's language center controls speech and language. Damage to the left side of the brain usually is the cause of communication issues after a stroke.
Is a brain bleed a type of stroke?
Yes, brain bleed is one type of stroke. Hemorrhagic strokes are caused when the blood vessel that helps supply oxygen and nutrients to the brain ruptures and bleeds, leading to pressure buildup, thus causing damage to the brain.
How do you improve brain function after a stroke?
Brain function after a stroke is generally improved by practicing rehabilitation activities. Rehabilitation centres can include speech therapy, physical therapy, and occupational therapy as they improve cognitive function in brain-stroke patients.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868