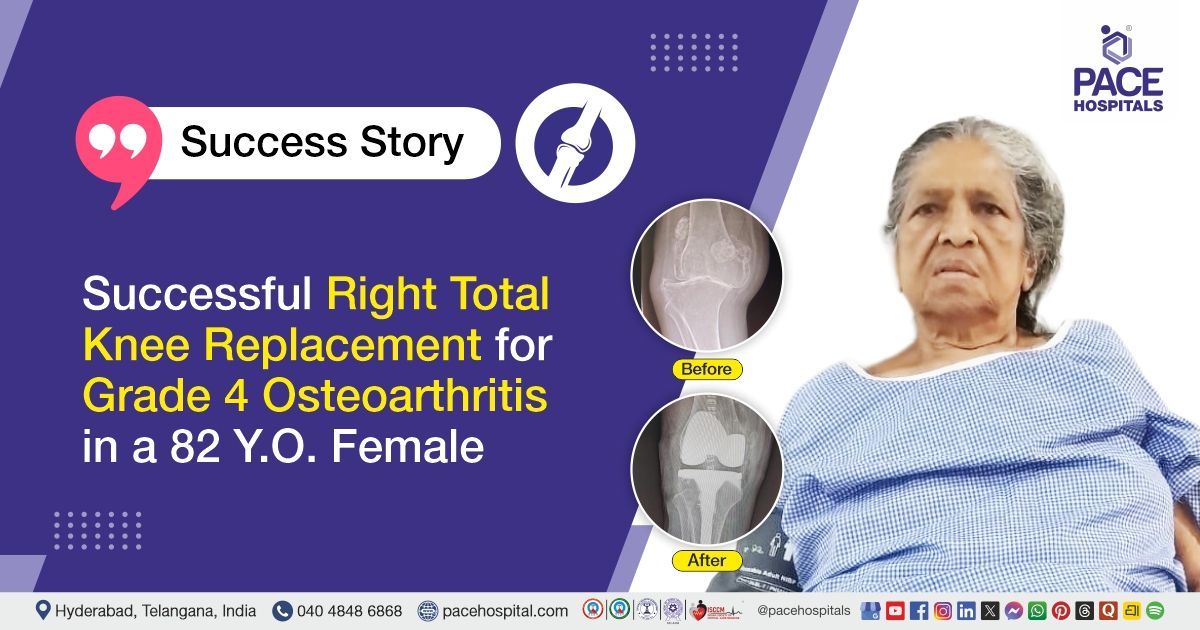
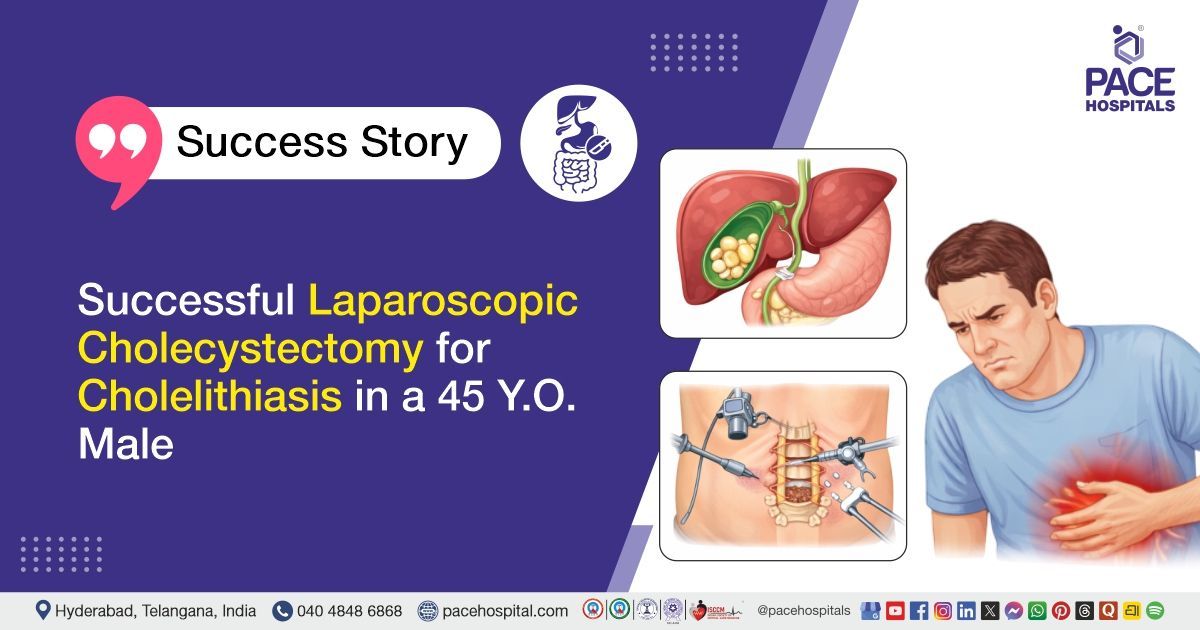
Successful Treatment of Hiatus Hernia & GERD With Lap. Nissen Fundoplication in a 44-Y.O
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals’ expert Gastroenterology team successfully performed a
Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication
on a 44-year-old female patient diagnosed with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and a hiatus hernia. She had presented with complaints of regurgitation, heartburn, and frequent belching. The procedure was aimed at correcting the anatomical defect and to relieve her reflux symptoms, promote functional recovery, and improve her overall quality of life.
Chief Complaints
A 44-year-old female patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 21.4 presented to the Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with chief complaints of regurgitation, heartburn, and frequent belching.
Past Medical History
The patient had no known history of hypertension or diabetes, which was considered clinically favourable, as the absence of these comorbidities reduced the risk of intraoperative and postoperative complications and supported a smoother, more stable recovery. Additionally, the patient had no known food or drug allergies.
On Examination
On clinical examination, patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented with stable vital signs. A systemic examination, including an abdominal assessment, revealed a soft, non-tender abdomen with no palpable masses, which was consistent with her clinical stability, Cardiovascular and respiratory examinations were normal. Although her ongoing symptoms suggested an underlying issue that required further investigation.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the Gastroenterology team, which included a detailed review of her medical history and a comprehensive clinical examination. Given her history of regurgitation, heartburn, and frequent belching. There was a strong clinical suspicion of significant Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and a hiatus hernia.
The patient underwent an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (UGIE), which revealed a hiatus hernia accompanied by gastropathy. Esophageal manometry showed normal esophageal motility, indicating no abnormalities in muscular function. Laboratory investigations indicated a prolonged prothrombin time and an elevated international normalized ratio, suggestive of impaired coagulation.
Based on the confirmed findings, the patient was advised to undergo
Hiatus Hernia and
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with the consultant gastroenterologists Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. M Sudhir, and Dr. Padma Priya, and cross consultants Dr. Suresh Kumar S, a surgical gastroenterologist, a comprehensive evaluation was carried out to determine the most suitable diagnostic and therapeutic approach for the patient. The multidisciplinary team worked together to address the patient's complex clinical presentation, ensuring a tailored treatment plan specific to her condition. Based on their collective expertise and assessment, it was determined that laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication was identified as the most effective interventions to relieve her symptoms.
The patient and her family were informed about her condition, the procedure, its associated risks, and its potential to alleviate symptoms and enhance her quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication procedure was carried out in the following steps:
- Anesthesia and Positioning: The patient was taken to the operating theatre and placed under general anesthesia. She was positioned supine with appropriate support, and aseptic precautions were taken. A pneumoperitoneum was created using CO₂ gas to provide working space within the abdominal cavity.
- Port Placement and Access: Five laparoscopic ports were placed strategically for optimal access to the upper abdominal structures. The laparoscopic camera and surgical instruments were introduced through these ports, and the surgical field was visualized.
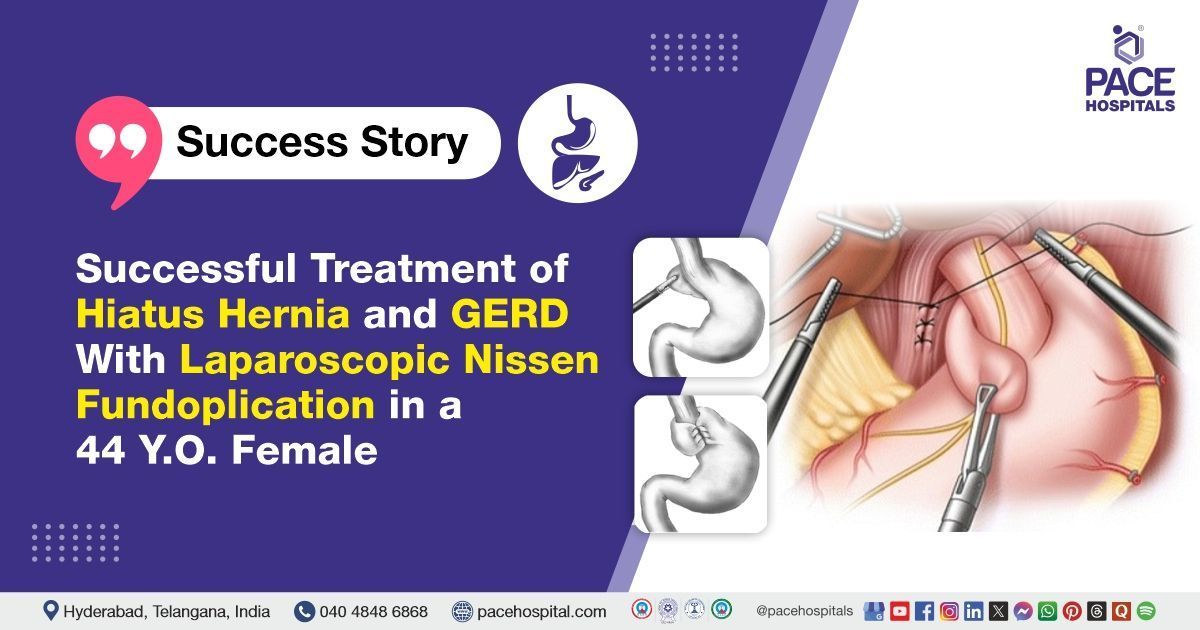
- Esophageal and Hiatal Dissection: The lower esophagus and gastroesophageal (GE) junction were carefully mobilized and dissected up to a length of 3 cm into the mediastinum, ensuring sufficient intra-abdominal esophagus to prevent wrap migration. This step was crucial due to the presence of the hernia.
- Crural Repair: After adequate mobilization, the right and left crura of the diaphragm were identified. A posterior crural repair was performed to close the widened esophageal hiatus. Non-absorbable sutures were used to approximate the crura, ensuring a snug but not constrictive closure around the esophagus to prevent recurrence of the hernia.
- Fundus Mobilization: The greater curvature of the stomach, specifically the fundus, was mobilized by dividing the short gastric vessels. This provided sufficient length and mobility of the fundus, which was necessary to perform a tension-free 360° wrap around the lower esophagus.
- Nissen Fundoplication: A "floppy" Nissen fundoplication was performed by wrapping the gastric fundus completely (360°) around the distal esophagus. The wrap was secured using sutures to maintain its position and function effectively as a valve to prevent reflux. This technique is the gold standard for treating GERD associated with hiatal hernia.
Completion and Closure
After ensuring hemostasis and confirming the position of the wrap, the CO₂ was released, and all laparoscopic instruments and ports were removed. The port sites were closed in layers. The patient tolerated the procedure well, and there were no intraoperative or immediate postoperative complications.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative period was uneventful. During the hospital stay patient was managed with intravenous (IV) antibiotics, analgesic, and intravenous proton pump inhibitors (PPI). She experienced no significant complications and was stable at the time of discharge.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed a course that included an antibiotic for bacterial infections, a proton pump inhibitor with a prokinetic to reduce stomach acid and aid digestion, an osmotic laxative to relieve constipation, and an analgesic for pain and inflammation management.
Dietary Advice
The patient was advised to follow a liquid diet for one week postoperatively.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms like fever, abdominal pain, or vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after one week with the Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, to review her condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights the effectiveness of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in managing hiatus hernia with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), leading to significant symptom relief and a marked improvement in the patient's quality of life.
Role of Esophageal Manometry in Preoperative Assessment of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
In clinical practice, esophageal manometry is a key diagnostic test used by the
gastroenterologist / gastroenterology doctor to assess the function and motility of the esophagus, especially in patients presenting with symptoms of GERD such as heartburn and regurgitation. This test measures how well the esophageal muscles contract and the competence of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), helping to differentiate GERD from other motility disorders like achalasia or diffuse esophageal spasm. Accurate evaluation through manometry is crucial before planning anti-reflux surgery, as it ensures that the patient does not have underlying motility issues that could complicate surgical outcomes. The gastroenterology doctor uses the information from manometry to tailor effective treatment planswhether through medication or surgery. By guiding the choice of therapy and helping to predict postoperative prognosis, esophageal manometry plays a pivotal role in the optimal management of esophageal diseases.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868