Carbohydrate Metabolism in CKD: Impact on Heart & Stroke Risk
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by:
Dr. A Kishore Kumar - Consultant Nephrologist and Renal Transplant Physician
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, playing a central role in maintaining blood glucose levels and supporting vital organ function. In individuals with kidney disease, particularly Chronic kidney disease (CKD), carbohydrate metabolism undergoes significant alterations that can affect energy balance, metabolic stability, and long-term cardiovascular health.
At PACE Hospitals, our nephrologists, diabetologists, and renal nutrition specialists follow an integrated, evidence-based approach to manage metabolic changes in CKD. This article examines the effects of kidney disease on carbohydrate metabolism and reviews the clinical implications and management considerations.
Role of Carbohydrates in Normal Metabolism
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which serves as a key energy source for cells, especially the brain and muscles. Insulin and other hormones regulate glucose uptake, storage, and utilization, maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Healthy kidneys contribute to carbohydrate metabolism by:
- Participating in glucose production through gluconeogenesis
- Clearing insulin and other metabolic hormones from circulation
- Maintaining acid–base balance, which influences glucose utilization
When kidney function slowly gets affected and declines, these regulatory processes are disrupted.
How Kidneys Influence Glucose Regulation?
The kidneys play an important but often underappreciated role in glucose homeostasis. They help filter glucose from the blood, reabsorb it as needed, and contribute to insulin degradation.
In CKD, reduced kidney function leads to:
- Altered insulin clearance, increasing the risk of low blood sugar
- Impaired glucose production and utilization
- Greater variability in blood glucose levels
These changes complicate glycemic control, particularly in patients with coexisting diabetes.
Carbohydrate Metabolism in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
In Chronic kidney disease (CKD), metabolic disturbances become more severe as kidney function gets affected with improper functioning. Alterations in insulin action, glucose utilization, and hormonal regulation contribute to unstable blood sugar levels and increased metabolic risk.
Key metabolic changes include:
- Increased insulin resistance in early stages of CKD
- Reduced insulin clearance as kidney function worsens
- Greater variability in blood glucose levels
These abnormalities require careful monitoring and individualized management.
Insulin Resistance in Chronic Kidney Disease
Insulin resistance is a common metabolic abnormality in patients with CKD and plays a major role in disturbed carbohydrate metabolism. As kidney function declines, the body’s ability to respond effectively to insulin becomes impaired, leading to unstable glucose levels even in individuals without diabetes.
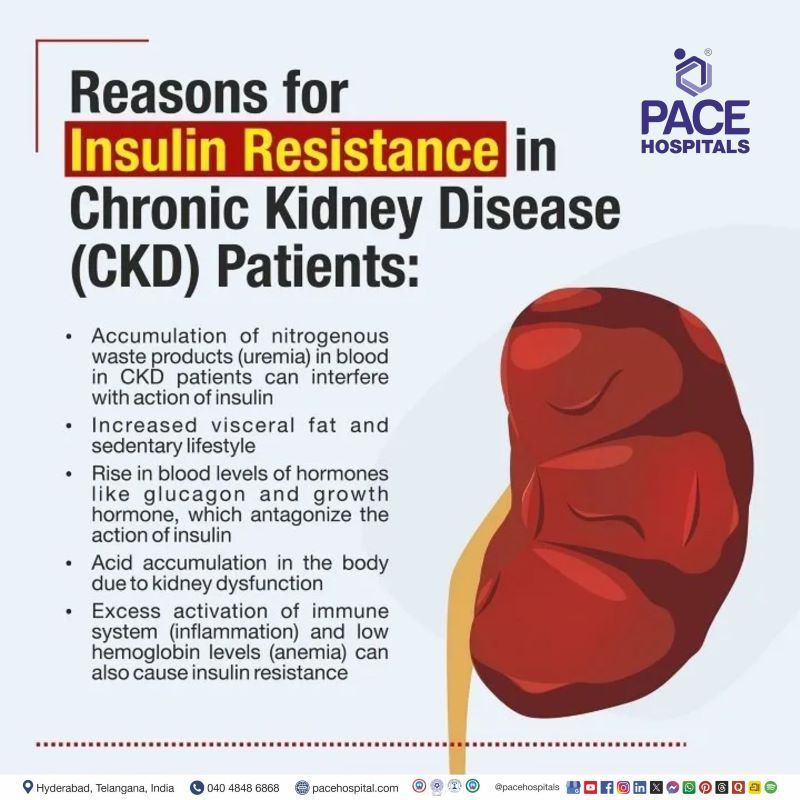
Reasons for Insulin Resistance in CKD Patients
- Chronic inflammation that interferes with insulin signaling pathways
- Accumulation of uremic toxins that reduce cellular insulin sensitivity
- Metabolic acidosis affecting glucose uptake by muscles
- Reduced physical activity and loss of muscle mass
- Hormonal imbalances involving insulin and counter-regulatory hormones
- Vitamin D deficiency, which is common in CKD
Hypoglycemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Patients with CKD are at increased risk of hypoglycemia, particularly in advanced stages and in those receiving glucose-lowering medications. Declining kidney function alters insulin handling and reduces endogenous glucose production, making blood sugar levels unpredictable.

Reasons for Hypoglycemia in CKD Patients
- Reduced insulin clearance leading to prolonged insulin action
- Accumulation of oral antidiabetic medications in the body
- Decreased renal gluconeogenesis during fasting states
- Poor appetite or reduced food intake
- Glucose fluctuations related to dialysis sessions
- Impaired hormonal response to falling blood sugar levels
Impact of CKD on Diabetes and Glycemic Control
Diabetes is a leading cause of CKD, and the coexistence of both conditions significantly alters carbohydrate metabolism. As kidney disease progresses, standard diabetic management strategies may need adjustment.
Common challenges include:
- Reduced reliability of HbA1c in advanced CKD
- Increased risk of hypoglycemia due to reduced insulin clearance
- Need for frequent glucose monitoring
Optimizing carbohydrate intake plays a critical role in maintaining metabolic stability.
Dietary Carbohydrates in CKD: Quality Matters
Not all carbohydrates affect the body in the same way. In CKD, the quality and timing of carbohydrate intake are similarly given same importance as quantity.
Recommended dietary approaches include:
- Adequate fiber intake to improve glucose control
- Preference for complex carbohydrates with low glycemic index
- Avoidance of refined sugars and highly processed foods
Renal diet planning focuses on meeting energy needs without worsening metabolic complications.
Energy Balance and Carbohydrate Intake in CKD
Adequate carbohydrate intake is essential to prevent excessive protein breakdown for energy. When calorie intake is insufficient, the body uses protein stores, leading to muscle loss.
Balanced carbohydrate consumption helps in several ways to:
- Preserve muscle mass
- Support daily activity levels
- Maintain metabolic stability
This is particularly important in patients with reduced appetite or dietary restrictions.
Clinical Statistics Highlighting Carbohydrate Metabolism in CKD
Research evidence shows that disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism are common and clinically significant in patients with Chronic kidney disease (CKD), even before advanced stages are reached.
- Insulin resistance is frequently observed in CKD patients, including those without diabetes, and tends to worsen as kidney function declines. This contributes to unstable glucose utilization and increased metabolic stress.
- As CKD progresses, the kidney’s ability to clear insulin is reduced, leading to prolonged insulin action and a higher likelihood of hypoglycemia, particularly in patients receiving insulin or oral glucose lowering medications.
- Clinical studies have shown that patients with CKD and diabetes experience a substantially higher rate of hypoglycemic episodes compared to those with preserved kidney function.
- Poor glycemic control in CKD is strongly associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including coronary artery disease and stroke.
- Population based studies demonstrate that individuals with CKD carry a markedly higher risk of stroke compared to the general population, with risk increasing as kidney function declines.
These findings emphasize the need for careful glucose monitoring, individualized dietary planning, and coordinated specialist care to reduce metabolic instability and long term vascular complications in CKD patients.
Key observations include:
- Insulin resistance is observed in approximately one-third of individuals with Chronic kidney disease (CKD), even in the absence of diabetes
- With advancing CKD, the kidney’s ability to clear insulin decreases significantly, leading to prolonged insulin action and higher hypoglycemia risk
- Episodes of low blood sugar are reported in a substantial proportion of CKD patients with diabetes, particularly in later stages of disease
- Poor long-term glucose control in CKD is consistently linked to a marked increase in cardiovascular complications, including coronary events and stroke
- Epidemiological studies show that people with CKD carry a several-fold higher risk of stroke compared to those with normal kidney function
- Nutritional strategies focused on appropriate carbohydrate quality and timing are associated with better metabolic stability and fewer hospital admissions
These findings reinforce the need for individualized dietary planning, regular glucose monitoring, and coordinated specialist care in patients with CKD.
Cardiovascular Risks Linked to Carbohydrate Metabolism in CKD
Disturbed carbohydrate metabolism in CKD contributes to cardiovascular disease, which is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in these patients.
Poor glycemic control increases the risk of:
- Atherosclerosis
- Heart disease
- Stroke
Managing blood glucose levels effectively is essential to reduce long-term vascular complications.
Hypoglycemia Risk in Advanced Kidney Disease
As kidney function gradually gets reduced, insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents remain in the body longer, increasing the risk of low blood sugar episodes.
Symptoms may include:
- Dizziness and confusion
- Sweating and tremors
- Loss of consciousness in severe cases
Education and medication adjustments are crucial in preventing hypoglycemia.
Nutritional Assessment in CKD
Evaluating nutritional status is an essential part of managing carbohydrate metabolism in kidney disease.
Assessment typically is based on following:
- Dietary intake and regular meal patterns
- Body weight and energy levels
- Blood glucose trends
Regular review helps identify metabolic imbalances early.
Individualized Dietary Planning at PACE Hospitals
At PACE Hospitals, dietary planning for CKD patients is personalized and dynamic to support the well-being of the patients.
Key principles include:
- Adjusting carbohydrate intake based on kidney function and activity level
- Coordinating diet with medications and insulin therapy
- Continuous reassessment as CKD progresses
This patient-centered approach supports both metabolic control and need for improvement in quality of life.
Special Considerations in Elderly CKD Patients
Older adults with CKD are particularly more proned to metabolic instability due to reduced physiological reserves and comorbidities arised due to aging.
Careful carbohydrate planning helps:
- Prevent hypoglycemia
- Maintain energy for daily activities
- Reduce hospitalization risk
Lifestyle Measures Supporting Carbohydrate Metabolism
Beyond diet, lifestyle habits influence glucose regulation in CKD affected persons.
Supportive measures needed to be included in daily life as follows:
- Regular, moderate physical activity
- Stress management
- Consistent meal timing
These strategies complement medical and nutritional interventions.
Importance of Patient Education and Follow-Up
Giving patients information and awarness about the different carbohydrate choices, portion control, and symptom awareness enhances self-management.
Ongoing monitoring ensures that dietary interventions remain successful as kidney function and treatment requirements change.
Frequently Asked Questions on Carbohydrate Metabolism in CKD
How does chronic kidney disease affect carbohydrate metabolism?
In Chronic kidney disease (CKD), the kidneys gradually lose their ability to regulate glucose and insulin balance as the disease slow progress. This affects how carbohydrates are processed for energy, leading to unstable blood sugar levels and increased metabolic stress over time.
How does reduced kidney function affect insulin clearance?
Healthy kidneys help break down and remove insulin from circulation. In CKD, this process gets reduced, causing insulin to remain active longer and increasing the risk of blood sugar fluctuations.
Why are CKD patients at higher risk of hypoglycemia?
As kidney function declines, insulin remains in circulation longer and the kidney's contribution to glucose production decreases. When this is combined with glucose-lowering medications and poor food intake, the likelihood of hypoglycemic episodes rises, particularly in later stages of CKD.
How does carbohydrate metabolism change as CKD progresses?
During the earlier stages of CKD, reduced insulin responsiveness is the main metabolic issue. The metabolic pattern in CKD changes as the disease progresses. Early stages are mainly affected by reduced cellular response to insulin, whereas later stages are dominated by delayed insulin removal.This progression contributes to wide fluctuations in glucose levels and complicates metabolic management.
Does CKD affect blood sugar control in people with diabetes?
Yes. CKD disrupts normal insulin activity and glucose balance, adding complexity to diabetes treatment. Continuation of medication review and enhanced glucose surveillance are commonly required to overcome these challenges and avoid major health problems.
Is HbA1c always reliable in advanced CKD?
The accuracy of HbA1c can be affected in later stages of CKD due to changes in red blood cell turnover and the presence of anemia. As a result, doctors may use other monitoring approaches to better assess ongoing glucose control.
Does dialysis affect carbohydrate metabolism?
Yes. Dialysis changes insulin clearance and can cause glucose fluctuations during and after treatment. Careful monitoring is an effective way to maintain stable blood sugar levels around these sessions and need guidance from specialist.
Why do patients with CKD often develop insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance in CKD develops due to chronic inflammation, accumulation of metabolic waste, metabolic acidosis, and loss of muscle mass. Together, these factors decreases the body's response to insulin and impair glucose uptake by tissues.
Can insulin resistance occur in CKD patients without diabetes?
Yes. Insulin resistance is commonly seen in CKD even in individuals without diabetes. Kidney-related metabolic changes alone can interfere with insulin signaling as kidney function declines.
Why is carbohydrate quality important in CKD?
The type of carbohydrates consumed affects blood sugar stability. Complex carbohydrates with lower glycemic impact help reduce glucose spikes and support better metabolic balance in CKD patients to manage blood-glucose level.
How does poor carbohydrate metabolism increase cardiovascular risk?
Unstable glucose levels increases inflammation and blood vessel damage. Over time, this enhances the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and stroke, particularly in CKD patients.
Why is stroke risk higher in CKD patients?
CKD causes vascular damage by increasing insulin resistance, inflammation, and glucose instability. These factors increases the main risk of stroke, especially when diabetes is present.
Can diet alone correct carbohydrate metabolism problems in CKD?
Diet plays a key role, but it is seldom sufficient by itself. Along with dietary planning, physical activity, medication modifications, and regular metabolic monitoring all together are the common components of effective management.
How does poor appetite in CKD affect blood sugar levels?
Irregular or reduced meal consumption may result in an incorrect medication dosage, raising the risk of hypoglycemia. Consistent meal timing and maintaining appropriate portion control are essential for glucose stability and balancing to avoid any risk further.
Can physical activity improve carbohydrate metabolism in CKD?
Appropriate exercise improves insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization by muscles. Exercise routines and activity plans should be planned according to kidney function, stamina, and overall health status of an individual patient.
How does PACE Hospitals reduce hypoglycemia risk in CKD?
PACE Hospitals gives importance on time to time regular glucose monitoring, careful medication review, and individualized nutrition guidance. Treatment is adjusted according to kidney function to minimize prolonged insulin effects.
Does PACE Hospitals offer personalized diet plans for CKD patients?
Yes. Dietary plans at PACE Hospitals are provided based on CKD stage, metabolic needs, and activity level. Carbohydrate quality, portion size, and meal timing are carefully planned so that patients can have big relief from worsening further.
When should CKD patients consult specialists at PACE Hospitals?
Specialist consultation is advised if patients experience frequent glucose fluctuations, unexplained fatigue, dizziness, or repeated hypoglycemic episodes.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for CKD Metabolic Care?
At PACE Hospitals, the management of kidney disease involves collaborative care from specialists across different medical fields to ensure complete and well-rounded treatment that includes:
- Highly experienced nephrologists and well-renowned diabetologists
- Specialized renal nutrition services
- Evidence-based, personalized treatment and care plans
- Continuous monitoring and patient education
Our goal is to optimize metabolic health, reduce complications, and improve long-term outcomes.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868