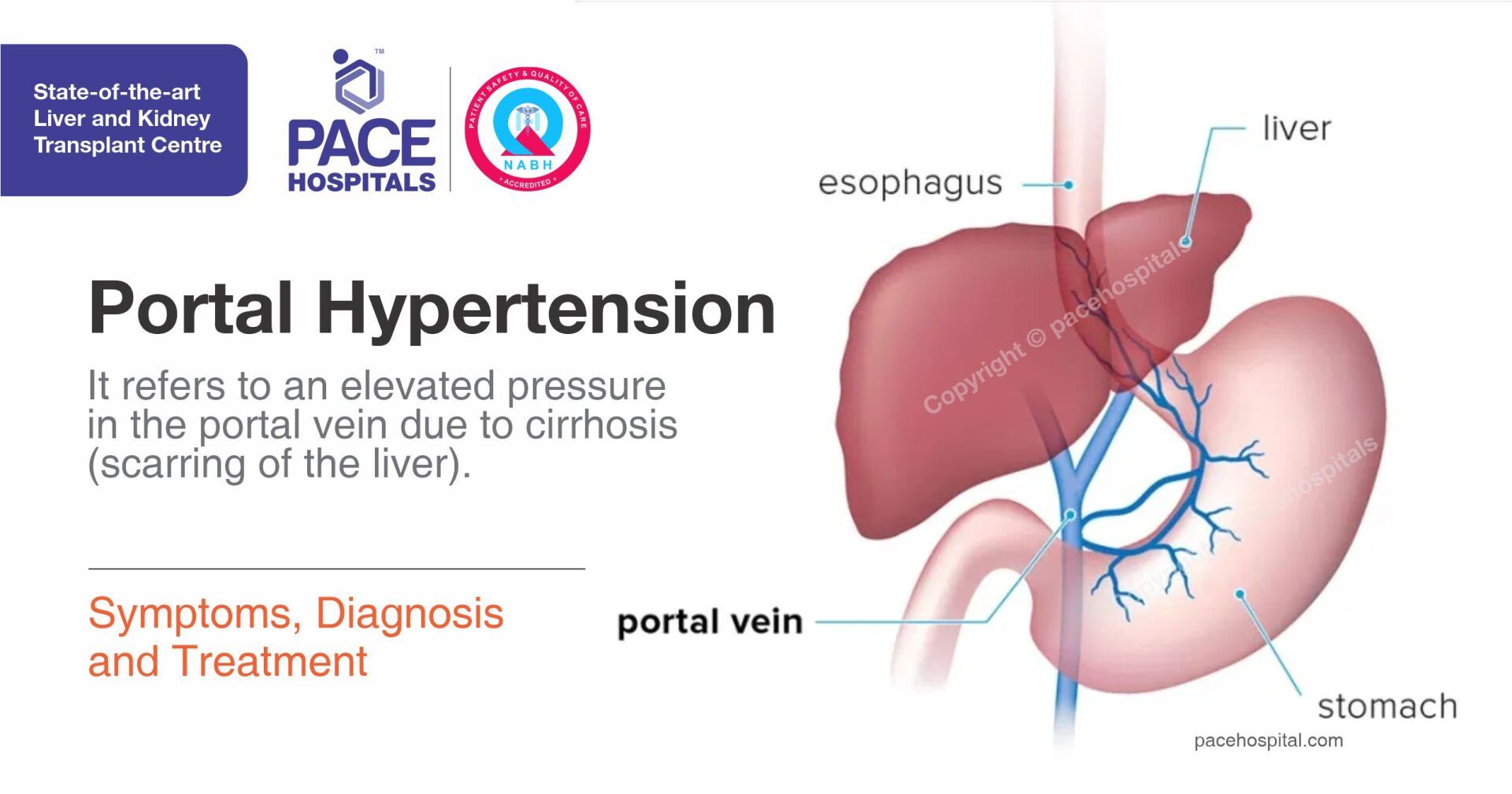
(Portal Hypertension) - Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Portal hypertension is an elevated pressure in the portal vein (veins that carry blood from stomach, intestine, spleen and pancreas to the liver). Elevated pressure is caused by blockage in blood flow through the liver. Increased pressure on portal veins causes large blood vessels (varies) to grow across the throat and the stomach to go around the blockage. The main cause of portal hypertension is cirrhosis (scarring of the liver).
Many times, people suffering from portal hypertension do not realize that there is a problem until they experience an episode of pain on one side of their body. This could be in the form of a dull ache or throbbing pain that spreads across the lower portion of the arm, or perhaps it happens when you flex your wrist.
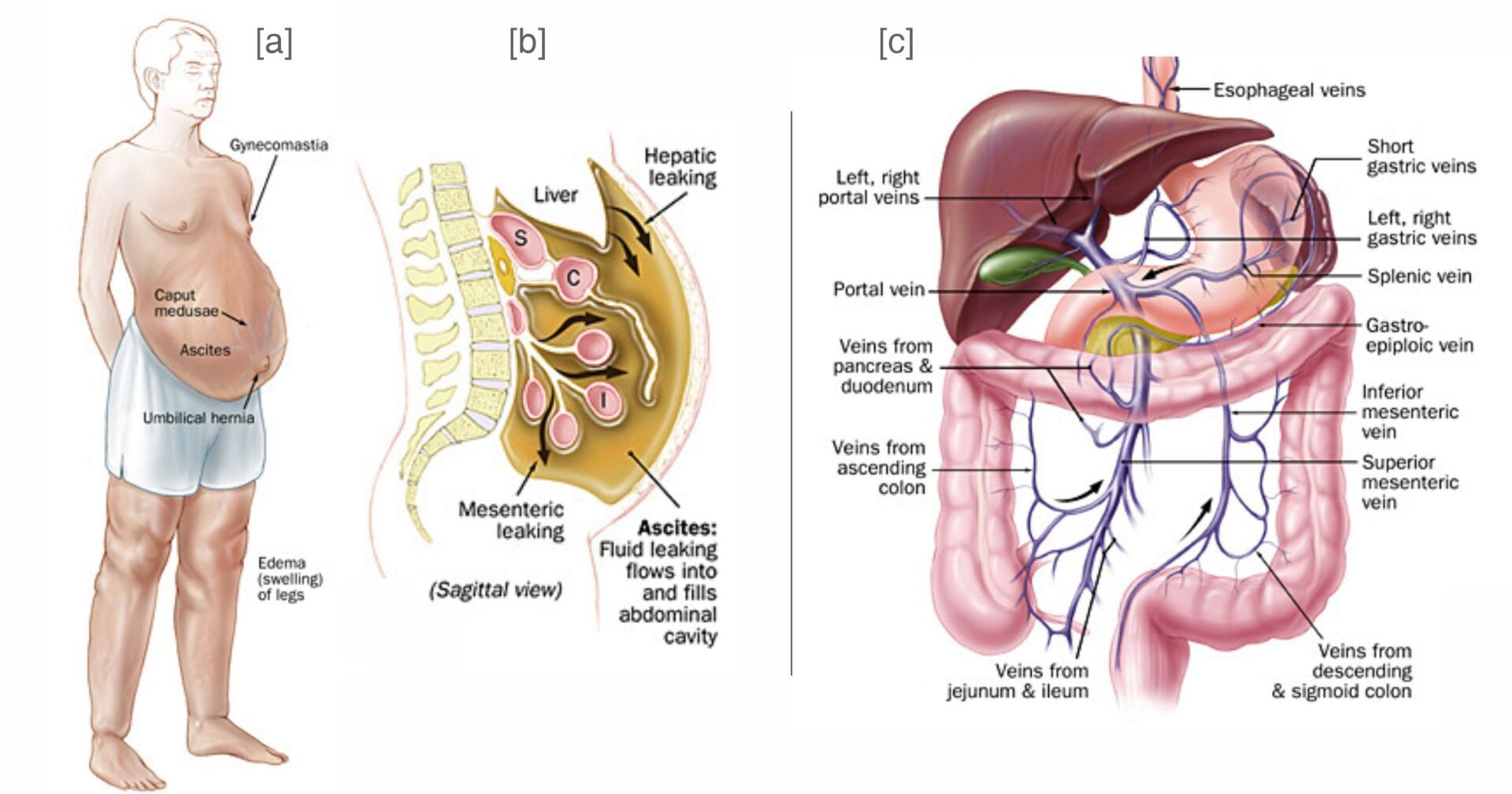
Figure 1 - [a] Clinical manifestations of portal hypertension. [b] Mechanism of ascites in portal hypertension; S=stomach; C=colon; I=intestine. [c] Anatomy of the portal venous system.
What are the treatment options for portal hypertension?
Treatment start with preventing complications of Portal hypertension. Once the complications identified, treating the underlying cause and alcohol abuse (due to the risk of further liver damage). It can be managed through diet, medications, endoscopic treatment, radiology or finally surgery. Treatment options are prescribed based on the symptoms severity and on how good your liver is working.
Lifestyle changes such as these can help treat portal hypertension:
- Dietary changes
- Avoiding alcohol intake
- Regular exercising
- Quitting smoking (if you smoke)
Acute bleeding from varices or nonvariceal sites in patients with portal hypertension requires prompt and appropriate measures to control bleeding and prevent recurrent episodes. Treatment is aimed at the prevention of recurrent episodes of variceal bleeding by lowering portal pressure and eliminating varices.
Medical Treatment: Medical management of bleeding esophageal or gastric varices may be instituted once the cause of the hemorrhage is documented to be variceal in origin. Drug treatment is aimed at reducing portal inflow, or collateral or intrahepatic resistance
Endoscopic Treatment: Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Treatment options include sclerotherapy, banding of esophageal varices and balloon tamponade to control bleeding.
Banding: Acute variceal hemorrhage is ideally managed by variceal ligation with elastic rings. This is performed endoscopically, and is safe and effective.
Surgical Shunts: The aim of surgical shunting in portal hypertension is:
- to maintain hepatic and portal blood flow
- to reduce portal venous pressure
to try to reduce or not complicate hepatic encephalopathy
Figure 2 - Illustration of the placement of the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) endoprosthesis between the portal vein and a hepatic vein
TIPS or TIPSS (Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) is an artificial channel within the liver that establishes communication between the inflow portal vein and the outflow hepatic vein.
- An interventional radiologist creates the shunt using an image-guided endovascular (via the blood vessels) approach, with the jugular vein as the usual entry site. The procedure widely accepted as the preferred method for treating portal hypertension that is refractory to medical therapy, replacing the surgical portocaval shunt in that role. TIPS is a life-saving procedure in bleeding from esophageal or gastric varices. Figure 2 illustrates the generic placement of the shunt between the portal vein and a hepatic vein.
Liver Transplantation: Liver transplantation is the only effective treatment for end-stage liver disease. This option offers excellent patient survival and rehabilitation. Challenges of liver transplantation include a scarcity of human cadaver donors, rejection, and the limited financial resources of most patients.
Complications secondary to portal hypertension can be life threatening and are often the main indication for transplantation in patients with advanced liver disease.
References:
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, "New non-operative treatment for variceal haemorrhage" [1] [2]
- Figure 1 Clinical manifestations of portal hypertension. Mechanism of ascites in portal hypertension; S=stomach; C=colon; I=intestine. Anatomy of the portal venous system
- Figure 2 Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Literature Review
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868