High blood levels of potassium in patients with kidney disease: Role of diet and ways to control
PACE Hospitals
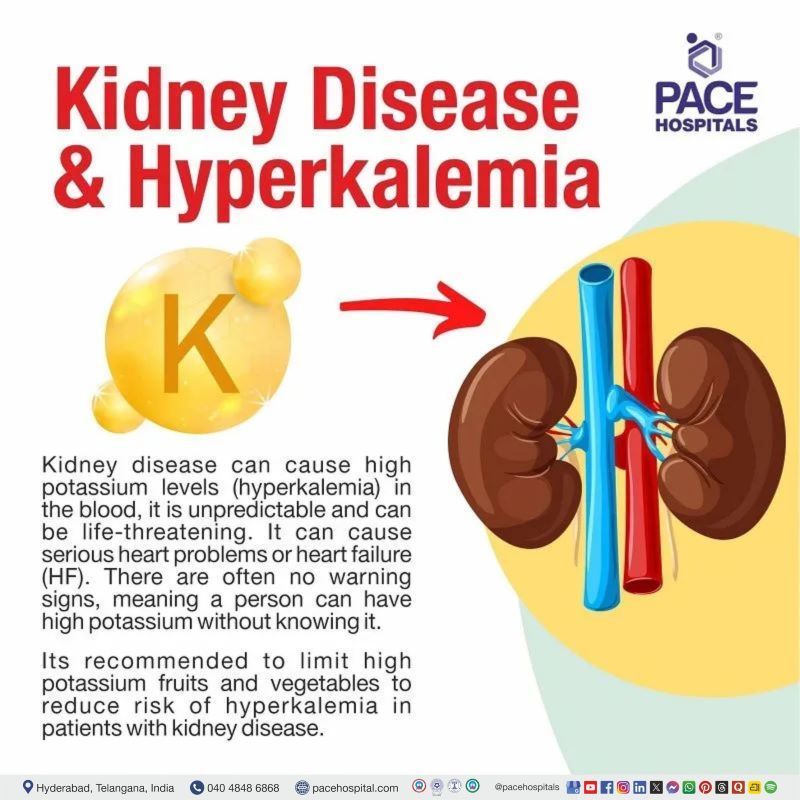
Potassium is one of the essential components of many processes which occur in the cells of the human body. It is important for nerves and muscles in the body for their proper functioning. Potassium is mainly present inside the cells, and a small amount is present in compartments outside the cells, like in blood. This outside component is important as high levels can adversely affect a person, and the definition of high potassium in the blood is related to this compartment. Kidney disease is a causative factor for both high and low potassium levels in the blood. An increase in potassium levels in the blood is called hyperkalemia, and low levels are called hypokalemia.
Potassium Balance in Health
Potassium content in the body is determined by the amount of intake of potassium and the amount which is sent out of the body. The main source of potassium intake in the diet and routes of loss from the body are urine, stools and sweat. Potassium in the diet is absorbed in the small intestines, and whatever is not absorbed is excreted in the stool. Increased fibre in the diet increase's potassium loss in the stools.
The loss of potassium in the sweat is usually small. Kidneys are mainly responsible for excreting potassium from the body to maintain the potassium balance. Potassium is lost in the urine, and kidneys adjust the amount of potassium to be excreted in the urine based on the blood level of potassium. If the potassium is high in the blood, kidneys will excrete more to maintain normal levels in the blood and vice versa.
A typical meal contains enough potassium to increase its level in the blood by 1-2 mEq/L. But this won’t happen in healthy individuals because of something called internal potassium balance. There are pumps on cells which are activated after a meal and transport potassium from blood to the inside of the cells. This process is mediated by insulin, which increases the pumps which transport potassium inside the cells.
So, for the insulin to increase along with potassium intake, carbohydrates and amino acids are to be consumed along with potassium, which is the usual case when we eat a normal diet. If we take potassium supplements, there is no increase in insulin in the blood and potassium level increases in the blood. The same mechanism is seen in patients with untreated insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, who are deficient in insulin and at high risk of hyperkalemia.
Kidney Disease and Potassium Balance
Kidney disease can cause high potassium levels (hyperkalemia) or low potassium levels (hypokalemia).
- The main reason for hyperkalemia in patients with kidney disease is due to impaired excretion of potassium in the urine. When the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) drops to below 15ml/min/1.73m2, there is a significant increase in the risk of hyperkalemia. Once the GFR falls to this level, the intestines take over the responsibility of potassium loss from the body. In such situations, up to 75% of external potassium, which is taken in the diet, can be excreted in stools. So, if there is constipation, this process is affected, and hyperkalemia can occur.
- Drugs which can increase potassium levels in the blood are RAAS (Renin angiotensin activating system) inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics and antihypertensive drugs like beta blockers.
- Acidosis can occur in patients with kidney disease as kidneys maintain acid-base balance in the body. Impaired kidney function will lead to acid accumulation. This acidosis can also cause hyperkalemia.
- Abnormalities in aldosterone levels which can occur in patients with diabetes and kidney disease, can also cause high potassium levels. Aldosterone is a hormone which acts on tubules in the kidney and excretes potassium in the urine.
- High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) in patients with insulin resistance and diabetes type 2 can also cause high potassium levels.
Hazards of Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia can cause clinical symptoms, which sometimes can need emergency management.
- Muscle weakness, paralysis, paresthesia (abnormal skin sensations)
- Cardiac arrhythmias (abnormal cardiac conduction changes which can be life-threatening)
Assessment to identify the cause of hyperkalemia
Usually, in patients with kidney disease, the cause of hyperkalemia is a combination of multiple factors. Many reasons together may culminate into hyperkalemia.
Diet history: Diet is the source of potassium intake, and proper diet history is taken from patients with high potassium levels. A detailed 3-day food record is used to assess the amounts of various food components which the patient is consuming. Some of the foods with high and low potassium contents are mentioned in the following table.
| Food | High potassium | Low potassium |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables | Potatoes, tomatoes, spinach | Cucumber, green beans |
| Fruits | Bananas, oranges, kiwi, avocado, cantaloupe, dry fruits | Apples, grapes, pineapple, strawberries, watermelon |
| Grains | - | Majority |
| Dairy | Milk, yoghurt | Cheese |
| Protein | Nuts, seeds, legumes, fish | Eggs, poultry |
Medication history: to check if the patient is consuming any of the previously mentioned drugs, which can cause high potassium levels
24-hour urine potassium: Usually, if the potassium levels are high in the blood, kidneys should excrete more potassium in the urine and potassium levels in the urine increase proportionately. If the potassium levels in the urine are low with high potassium levels in the blood, it means that kidneys are unable to excrete the potassium in the urine leading to hyperkalemia.
Check the acid-base status in the blood and history of constipation can help identify associated contributing factors.
Dietary Approaches to Manage Hyperkalemia
1. Lowering potassium intake
- Limit consumption of potassium rich foods like nuts, seeds and dry fruits. This is because it is easy to consume large quantities of potassium via these sources if we don’t restrict them. It is important, especially when there is kidney impairment where excretion of potassium is a problem.
- Avoid food products prepared with additives based on potassium. Potassium is added in the form of salts like potassium chloride, potassium citrate and potassium lactate. Potassium additives can provide a significant load of potassium.
- Food products with potassium-based food additives should be checked for the potassium content in their ingredients. If the potassium content of the product is ≥200 mg/serving, then such food is considered to be high-potassium. Sometimes labelling from the manufacturers is not correct, and potassium content may not be represented correctly. So, it is better to avoid any processed foods with potassium-based additives.
- Low sodium salt with potassium additives: Low sodium salt can be a significant source of potassium. In low sodium salts, sodium chloride (table salt) is replaced by potassium chloride to decrease sodium content. Potassium chloride also tastes salty, so it is used for this purpose. Before using such products, check the package ingredients list to see whether potassium chloride is added and avoid such salt preparations. Additive-free alternatives are also available in the market, which can be used.
- Take whole fruits and vegetables instead of juices. Juices are less in fibre and high in potassium and can be consumed in excess quantities than required increasing the risk of hyperkalemia. Excess consumption of juice, even from low-potassium fruits like apples, can also cause hyperkalemia. Dried fruits, compared to normal fruits (raisins vs grapes), have more potassium and increase the risk of hyperkalemia if consumed in excess quantities.
- Limit consumption of outside foods as the preparation method is different, and there is less control over the food processing and size of the portion consumed.
- Eat balanced meals and snacks with more than three food groups in moderate amounts. Balanced meals have better nutrient profiles and help in avoiding eating high-potassium foods.
- Soaking vegetables, meats and beans etc., in water leads to the transfer of potassium from foods into the water. The amount of transfer depends on the duration of soaking and the temperature of the water. 30-60 min soaking in hot water of around 100 degrees Fahrenheit can decrease the potassium content of the foods by 50%. This water is to be drained, and then the vegetables or meat is cooked.
This is called the wet cooking method. Through this process, sodium and phosphorus content also decreases in the food, which is also problematic in patients with kidney disease. Cutting the vegetables or meat and then soaking them in hot water gives even more, better results.
2. Increasing potassium excretion
- As the kidney fails, the kidneys cannot excrete potassium adequately in the urine. In advanced CKD (chronic kidney disease) the intestinal tract becomes an important source of potassium loss from the body. Potassium excretion increases in stools in patients with advanced CKD. Constipation is relatively common in patients with CKD.
- For treating constipation, increasing the fibre content of the food along with fluids and physical activity are necessary. Fibre sources in the food are fruits, vegetables, whole grains, seeds and legumes.
- Fibre supplements also improve constipation, but the potassium content of such supplements needs to be checked before consumption and after consulting the treating nephrologist.
3. Increasing potassium uptake into the cells
- As discussed previously, potassium is mainly a component inside the cells, with a very small amount present outside the cells, like in blood. In patients with kidney disease, there is an accumulation of acid in the body because kidneys are not able to excrete it in the urine adequately. This acid will cause potassium from inside cells to shift into the blood, leading to hyperkalemia.
- Up to half of the acid load that the kidney excretes is derived from the diet in healthy individuals. Animal-based food sources of protein are the main sources of acid load in the diet. Acid can be neutralized by base-forming components present in fruits and vegetables. So, an alkaline diet which has fewer animal-based protein foods and high quantities of base-forming components from fruits and vegetables is to be consumed to prevent or treat acid accumulation and hyperkalemia.
- Sugar levels in patients with diabetes mellitus are to be controlled adequately with proper diet and medication to prevent high blood sugar levels, which can cause hyperkalemia.
Frequently Asked Questions on High Potassium and Kidney Disease
Why is high potassium more dangerous in people with kidney disease?
Under normal conditions, healthy kidneys helps to remove excess potassium from the body. When kidney function is impaired, this removal process becomes improper, allowing potassium to build up in the bloodstream. Elevated levels can increase the risk of muscle weakness and serious disturbances in heart rhythm.
What does hyperkalemia mean in kidney patients?
Hyperkalemia is the term used to describe higher-than-normal potassium levels in the blood. In individuals with CKD (chronic kidney disease), even small elevations can have clinical importance because the kidneys are less able to clear potassium effectively.
How does CKD affect potassium balance in the body?
As CKD (chronic kidney disease) advances, the kidneys gradually lose their capacity to regulate potassium levels. This makes potassium balance more vulnerable to dietary intake, medications, and intercurrent illnesses.
Why is potassium control important for heart health?
Potassium plays an important role in regulating heart rhythm. When levels become too high, electrical signaling within the heart may be disrupted, increasing the risk of rhythm abnormalities. Careful potassium control is therefore essential in CKD management.
Does dehydration affect potassium levels?
Yes. Dehydration reduces the proper blood flow to the kidneys, thus reducing potassium excretion. Even minor fluid imbalances in persons with kidney disease can produce significant fluctuations in potassium levels.
How often should potassium levels be checked in CKD?
The frequency of testing depends on the stage of CKD, current medications, and overall health status of an individual. Patients with advanced CKD (chronic kidney disease) or recent treatment changes usually require more frequent monitoring.
Does dialysis affect potassium levels?
Yes. Dialysis helps remove excess potassium from the blood when the kidneys can no longer do so adequately. Maintaining safe potassium levels is one of the primary objectives of dialysis therapy.
Can high potassium develop without noticeable symptoms?
Yes. Potassium levels may rise without causing early warning signs. Many people with kidney disease become aware of abnormal potassium values only during routine blood investigations, which is why regular monitoring is strongly recommended.
Are certain foods riskier for high potassium in kidney disease?
Yes. Several commonly consumed fruits, vegetables, and packaged foods are naturally high in potassium. For people already suffering with CKD, managing portion size and using appropriate cooking methods is often more effective than eliminating foods entirely.
Can medications increase potassium levels in kidney patients?
Some medications prescribed for blood pressure or heart conditions can contribute to higher potassium levels. In patients with kidney disease, such medication-related increases require close supervision, dose adjustments, and periodic blood testing.
Can lifestyle changes alone control high potassium?
Dietary adjustments and adequate hydration play an important role, but they may not be sufficient in later stages of kidney disease like Stage 4 and Stage 5. In many cases, medical treatment is required to maintain potassium within a safe range.
Can potassium levels fluctuate suddenly?
Potassium levels may rise quickly due to infections, dehydration, medication changes, or excessive dietary intake. Sudden rise of potassium level are more commonly seen in patients with CKD and require prompt medical attention.
Is high potassium always a long-term problem?
Not necessarily. Some episodes of hyperkalemia are temporary and resolve once the underlying cause is corrected. However, in chronic kidney disease, long-term monitoring and management are often required to resolve health issues.
How does potassium imbalance affect muscle function?
Excess potassium interferes with normal nerve and muscle signaling. This may cause muscle weakness, fatigue, or a feeling of heaviness, and in severe cases, it can affect breathing muscles.
Why is individualized potassium management important?
Potassium tolerance varies significantly among people with kidney disease. Personalized management helps prevent both dangerously high potassium levels and overly aggressive restriction that could lead to deficiencies affecting body.
How does PACE Hospitals manage high potassium in kidney disease?
PACE Hospitals manages hyperkalemia through:
- Detailed assessment of kidney function and potassium trends by experienced nephrologists
- Careful review of medications that may affect potassium balance
- Dietary guidance tailored to the stage of CKD (chronic kidney disease)
- Ongoing monitoring to reduce the risk of sudden potassium elevation
When should a patient with CKD consult PACE Hospitals urgently?
Immediate medical attention at PACE Hospitals is advised when a patient has following signs:
- Symptoms such as palpitations, muscle weakness, or fatigue appear
- Blood tests reveal significantly the rise of potassium levels
- Recent medication changes affect potassium balance in the body
How does PACE Hospitals personalize dietary potassium guidance?
Dietary planning at PACE Hospitals is individualized by:
- Evaluating potassium tolerance under the guidance of experienced nephrologists
- Adjusting food choices based on level of CKD stage and laboratory results
- Educating patients on cooking and preparation techniques that lower potassium content
- Aligning dietary plans with the overall kidney treatment strategy
How does PACE Hospitals handle recurrent hyperkalemia in kidney patients?
Management of recurring hyperkalemia includes:
- Identifying underlying the main contributors such as dehydration or medication effects
- Modifying treatment plans under nephrologist supervision
- Close laboratory follow-up to track potassium trends
- Escalation of care, including dialysis, when clinically indicated
Why choose PACE Hospitals for potassium and kidney care?
PACE Hospitals provides comprehensive kidney treatment and care through:
- Dedicated nephrologists with expertise in electrolyte and kidney disorders related diagnosis
- Advanced diagnostic tests and monitoring capabilities
- Integrated dietary, medical, and dialysis services
- A patient-focused approach aimed at long-term kidney safety and quality of life
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868