Choledochotomy Procedure Indications & Cost
PACE Hospitals stands among the
top hospitals for the Choledochotomy procedure in Hyderabad, India. Our dedicated team of surgical gastroenterologists provides expert care in removing stones and blockages from the common bile duct, helping relieve symptoms and prevent serious complications.
At PACE Hospitals, we combine modern surgical techniques with personalized care to ensure the best outcomes. With transparent pricing and state-of-the-art facilities, we remain a preferred center for both open and laparoscopic choledochotomy procedures in Hyderabad.
Book an Appointment for Choledochotomy Procedure
Choledochotomy procedure appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Choledochotomy Procedure?
Team of the Best Hepatobiliary Surgeon & Surgical Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad
Open & Laparoscopic Choledochotomy Procedures with 99.9% Success Rate
Affordable Choledochotomy Surgery with Cashless and Insurance Options
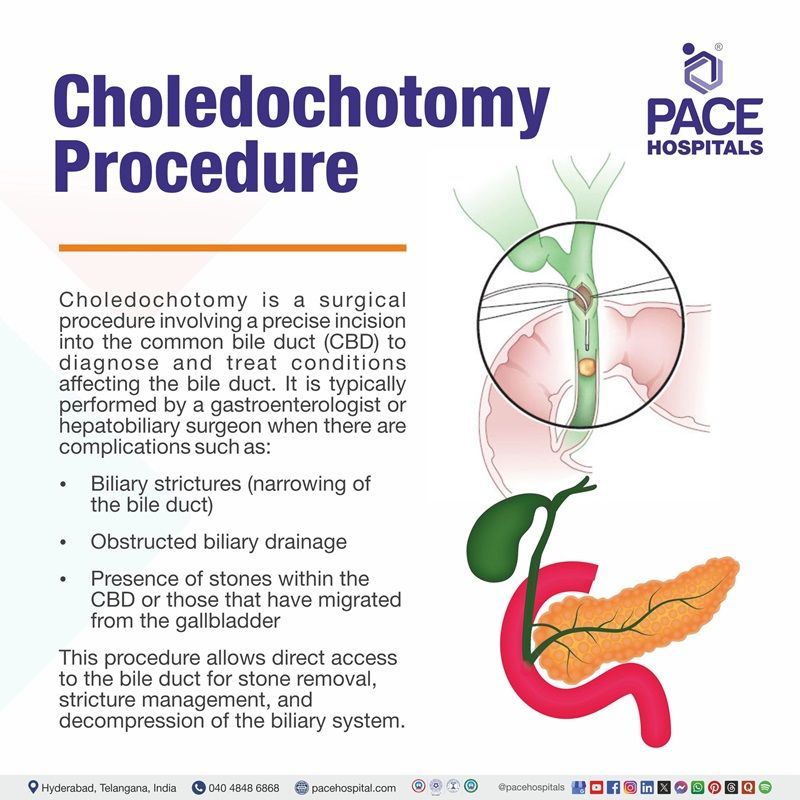
What is a Choledochotomy Procedure?
The choledochotomy procedure is a surgical incision of the common bile duct (CBD) performed by a gastroenterologist to access and address common bile duct issues, including biliary strictures (narrowing of the bile duct), biliary drainage, and removal of stones from CBD and those that migrate from the gallbladder.
Laparoscopic choledochotomy is suggested when the transcystic approach is unsuccessful or when large, multiple or stubbornly stuck stones are present in the common bile duct.
A common bile duct is a tiny tube-like structure that connects the gallbladder and liver to the small intestine. It is formed by the union of the gallbladder cystic duct and liver common hepatic duct. Common Bile duct stones usually occur when the stones move from the gallbladder into the bile duct or form within the duct, leading to duct blocking.
The stones, if untreated, led to complications such as jaundice, cholangitis, pancreatitis, and bile leaks. It is estimated that around 10% of patients who experience symptoms of gallstones also have stones in the common bile duct (CBD).
Choledochotomy meaning
Choledochotomy means surgical incision of the common bile duct.
Choledochotomy Indications
Mainly, a choledochotomy procedure is only required if there is a clear indication that the common bile duct contains stones or other blockages, which includes the following conditions:
- Choledocholithiasis: Gallstones in the common bile duct (Multiple CBD stones, more than 5 in number (>5))
- CBD stones found during cholecystectomy
- Palpable stone in hepatic bile duct
- Cholelithiasis: Gallbladder stones (small stones)
- Clinical evidence (signs, symptoms) of cholangitis (inflammation of the bile duct system, which carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine)
- Recent Jaundice (It occurs when the stones obstruct the common bile duct, and conjugated bilirubin enters the bloodstream)
- Dilation or thickening of bile ducts
- Induration (thickening and hardening of soft tissues) of the head of the pancreas
- Stones found at the intersection of the cystic duct and common bile duct
- Pain without stones in the gallbladder
- CBD stones that cannot be removed endoscopically (due to scope inaccessibility, large size, or multiple stones)
Choledochotomy Contraindications
The choledochotomy is contraindicated if the patient has any of the following conditions, that includes:
- Small bile duct (<7mm)
- Severe inflammation
- Immunosuppression / poor wound healing (bile leak risk)
- Severe reactions to general anaesthesia
- Suspect malignancy (painless jaundice, extensive weight loss, presence of mass etc)
- Multiple (9) large stones in CBD
Choledochotomy Types
Based on the technique used by the surgical gastroenterologist, the choledochotomy procedure can be classified into two types, such as:
- Open choledochotomy procedure
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Laparoscopic choledochotomy procedure
- Robotic-assisted choledochotomy procedure
Open choledochotomy procedure
Open choledochotomy is the vertical surgical incision of the common bile duct through a large cut in the patient's stomach. With the introduction of laparoscopic techniques, the requirement for open cases has decreased.
Minimally invasive procedure
Minimally invasive procedures are surgical techniques that use specialised tools and are performed through tiny incisions instead of larger incision. This procedure aims to shorten recovery time and minimise trauma to the body compared to open surgeries. The minimally invasive procedures might include laparoscopic or robotic -assisted choledochotomy.
- Laparoscopic choledochotomy procedure: Laparoscopic choledochotomy (keyhole) is a less invasive procedure, that involve placing 4 small cuts on the patient's stomach through which surgical tools and laparoscope will be inserted. Once the surgical gastroenterologist gain access to the common bile duct, the surgeon makes an incision in the patient’s common bile duct to treat the various bile duct conditions. The laparoscopic common bile duct is an advanced, minimally invasive method to perform surgery on the CBD-common bile duct, and this process provides multiple advantages such as quicker recovery, fewer complications, and better results. Laparoscopic techniques are used not only for planned surgeries, but also for emergency cases and when the endoscopic cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is not successful.
- Robotic - assisted choledochotomy : A robotic-assisted procedure involves using a robotic system to aid surgical gastroenterologists in performing the surgery. The surgical procedure involves in the robotic choledochotomy is similar to the laparoscopic choledochotomy apart from the usage of robotic arms. In some cases, using conventional laparoscopic procedures might be challenging for surgical gastroenterologists to remove the stones from the common bile duct. The "da Vinci" robotic technology helps insert a kehr drain and suture the CBD.
Surgical Gastroenterologist Considerations Before Performing Choledochotomy Procedure
Before performing the choledochotomy procedure, surgical gastroenterologists will consider the patient's overall health condition, including underlying medical conditions and medication history, and estimate the patient's risk for complications from anaesthesia and surgery. Before making any recommendations, the patient's age plays a crucial role when considering the benefits and risks of a procedure. Surgical gastroenterologists will perform imaging tests to determine the actual size and location of the obstruction/stone and choose the best surgical approach.
For all patients considered for minimally invasive procedures, the surgical gastroenterologist may evaluate the presence of stones in the common bile duct (CBD) because, in patients undergoing cholecystectomy (gall bladder removal surgery), it is estimated that 5 to 15% have been associated with choledocholithiasis (gallstones in the common bile duct), which rises with age, reaching up to 60% in elderly patients.
The surgical gastroenterologist will prefer the type of choledochotomy (open and minimally invasive) based on the patient's age, common bile duct stone location, and overall health condition. In some cases, the minimally invasive choledochotomy procedure might be changed to open when the patient is severely obese and has excessive bleeding during surgery.
Before the procedure, the surgical gastroenterologist may discuss with the patient regarding the need for additional procedures, such as cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder).
Choledochotomy Procedure
Before choledochotomy procedure
The surgical gastroenterologist will explain the entire procedure and risks of the choledochotomy surgery to the patient, and they will be provided with a consent form to sign, which gives permission to do the procedure.
The surgical gastroenterologist gives specific instructions to the patient that may include fasting before the procedure and avoiding certain medications to prevent interference with anaesthesia, surgery or recovery. For instance, during the week before surgery, the patient may be asked to stop taking blood thinners and other drugs to avoid a higher risk of bleeding during surgery.
Before the surgery, the patient's blood pressure or diabetes will be checked and well-controlled. If the bile duct has blockages, the surgical gastroenterologist might prescribe for certain procedures, that may be performed to clear the ducts prior to surgery, ensuring a smoother choledochotomy.
During the choledochotomy procedure
The surgical gastroenterologists might perform MRCP or other tests, procedures to reveal the location of several stones in the cystic duct, the common bile duct, and the hepatic duct.
General anaesthesia will be given to the patient before performing the surgery to make the patient unconscious.
Based on the patient's overall clinical condition, the surgical gastroenterologists might choose either for open choledochotomy or minimally invasive procedures (laparoscopic choledochotomy or robotic -assisted choledochotomy).
In the case of open surgery, the surgical gastroenterologist will make a large incision on the abdomen to perform the choledochotomy.
In the case of laparoscopic choledochotomy, the surgical gastroenterologist will make the 3-4 small cuts (0.5–2.5 cm long) in the abdomen.
- First, a small incision will place above the umbilicus. Then, a hollow needle will be employed (used) to insert through the abdominal wall.
- A thin tube with a light and camera called a laparoscope will insert through the umbilical port. Three small incisions will be made with care. Once placed, the laparoscope will give video images, which help the surgical gastroenterologist to locate and pull back the liver and gallbladder.
A choledoschoscope is used to examine the stones and strictures in CBD-common bile and bile ducts within the liver.
For a clear view, the choledochoscope might be inserted in the upper abdomen, above the CBD opening, which helps surgical gastroenterologists prevent excessive bending or angling during the examination.
After acquiring the critical view, the cystic artery (that carries oxygenated blood to the gallbladder) will be clipped and divided. An intraoperative ultrasound will then be utilised to verify (confirm) the location of the common bile duct and the adjacent hepatic artery and portal vein.
The choledochotomy procedure (cut in common CBD), will be performed vertically parallel to the common bile duct to avoid injury of the vascular branches.
When there is a risk of bile duct inflammation (cholangitis), surgical gastroenterologists apply gentle pressure to prevent complications.
The gallstones will be retrieved using atraumatic graspers. Stones can also be pushed out by exerting pressure with graspers on the surrounding CBD wall.
The laparoscopic suction tip can be used to place the stones towards the choledochotomy (vertical cut) in a process termed "milking" of the duct.
Smaller stones will be removed by using a choledochoscope with attached balloon catheter or a wire basket. If the stones are stuck or large, they may need to be broken into smaller pieces using laser or electro-hydraulic lithotripsy methods.
After choledochotomy, tiny stones will be washed out using flushing water or an irrigator via a rubber catheter.
The choledochotomy incision will be closed, the cystic duct clipped, and the gallbladder will be removed.
During choledochotomy, surgical gastroenterologists preserve the blood supply to the proximal duct to prevent complications such as ischemia or stricture.
Choledochotomy T- tube
After choledochotomy, a T-tube might be inserted into the common bile duct through the choledochotomy site to remove stones and help drain bile from the liver and gallbladder into the duodenum.
The T-tube is a T-shaped latex, silicone, or red rubber tube, positioned in the common bile duct following exploration with supraduodenal choledochotomy.
T-tube placement is a delicate method that requires professional help with high skills. Sometimes, the common bile duct is closed with T-tube drainage for multiple weeks to avoid postoperative complications such as biliary fistula and stricture. In some cases, the surgical gastroenterologist closes the common bile duct directly without placing a T-tube.
The most common complication of T-tube placement is bile leak around the tube, and a rare complication is T-tube sinus tract duodenal fistula.
Other possible complications include a tight closure of choledochotomy and inclusion of t-tube in suturing. Generally, surgical gastroenterologists recommend keeping the T-tube for two weeks, based on the patient's condition.
After the choledochotomy procedure
For open surgery, the patient has to remain in the hospital for 3–5 days. The patient will be returned to day surgery or ward after staying sometime in the recovery area of the operating suite. Nurses will monitor the patient's progress and give painkillers.
Patients may be asked to breathe into an incentive spirometer device to keep the lungs working well during that time. Fluids will be given to the patient through an intravenous (IV) tube to maintain hydration. Post that, based on the patient's condition, the liquids will be provided through the mouth. More extended hospitalisation is needed if the patients have problems such as pain, fever or bleeding.
For Laparoscopic surgery, the patient will be returned to ward after staying sometime in the recovery area of the operating suite. Nurses will monitor the patient's progress and give painkillers.
In this procedure, the patient may leave the hospital later that day, based on how well the patient is recovering from the operation and anaesthetic. The patient can take a normal diet soon after the operation. A healthy, balanced diet is the best approach. Avoid lifting heavy weights for at least two weeks to prevent a rupture where the cuts.
Choledochotomy Complications
Possible complications of this surgery can include:
- Bile leak
- Strictures (narrowing of bile duct)
- Cholangitis (Inflammation of bile duct)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreas)
Frequent patient questions to the surgical gastroenterologist post choledochotomy procedure?
- When can I get back to my normal activities?
- What dietary restrictions should I follow for recovery?
- What should I expect during the recovery period?
- What are the complications that occur after the choledochotomy?
- When should I schedule follow-up appointments?
- What signs or symptoms should I watch for that might indicate a complication?
- How long can I expect to stay in the hospital after the choledochotomy?
- Will any tests or evaluations be required after the surgery?
- What are the wound care instructions for my incision site?
Difference between Choledochotomy and Choledocholithotomy
Choledochotomy vs Choledocholithotomy
Choledochotomy and choledocholithotomy are both effective procedures in removing the gallstones that are migrated to common bile duct. Although these are similar, they have some differences:
| Elements | Choledochotomy | Choledocholithotomy |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Surgical cut (incision) of common bile duct (CBD) to access and treat several conditions of CBD | Surgical removal of stones from common bile duct. The preferred method for treating common bile duct stones |
| Indications | It is used for biliary drainage, biliary stent placement, and choledochal cyst repair | It is indicated for recurrent stones associated cholangitis and is also used when they cannot remove through ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) |
| Methods | Open or minimally invasive procedures (laparoscopic or robotic assisted) | Usually minimally invasive (laparoscopic or robotic assisted) |
| Recovery time | Longer recovery time (7-10 days) | Shorter recovery time (3-5 days) |
| Purpose | Allow surgeons to treat various CBD issues such as stones, obstructions etc | Mainly prefers for removal of stones from CBD |
| Risks | Bile leakage, Bleeding, infection and damage to nearby tissues and structures | Risks are similar to choledochotomy and the risk of stone migration. |
Difference Between Choledochotomy and Cholecystectomy
Choledochotomy vs Cholecystectomy
These two procedures are different methods for treating gallstones and other gallbladder disease. These are the following differences:
| Elements | Choledochotomy | Cholecystectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Surgical cut (incision) of common bile duct (CBD) to access and treat several conditions | Surgical removal of gall bladder |
| Location | Common bile duct | Gallbladder |
| Approach | It involves the making a cut (incision) in CBD | It involves the removal of complete gallbladder |
| Indications | It is used for biliary drainage, biliary stent placement, and choledochal cyst repair | It is used to treat gallbladder-related issues such as gallbladder polyps, cirrhosis and gallbladder cancer and also used when gallstones become troublesome. That includes biliary colic (pain), gallbladder infection (Acute cholecystitis), blockage of pancreatic duct-pancreatitis, blockage of bile flow out of gall bladder-Obstructive jaundice, blockage of bowel. |
| Purpose | To identify and explore the CBD for strictures, stones and other abnormalities | To remove gallbladder |
Choledochotomy Procedure Cost in Hyderabad, India
The
cost of a Choledochotomy Procedure (surgical opening of the common bile duct to remove stones or relieve obstruction) in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹65,000 to ₹1,85,000 (approximately US $785 – US $2,235). The exact cost varies depending on the underlying condition (CBD stones, strictures, infection), whether the procedure is open or laparoscopic, the complexity of bile duct exploration, surgeon expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen including - cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost breakdown according to type of choledochotomy / bile duct exploration procedure:
- Open Choledochotomy (CBD Stone Removal) –
₹65,000 – ₹1,20,000 (US $785 – US $1,445)
- Laparoscopic Choledochotomy (Minimally Invasive) –
₹85,000 – ₹1,60,000 (US $1,020 – US $1,920)
- Choledochotomy with T-Tube Placement –
₹75,000 – ₹1,40,000 (US $900 – US $1,680)
- Choledochotomy with CBD Exploration + Stone Retrieval –
₹90,000 – ₹1,85,000 (US $1,080 – US $2,235)
- Emergency Choledochotomy (For Acute Obstruction / Cholangitis) – ₹80,000 – ₹1,70,000 (US $965 – US $2,055)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Choledochotomy Procedure
Why is a choledochotomy performed?
Usually, choledochotomy is recommended when the transcystic approach is unsuccessful or when large, multiple or stubbornly stuck stones are present in the common bile duct. It is commonly used in the conditions including stone removal, biliary strictures (narrowing of bile duct), tumour resection, biliary drainage and during gallbladder surgery.
What is choledochotomy with T-tube drainage?
The T-tube is a T-shaped latex, silicone, or red rubber tube, T-tube placement is a delicate method that requires professional help with high skills. After choledochotomy, a T-tube is inserted into the common bile duct through the choledochotomy site to remove stones and help drain bile from the liver and gallbladder into the duodenum. Generally, surgeons recommend keeping the T-tube for two weeks, based on the patient's condition. Sometimes, the surgical gastroenterologist closes the common bile duct directly without placing a T-tube. Choledochotomy with T-tube drainage has some possible complications, including a leak around the tube, tight closure of choledochotomy and inclusion of T-tube in suturing.
Which is the best hospital for Choledochotomy Procedure in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is a highly trusted centre for advanced hepatobiliary and biliary duct surgeries, including choledochotomy and common bile duct exploration. Our expert gastroenterology and surgical teams specialise in managing complex conditions such as CBD stones, biliary obstruction, strictures, recurrent jaundice, and cholangitis.
With high-precision surgical techniques, advanced imaging support (MRCP, ERCP), modern laparoscopic systems, and 24×7 emergency care, PACE Hospitals ensures safe, effective, and reliable outcomes for patients undergoing choledochotomy or bile duct exploration — supported by cashless facilities, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance processing for eligible patients.
Is a T-tube always required after choledochotomy?
No, a T-tube is not always required; it's used selectively to drain bile and reduce pressure, especially in complex or inflamed cases.
What is the recovery time after choledochotomy?
Recovery time after a choledochotomy typically ranges from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the patient’s overall health and the complexity of the surgery. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few weeks, but full recovery may take longer. Follow-up care, including monitoring for infection or bile leaks, is important.
What is the cost of Choledochotomy Procedure in Hyderabad, India?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of a choledochotomy procedure typically ranges from ₹70,000 to ₹1,55,000 and above (approximately US $850 – US $1,875), making it slightly more affordable. However, the final cost depends on:
- Open vs laparoscopic approach
- Presence of CBD stones, strictures, or infection
- Need for T-tube drainage or CBD stent
- Anaesthesia, hospital stay, and post-operative monitoring
- Additional procedures (ERCP, MRCP, bile duct dilation) if required
For planned, non-emergency choledochotomy cases, PACE offers one of the most cost-effective surgical packages in Hyderabad, without compromising on surgical expertise or patient safety.
After evaluating your imaging reports (USG/CT/MRCP) and clinical findings, our surgical team provides a personalised treatment plan and transparent cost estimate tailored to your condition.
What is a choledochotomy procedure?
The choledochotomy procedure is a surgical incision of the common bile duct (CBD) indicated to access and address common bile duct issues that include biliary strictures (narrowing of the bile duct), biliary drainage, removal of stones from CBD and those migrate from gallbladder. The surgical gastroenterologist performs this procedure, either through an open or a minimally invasive (laparoscopic or robotic assisted) techniques. Laparoscopic choledochotomy is suggested when the transcystic approach is unsuccessful or when large, multiple or stubbornly stuck stones are present in the common bile duct.
How is choledochotomy performed?
Choledochotomy is a surgical cut (incision) of the common bile duct (CBD) to access and treat several conditions. It can be performed by giving general anaesthesia to the patient before performing the surgery to make the patient unconscious and based on patient overall condition, the surgical gastroenterologist might choose the procedure type (open or minimally invasive).
Surgical gastroenterologists can visualize or access the common bile duct to address issues such as duct obstructions, strictures, or stones and makes an accurate incision in CBD to access and treat various conditions such as duct obstructions, strictures, or stones.
After the required treatment, the choledochotomy incision will be closed with sutures. T-tube or other drainage procedures may sometimes be positioned in a common bile duct or choledochotomy site to drain the bile. After completion of the procedure, the surgical gastroenterologist will close the abdominal incisions.
What is choledochoscopy?
Choledochoscopy, also known as cholangioscopy, is an endoscopic surgical technique that allows the gastroenterologist to visualize the biliary tract directly for diagnostic or therapeutic(treatment) purposes. This includes removing stones in the common bile duct and checking that the bile ducts are clear. It is also used to treat gallstone disease, malignant obstruction of the biliary tract, and choledocholithiasis (presence of at least one gallstone in the common bile duct).
What are the complications of laparoscopic choledochotomy?
Laparoscopic choledochotomy has no significant complications. However, few patients may experience some of the possible complications, that are rare and self-limited which includes bile leakage around the duct, strictures (narrowing of bile duct), cholangitis (inflammation of bile duct) and pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreas).